Accounting for PBU. A brief description of the provisions on accounting adopted in the Russian Federation. PBU in the preparation of financial statements
When restoring the accounting of organizations, we encountered a misunderstanding of some accountants of the provisions on accounting 18 \\ 02. in this connection, we decided to write a series of articles explainingA practical example of the calculation to determine the current income tax is in
Who applies PBU 18/02?
Reading the section “ General Provisions", We certainly answer this question. This PBU is applied by organizations that calculate and pay income tax. In other words, if you do not calculate and do not pay income tax in accordance with the law, then you do not need to apply PBU 18/02. PBU 18/02 does not apply:- credit institutions;
- state (municipal) institutions;
- applying simplified methods of accounting, including simplified accounting (financial) statements;
Why should PBU 18/02 be used at all?
The answer is contained in the same section. The use of PBU 18/02 allows you to reflect in accounting and accounting statements difference between tax on accounting profit (loss) from income tax generated and reflected in tax return for income tax. In other words, this PBU reflects in accounting a certain amount that in the future will affect income tax. As a result of different rules for accounting for income and expenses set out in the regulatory legal acts on accounting and in the legislation on taxes and fees in the Russian Federation, there is a difference between accounting profit (loss) and profit (loss) reflected in the tax return for income tax and formed from temporary and permanent differences, clause 3 PBU 18/02.SHE (deferred tax asset) -
first, we recognize expenses in accounting, and in subsequent periods in tax. Income in tax, and later in accounting. The practice of using the abbreviation TNP (current tax on profit) and URNP (conditional income tax expense) has developed.Reflected in the reporting:
Balance sheet: Assets:IT (deferred tax liability) -
the opposite of SHE. First, we recognize expenses in tax accounting, and in subsequent periods in accounting. Income in accounting, and later in tax. Reflected in the reporting: Balance sheet: Passive:Constant differences
–income and expenses recognized only in accounting or only in tax accounting. They are: PNA - permanent tax assets; PNO-permanent tax liabilities; Reflected in the reporting:
Temporary differences.
So, we come to the most "serious" moment, which always raises a lot of questions from accountants. These are temporary differences. What it is, and how to "fight" it, we will consider in this article. Temporary differences are such differences that will affect the tax, increasing or decreasing it in the future. Accordingly, those differences that will increase income tax will be called taxable temporary differences, and those that will reduce income tax - deductible temporary differences. Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. Deferred tax assets (DTA) are deductible temporary differences multiplied by the income tax rate at the time the DTA is recognized. As the deductible temporary differences decrease or disappear, IT will decrease or be fully repaid. Accounting entries: Accrual of SHE Dt09 Kt68; Repayment of SHE Dt68 Kt09. Deferred tax liabilities (DTL) are taxable temporary differences multiplied by the income tax rate at the time the DTL is recognized. Deferred tax liabilities will decrease or be settled in full as the taxable temporary differences decrease or disappear. Accounting entries: IT accrual Dt68 Kt77; Repayment of IT Dt77 Kt68. In the financial statements it is allowed to reflect IT and IT in balance (collapsed). The amount of income tax (NP) is called conditional income (expense) (UD (R)), if NP is determined from accounting profit (loss). NP formed from tax profit is equal to UD (R) -PNO + (-) IT + (-) IT IT and IT are reflected in the balance sheet, respectively, as non-current assets and long-term commitments. Overpayment of income tax is recorded as an asset, debt is recognized as a liability. The statement of financial results reflects PNO, IT, IT and current income tax.Income statement:
 In addition, the following are disclosed separately in the notes to the balance sheet and the income statement:
In addition, the following are disclosed separately in the notes to the balance sheet and the income statement: - conditional expense (conditional income) for income tax;
- permanent and temporary differences arising in the reporting period and resulting in the adjustment of the notional expense (notional income) for income tax in order to determine the current income tax;
- permanent and temporary differences that arose in previous reporting periods, but resulted in the adjustment of the notional expense (notional income) for income tax of the reporting period;
- the amount of a permanent tax liability (asset), a deferred tax asset and a deferred tax liability;
- reasons for changes in applied tax rates compared to the previous reporting period;
- the amounts of a deferred tax asset and a deferred tax liability written off in connection with the disposal of an asset (sale, transfer at no cost or liquidation) or a type of liability.
All PBU for accounting for 2019 in the activities of economic entities must be applied without fail, unless otherwise established by a specific source of law. Which PBUs are in operation this year and which are expected in the next, we will tell in our article.
Accounting PBUs are generally published by the RF Ministry of Finance, for credit institutions - The Bank of Russia. It is necessary for all organizations to comply with the norms established by the PBU, unless exceptions are expressly indicated in a particular provision. For example, paragraph 3 of PBU 8/2010 states that the rules enshrined in the relevant source may not be applied by organizations that use simplified accounting schemes. These include, in particular, small businesses, NPOs and other entities (information of the Ministry of Finance dated June 29, 2016 No. PZ-3/2016).
In 2017, 24 different PBUs are applied in the Russian Federation, which determine the accounting rules. Let's consider them in more detail.
List of PBU on accounting in 2017
Accounting rules applied in the Russian Federation in 2017 are represented by the following list:
- PBU 7/98 - establishes the procedure for reflecting events in the accounting after the reporting date;
- PBU 4/99 - establishes the methodological foundations of the accounting statements of legal entities;
- PBU 9/99 - establishes the procedure for reflecting income in the accounting of organizations;
- PBU 10/99 - fixes the procedure for reflecting expenses in the accounting of legal entities;
ABOUT PBU 9/99 and 10/99 read .
- PBU 13/2000 - regulates the reflection in accounting of information about state aid to commercial firms;
- PBU 5/01 - regulates the reflection of the MPZ in accounting;
- PBU 6/01 - establishes the rules for reflecting fixed assets in accounting;
- PBU 16/02 - regulates the disclosure of information on terminated activities in accounting;
- PBU 17/02 - regulates the reflection of information on research expenditures in accounting;
- PBU 18/02 - establishes the rules for reflecting information about calculations of income tax in accounting;
- PBU 19/02 - regulates the rules for reflecting financial investments in accounting;
- PBU 20/03 - establishes the rules for reflecting in accounting information on the participation of a business entity in joint activities;
- PBU 3/2006 - regulates the reflection in the accounting of information about the assets and liabilities of the company in foreign currency;
- PBU 14/2007 - establishes the rules for reflecting information about intangible assets in accounting;
- PBU 1/2008 - determines how an enterprise should form and disclose accounting policies;
- PBU 2/2008 - establishes the rules for disclosing information about the activities of construction contractors (or subcontractors) in accounting;
- PBU 11/2008 - establishes how to disclose information about related parties in the reporting;
- PBU 15/2008 - establishes how to reflect information on expenses on loans and borrowings in accounting;
- PBU 21/2008 - establishes how to disclose information about changes in estimated values \u200b\u200bin the reporting;
- PBU 8/2010 - regulates how the estimated and contingent liabilities, as well as contingent assets in accounting;
- PBU 12/2010 - establishes the procedure for reflecting segment information in the accounting records of organizations;
- PBU 22/2010 - regulates the procedure for correcting errors and reflecting information about them in accounting;
- PBU 23/2011 - regulates how a traffic report should be drawn up money;
- PBU 24/2011 - establishes the procedure for reflecting in accounting information on the costs of the development of natural resources.
New PBUs in 2018-2021
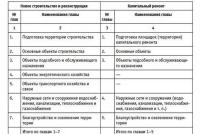
Since 2017, the Ministry of Finance has begun the global development of federal accounting standards for 2018-2020. According to the order of the Ministry of Finance "On the approval of the program for the development of federal accounting standards ..." dated April 18, 2018 No. 83n, new PBUs will be developed and amendments to the already issued provisions will be made. The plan for the development and implementation of innovations is shown in the table below.
|
Name of the PBU project |
Estimated effective date for mandatory application |
|
|
Development of new federal standards |
||
|
Intangible assets |
||
|
Incomplete capital investments |
||
|
Accounts receivable and creditor |
||
|
Documents and workflow | ||
PBU 1/2008 Accounting policy authority.
This PBU sets the rules for the formation. Accounting policy by the chief accountant or other person who is entrusted with maintaining the organization's accounting. The document regulates the procedure for approval: slave. chart of accounts, forms of primary accounting documents, registers, the procedure for taking an inventory of assets and liabilities of the body., methods of assessing A and O, document flow rules and processing technology for accounting information. In addition, the regulation establishes the procedure and rules for making changes to the accounting policy of the authority ..
PBU 2/2008 Accounting for construction contracts
discloses the procedure for the forms and disclosure of information on income, expenses and financial results of organizations that are contractors or subcontractors in construction contracts, the duration of work on which is of a long nature and is more than 1 reporting year or the start and end dates of which fall on different reporting years. In addition, PBU is used when accounting for contracts for the provision of services in the field of architecture, construction and other services inextricably linked with the object under construction. The document defines the requirements for the organization of accounting facilities under these agreements, the conditions for recognizing income and expenses, as well as the rules for determining the financial rez.
PBU 3/2006 Accounting for assets and liabilities, the cost of which is expressed in foreign exchange. currency
The document establishes the features of the form-I in the bu and reporting information about A and O, the cost of the cat. expressed in in. currency, including those payable in rubles, by organizations that are legal entities. persons according to the law of the Russian Federation. PBU regulates the procedure for recalculation expressed in foreign exchange. in the currency of the value Ai O in rubles, the requirements for accounting for exchange rate differences, and also establishes the procedure for reflecting in the BU A and O used by the organization to conduct business outside the Russian Federation.
PBU 4/99 Accounting reporting of the organization
This PBU establishes the composition, content and methodological foundations of the formation of buh. reporting - unified system data on property and the financial position of the organization and the results of its households. activity, compiled on the basis of data from bu in the established forms. The document defines a list of accounting forms and general requirements for it: rules for assessing accounting articles. reporting, audit bukh. reporting.
PBU 5/01 Accounting for inventories
establishes the rules for the formation in bu info about mat-prod. stocks of the organization. Determines the procedure for assessing material and production stocks and requirements for the procedure for recording the actual costs of their acquisition (procurement and delivery costs, interest on loans, customs duties, etc.). Regulates the procedure for determining their s / s when transferring to production and other disposal and the requirements for disclosing information in accounting reports.
PBU 6/01 Accounting for fixed assets
Pos. establishes requirements for the rules for the formation of information about the enterprise in the bu. Describes the criteria by which an asset is accepted by the organization for accounting as an asset. The methodology for assessing the wasp and the composition of costs for the formation of the initial. the cost of the object (amounts paid in accordance with the contract to the supplier; costs of delivery of the object, customs duties and customs duties, interest on loans, etc.). Methods for calculating depreciation of objects of fixed assets are established: linear, method of decreasing balance, method of writing off value by the sum of the number of years useful use, the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (works). The procedure for accounting for the costs of the organization for the repair and restoration of objects. Requirements for reflecting the disposal of wasps in buoperations in cases: sale, termination of use due to moral or physical wear, liquidation in case of an accident, natural disaster and other emergency, transfers as a contribution to authorized capital other body., mutual fund and other cases.
PBU 7/98 Events after the reporting date
For the purposes of a bu event after the reporting date is recognized the fact of economic activity that has had or may have an impact on the financial. condition, movement den. funds or results of the organization's activities and which took place between the reporting date and the date of signing the accounting statements for reporting year... This PBU establishes the procedure for reflection in accounting. reporting com-x organizations (except for credit agencies), which are legal. persons under the legislation of the Russian Federation, events after the reporting date. Determines the requirements for the reflection of such events and their consequences in accounting records. The annex to the PBU provides an approximate list of the facts of economic activity that can be recognized as events after the reporting date.
PBU 8/01 Conditional facts of households. activities
The conditional fact of economic activity in accordance with PBU is that it takes place as of reporting date fact households. an activity, the consequences of which and the likelihood of their occurrence in the future are uncertain, i.e. the occurrence of consequences depends on whether or not one or more uncertain events occur in the future. This Regulation establishes the procedure for reflecting the conditional facts of economic activity and their consequences in the bukh. reporting com-x organizations. Determines the composition of conditional facts for the bu. Establishes the rules for their reflection and the methodology for assessing the consequences in monetary terms. Disclosure of information about the consequences of conditional facts in the accounting of the organization.
PBU 9/99 Income of the organization
In accordance with PBU 9/99, the income of the organization is recognized as an increase in the economy. benefits from the receipt of assets, money. funds, other property or repayment of obligations, leading to an increase in the capital of this organization, with the exception of contributions from property owners. The document establishes the rules for the classification of income, discloses the list, composition of the organization's income and the procedure for their recognition. This PBU applies com. organizations (except for credit and fear) and regulates the procedure for displaying information.
PBU 10/9 Organization costs
Defines form rules in bu information about the costs of enterprises, classifies their composition and establishes the conditions for recognizing costs. Describes the procedure for the recognition and disclosure of companies and administrations. expenses in reporting.
PBU 11/2008 Information about related parties
This Regulation establishes the procedure for disclosing information about related parties in accounting statements. Determines the list of transactions with a related party, as well as the mandatory content of the info. subject to disclosure.
PBU 12/2000 Info. by segment
The regulation is applied by the organization in the preparation of consolidated accounting statements in the event that it has subsidiaries and dependent companies, as well as if the constituent documents of legal associations for it. persons (associations, unions, etc.), created on a voluntary basis, are entrusted with the compilation of a consolidated account. reporting.
PBU 13/2000 Accounting for state aid
The document establishes the rules for the formation. in the accounting for information on the receipt and use of state aid provided to com-organizations (except for credit Organizations), which are legal entities. persons under the legislation of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the organization), and recognized as an increase in the economy. benefits of a particular organization as a result of the receipt of assets (cash, other property)
PBU 14/2007 Accounting for intangible assets
Sets the rules for the formation of information and accounting reports of info nemat. assets of organizations. Determines the conditions for accepting an object as an intangible asset, and regulates the procedure for the initial assessment. Sets the rules for accounting for operations related to the grant (receipt) of the right to use intangible assets.
PBU 15/2008 Accounting for expenses on loans and credits
PBU discloses the features of the form in the accounting and accounting reporting of information on costs associated with the fulfillment of obligations on loans received (including raising borrowed funds by issuing bills of exchange, issuing and selling bonds) and loans (including goods and commercial).
PBU 16/02 Information on discontinued operations
Establishes the procedure for disclosing information on discontinued activities in the accounting records of the com. organizations. Describes the concept of discontinued operations, the conditions for its recognition and measurement. Specifies the requirements for information disclosure in reporting.
PBU 17/02 Accounting for R&D and technological work
establishes the rules of the form-I in the bu and accounting reporting com. organizations that are legal. persons under the legislation of the Russian Federation (excluding credit. organizations), information on the costs associated with the implementation of research, development and technological work.
PBU 18/02 Accounting for calculations of corporate income tax
This PBU determines the rules of the form in accounting and the procedure for disclosing in the accounting statements information about the calculations of corporate income tax for organizations recognized in the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation as taxpayers of income tax (except for credits of the Organization and budgetary institutions), and also determines the relationship of the indicator reflecting profit (loss) calculated in the manner prescribed by regulatory legal acts for the RF booth (hereinafter - accounting profit (loss), and tax base on income tax for reporting period (hereinafter referred to as taxable profit (loss) calculated in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees.
PBU 19/02 Accounting for financial investments
Determines the rules for the formation in the bu and reporting information about fin. investments of the organization. The rules for their initial and subsequent assessment, disposal, as well as requirements for the procedure for determining income and expenses for financial. investments.
PBU 20/03 Info about participation in joint activities
establishes the rules and procedure for disclosing information about participation in joint activities in the accounting reporting com. organizations (except for credit. organizations), which are legal. persons under the legislation of the Russian Federation. Discloses concepts: joint operations, jointly used assets and joint activities. Determines the requirements for information disclosure in accounting records.
PBU 21/2008 Change in estimated values
This PBU establishes the rules for recognition and disclosure in accounting statements), information on changes in accounting estimates and establishes the procedure for disclosing such data in an explanatory note to accounting. reporting.
Ministry of Finance order Russian Federation dated 06.11.2008 No. 106n "On the approval of accounting regulations (as amended on 28.04.2017 No. 69n).
In order to improve legal regulation in the field of accounting and financial reporting and in accordance with the Regulations on the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 30, 2004 N 329 (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2004, N 31, art. 3258; N 49, Art 4908; 2005, N 23, Art 2270; N 52, Art 5755; 2006, N 32, Art 3569; N 47, Art 4900; 2007, N 23, Art 2801 ; N 45, Art. 5491; 2008, N 5, Art. 411), I order:
1. To approve:
a) Regulation on accounting "Accounting policy of the organization" (PBU 1/2008) in accordance with Appendix N 1;
b) Regulation on accounting "Changes in estimated values" (PBU 21/2008) according to Appendix No. 2.
2. To recognize as invalid the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 9, 1998 N 60n "On approval of the Accounting Regulations" Accounting policy of the PBU 1/98 organization (the Order was registered with the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on December 31, 1998, registration number 1673; Bulletin of Normative Acts of Federal Executive Bodies, No. 2, January 11, 1999; " Russian newspaper", No. 10, January 20, 1999).
Deputy
Prime Minister
Russian Federation -
Minister of Finance
Russian Federation
A.L. Kudrin
Appendix N 1
to the Order of the Ministry of Finance
Russian Federation
(as amended on April 28, 2017 No. 69n)
Position
on accounting "Accounting policy of the organization"
(PBU 1/2008)
I. General provisions
1. This Regulation establishes the rules for the formation (selection or development) and disclosure accounting policies organizations that are legal entities under the laws of the Russian Federation (with the exception of credit institutions and public sector organizations) (hereinafter - organizations).
(as amended by the Orders of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 25.10.2010 N 132n, dated 28.04.2017 N 69n)
Branches and representative offices of foreign organizations located on the territory of the Russian Federation can form an accounting policy in accordance with this Regulation or based on the rules established in the country of location of a foreign organization, if the latter do not contradict International standards financial statements.
2. For the purposes of this Regulation, under accounting policies an organization is understood as a set of accounting methods adopted by it - primary observation, cost measurement, current grouping and final generalization of the facts of economic activity.
The methods of accounting include methods of grouping and evaluating the facts of economic activity, paying off the value of assets, organizing workflow, inventory, using accounting accounts, organizing accounting registers, processing information.
3. This Regulation applies to:
- in terms of the formation of accounting policies - for all organizations;
- in terms of disclosing accounting policies - to organizations that publish their financial statements in whole or in part in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, constituent documents, or on their own initiative.
II. Accounting policy formation
4. The accounting policy of the organization is formed by the chief accountant or another person who, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, is entrusted with maintaining the accounting of the organization, on the basis of these Regulations and approved by the head of the organization.
At the same time, the following are approved:
- a working chart of accounts of accounting, containing synthetic and analytical accounts necessary for accounting in accordance with the requirements of timeliness and completeness of accounting and reporting;
- forms of primary accounting documents, accounting registers, as well as documents for internal accounting reporting;
- the procedure for taking an inventory of the assets and liabilities of the organization;
- methods of assessing assets and liabilities;
- document flow rules and accounting information processing technology;
- the procedure for monitoring business operations;
- other solutions required for the organization of accounting.
5. When forming the accounting policy, it is assumed that:
- the assets and liabilities of the organization exist separately from the assets and liabilities of the owners of this organization and the assets and liabilities of other organizations (the assumption of property isolation);
- the organization will continue its activities in the foreseeable future and it has no intentions and the need to liquidate or materially reduce its activities and, therefore, the obligations will be extinguished in the prescribed manner (going concern assumption);
- the accounting policy adopted by the organization is applied consistently from one reporting year to another (assumption of the sequence of application of accounting policies);
- the facts of the organization's economic activities refer to the reporting period in which they took place, regardless of the actual time of receipt or payment of funds associated with these facts (the assumption of the temporal certainty of the facts of economic activity).
5.1. An organization chooses accounting methods regardless of other organizations' choice of accounting methods. If the parent company approves its accounting standards, which are binding on its subsidiary, then such subsidiary chooses the accounting methods based on the specified standards.
(Clause 5.1 introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
6. The accounting policy of the organization should ensure:
- completeness of reflection in accounting of all facts of economic activity (completeness requirement);
- timely reflection of the facts of economic activity in accounting and financial statements (timeliness requirement);
- greater readiness to recognize expenses and liabilities in accounting than possible income and assets, avoiding the creation of hidden reserves (prudence requirement);
- reflection in the accounting of the facts of economic activity proceeding not so much from their legal form as from their economic content and business conditions (the requirement of the priority of the content over the form);
- data identity analytical accounting turnovers and account balances synthetic accounting on the last calendar day of each month (consistency requirement);
- rational accounting, based on the conditions of management and the size of the organization, as well as on the basis of the ratio of the costs of generating information about a specific accounting object and the usefulness (value) of this information (requirement of rationality).
6.1. When forming an accounting policy, micro-enterprises and non-profit organizations that are entitled to use simplified accounting methods, including simplified accounting (financial) statements, may provide for accounting in a simple system (without double entry).
(Clause 6.1 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 18.12.2012 N 164n; as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.04.2015 N 57n)
7. Accounting for a specific object of accounting is maintained in the manner established by the federal accounting standard. If, on a specific issue of accounting, the federal accounting standard allows several methods of accounting, the organization chooses one of these methods, guided by clauses 5, 5.1 and 6 of these Regulations.
An organization that discloses consolidated financial statements drawn up in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards or the financial statements of an organization that does not create a group, has the right to be guided by federal accounting standards in forming its accounting policy, taking into account the requirements of International Financial Reporting Standards. In particular, such an organization has the right not to apply the accounting method established by the federal accounting standard when this method leads to inconsistency of the organization's accounting policy with the requirements of International Financial Reporting Standards.
(Clause 7 as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
7.1. If, on a specific issue of accounting, federal accounting standards do not establish accounting methods, then the organization develops an appropriate method based on the requirements established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting, federal and (or) industry standards. In this case, the organization, based on the assumptions and requirements given in clauses 5 and 6 of this Regulation, uses the following documents in sequence:
a) international financial reporting standards;
b) provisions of federal and / or industry accounting standards on similar and / or related issues;
(Clause 7.1 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
7.2. An organization that has the right to use simplified accounting methods, including simplified accounting (financial) statements, in the absence of appropriate accounting methods for a specific issue in federal accounting standards, has the right to form an accounting policy, guided solely by the requirement of rationality.
(Clause 7.2 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
7.3. In exceptional cases, when the formation of accounting policies in accordance with clauses 7 and 7.1 of this Regulation leads to an unreliable representation financial situation organizations, financial results its activities and the movement of its funds in the accounting (financial) statements, the organization has the right to deviate from the rules established by these paragraphs, subject to all of the following conditions:
a) the circumstances that prevent the formation of a reliable idea of \u200b\u200bits financial position, financial performance and cash flow in the accounting (financial) statements have been identified;
b) an alternative method of accounting is possible, the use of which makes it possible to eliminate the indicated circumstances;
c) an alternative method of accounting does not lead to other circumstances in which the accounting (financial) statements of the organization will give an unreliable idea of \u200b\u200bits financial position, financial performance and cash flow;
d) information on deviation from the rules established by clauses 7 and 7.1 of this Regulation, and the application alternative way accounting is disclosed by the organization in accordance with this Regulation.
(Clause 7.3 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
7.4. To the extent that the application of the accounting policy formed in accordance with clauses 7 and 7.1 of these Regulations leads to the formation of information, the presence, absence or method of reflection of which in the accounting (financial) statements of the organization does not depend economic solutions users of this reporting (hereinafter referred to as immaterial information), the organization has the right to choose the method of accounting, guided solely by the requirement of rationality (without applying paragraphs 7, 7.1 of these Regulations). The organization carries out the classification of information as insignificant on its own, based on both the size and nature of this information.
(Clause 7.4 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
8. The accounting policy adopted by the organization is subject to registration by the appropriate organizational and administrative documentation (orders, instructions, standards, etc.) of the organization.
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
9. The accounting methods chosen by the organization when forming the accounting policy are applied from January 1 of the year following the year of approval of the corresponding organizational and administrative document. At the same time, they are applied by all branches, representative offices and other divisions of the organization (including those allocated to a separate balance sheet), regardless of their location.
The newly created organization, the organization resulting from the reorganization, draws up the selected accounting policy in accordance with this Regulation no later than 90 days from the date of state registration of the legal entity. The accounting policy adopted by the newly created organization is considered to be applied from the date of state registration of the legal entity.
III. Change in accounting policies
10. A change in the accounting policy of an organization can be made in the following cases:
- changes in the legislation of the Russian Federation and (or) regulatory legal acts on accounting;
- development by the organization of new methods of accounting. The use of a new method of accounting involves improving the quality of information about an accounting object;
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n) - significant changes in business conditions. A significant change in the operating conditions of an organization may be associated with reorganization, change in activities, etc.
It is not considered a change in accounting policy to approve the method of accounting for the facts of economic activity, which differ in substance from the facts that occurred earlier, or arose for the first time in the activities of the organization.
11. The change in accounting policy must be justified and formalized in the manner prescribed by paragraph 8 of this Regulation.
12. A change in accounting policy is made from the beginning of the reporting year, unless otherwise determined by the reason for such a change.
13. The consequences of changes in accounting policies that have or are likely to have a significant impact on the financial position of the organization, financial results of its activities and (or) cash flows are estimated in monetary terms. Estimation in monetary terms of the consequences of changes in accounting policies is based on the data reconciled by the organization as of the date from which the changed accounting method is applied.
14. The consequences of a change in accounting policy caused by a change in the legislation of the Russian Federation and (or) regulatory legal acts on accounting are reflected in accounting and reporting in the manner prescribed by the relevant legislation of the Russian Federation and (or) a regulatory legal act on accounting. If the relevant legislation of the Russian Federation and (or) a regulatory legal act on accounting does not establish the procedure for reflecting the consequences of a change in accounting policy, then these consequences are reflected in accounting and reporting in the manner prescribed by paragraph 15 of these Regulations.
15. The consequences of changes in accounting policies caused by reasons other than those specified in paragraph 14 of these Regulations, and which have or are likely to have a significant impact on the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and (or) cash flows, are reflected in the financial statements retrospectively, for except in cases where the assessment in monetary terms of such consequences for the periods preceding the reporting period cannot be made with sufficient reliability.
When retrospectively reflecting the consequences of a change in accounting policy, it is assumed that the changed method of accounting has been applied since the occurrence of the facts of economic activity of this type. The retrospective reflection of the consequences of the change in accounting policy is to adjust the opening balance under the item "Retained earnings (uncovered loss)" and (or) other items balance sheet at the earliest date presented in the accounting (financial) statements, as well as the values \u200b\u200bof related items of the accounting statements disclosed for each period presented in the accounting statements, as if the new accounting policy was applied from the moment the facts of economic activity of this type appeared.
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
In cases where the assessment in monetary terms of the consequences of a change in accounting policy in relation to the periods preceding the reporting one cannot be made with sufficient reliability, the changed method of accounting is applied to the corresponding facts of economic activity that have occurred after the introduction of the changed method (prospectively).
15.1. Organizations that are entitled to use simplified accounting methods, including simplified accounting (financial) statements, may reflect in the financial statements the consequences of changes in accounting policies that have had or may have a significant impact on the financial position of the organization, its financial results and (or) cash flow. funds, prospectively, except for cases when a different procedure is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation and (or) a regulatory legal act on accounting.
(Clause 15.1 was introduced by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08.11.2010 N 144n; as amended by the Orders of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 27.04.2012 N 55n, dated 06.04.2015 N 57n)
16. Changes in accounting policies that have or are likely to have a significant impact on the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and (or) cash flows are subject to separate disclosure in the financial statements.
IV. Disclosure of accounting policies
17. The organization must disclose the accounting methods adopted in the formation of the accounting policy, without knowledge of the application of which interested users of accounting (financial) statements cannot reliably assess the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and (or) cash flow.
(Clause 17 as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
18. The paragraph is deleted. - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 11, 2009 N 22n.
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
If the financial statements are not published in full, information on the accounting policy is subject to disclosure, at least in the part directly related to the published data.
19. If the accounting policy of the organization is formed on the basis of the assumptions provided for in paragraph 5 of this Regulation, then these assumptions may not be disclosed in the financial statements.
When forming the accounting policy of the organization, based on assumptions different from those provided for in paragraph 5 of this Regulation, such assumptions, together with the reasons for their application, must be disclosed in the financial statements.
20. If, in the preparation of the financial statements, there is significant uncertainty about events and conditions that could give rise to material doubts about the applicability of the going concern assumption, then the entity should indicate such uncertainty and clearly describe what it is associated with.
20.1. An organization that forms an accounting policy in accordance with paragraph two of clause 7 of these Regulations must, in relation to each method of accounting that it has not applied established by the federal accounting standard, describe such a method, as well as disclose the corresponding requirement of the International Financial Reporting Standard and describe how Thus, this requirement will be violated if the accounting method established by the federal accounting standard is applied.
(Clause 20.1 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
20.2. An organization that has applied clause 7.3 of this Regulation in forming its accounting policy must disclose:
- the name of the federal accounting standard that establishes the method of accounting, from the application of which the organization has departed, with a brief description of this method;
- circumstances as a result of which the application of the rules established by clauses 7 and 7.1 of these Regulations leads to the fact that the accounting (financial) statements of the organization do not allow obtaining a reliable idea of \u200b\u200bits financial position, financial performance and cash flows and the reasons for these circumstances;
- the content of an alternative accounting method used by the organization and an explanation of how this method eliminates the inaccuracy of the presentation of the organization's financial position, financial results of its activities and cash flows;
- the values \u200b\u200bof all indicators of the accounting (financial) statements of the organization that have been changed as a result of deviation from the rules established by paragraphs 7 and 7.1 of these Regulations, as if the deviation had not been made, and the amount of adjustment for each indicator.
(Clause 20.2 was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
21. In the event of a change in accounting policy, an entity shall disclose the following information:
- the reason for the change in accounting policy;
- the content of the change in accounting policy;
- the procedure for reflecting the consequences of changes in accounting policies in financial statements;
- the amount of adjustments related to changes in accounting policies for each item in the financial statements for each of the reporting periods presented, and if the organization is required to disclose information on earnings per share, also according to data on basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share;
- the amount of the corresponding adjustment relating to the reporting periods preceding those presented in the financial statements - to the extent that it is practically possible.
If the change in accounting policy is due to the application of a regulatory legal act for the first time or a change in a regulatory legal act, the fact of reflecting the consequences of a change in accounting policy in accordance with the procedure provided for by this act is also subject to disclosure.
22. In case the disclosure of information, under paragraph 21 of this Regulation, for some separate previous reporting period presented in the financial statements, or for reporting periods earlier than those presented, is impossible, the fact that such disclosure is impossible is subject to disclosure together with an indication of the reporting period in which the application of the corresponding changes in accounting policies.
23. If the regulatory legal act on accounting provides for the possibility of voluntary application of the rules approved by it before the date of their mandatory application, the organization, when using this opportunity, must disclose this fact in the accounting (financial) statements.
(Clause 23 as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
24. Essential methods of accounting, as well as information on changes in accounting policies are subject to disclosure in the accounting (financial) statements of the organization.
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
In the case of submission of interim accounting (financial) statements, it may not contain information about the accounting policy of the organization, if the latter has not changed since the preparation of the annual accounting (financial) statements for the previous year, in which the accounting policy is disclosed.
(as amended by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n)
25. Abolished. - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017 N 69n.
On January 1, 1999, in pursuance of the Program of reforming accounting in Russia in accordance with international financial reporting standards, the Regulation on accounting and accounting reporting was put into effect, which consists of six sections.
Section 1. General Provisions
The procedure for organizing and maintaining accounting, drawing up and submitting financial statements by legal entities under the legislation of the Russian Federation, the organization's relationship with external consumers of accounting information is determined; the concept of accounting is considered; the objects and main tasks of accounting are named; the procedure for regulating accounting by legislative, regulatory and legal acts is determined, the persons responsible for their implementation are indicated, the purpose and content of the organization's accounting policy is established.
Depending on the volume of accounting work, the manager can:
- to establish an accounting service as a structural unit with a chief accountant at the head;
- introduce the position of an accountant into the staff:
- transfer, on a contractual basis, accounting to a centralized accounting department, or a specialized organization, or a specialist accountant;
- personally maintain accounting records.
Section 2. Basic rules of accounting
The section formulates the requirements for accounting; rules for documenting business transactions have been established; the purpose and procedure for the formation of accounting registers has been determined; the methods of assessing property and liabilities, the purpose and procedure for carrying out an inventory of property and liabilities, accounting rules for discrepancies between actual and accounting data revealed during the inventory are indicated.
Section 3. Basic rules for the preparation and presentation of financial statements
Consists of two subsections: in the first - the basic requirements for the content, forms, order of preparation are stated. signatures, changes in financial statements. All organizations prepare financial statements for the month, quarter and year on an accrual basis from the beginning of the reporting year in accordance with the established forms (composition of financial statements budgetary organizations determined by the Ministry of Finance of Russia); in the second, the rules for assessing accounting items are established: unfinished capital investment; financial investments; fixed assets; intangible assets: raw materials, materials, finished products and goods; work in progress and prepaid expenses; capital and reserves; settlements with debtors and creditors; profit (loss) of the organization.
Section 4. The procedure for presenting financial statements
For all organizations (except for budgetary ones), directions, forms, deadlines for submitting annual financial statements have been determined; it is indicated that the said reporting is open to interested users: banks, investors, creditors, buyers, suppliers, and other entities; the procedure for publishing financial statements in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation has been determined.
Section 5. Basic rules of consolidated financial statements
According to these rules:
- if the organization has subsidiaries and dependent companies in addition to its own accounting report consolidated financial statements are also compiled, including indicators of reports of such companies located on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad, in the manner established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation;
- the persons who sign the consolidated financial statements are indicated - the head and the chief accountant, whose responsibility is determined by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Section 6. Storage of accounting documents
When storing documents, organizations must comply with the following rules:
- storage periods for primary accounting documents, accounting registers, accounting statements are established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs (at least 5 years);
- withdrawal primary documents is carried out only by the bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation, prosecutor's office, courts, tax police, inspection;
- the head of the organization is responsible for organizing the storage of documents.
The chief accountant or other official of the organization has the right, with permission and in the presence of representatives of the bodies conducting the seizure of documents, to make copies of them indicating the grounds and date of seizure.
To date, the following accounting regulations have been developed, approved and are in effect.
|
Short designation |
Name |
Approval document |
|
Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of July 29, 1998 No. 34n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 30.12.1999 No. 107n, of 24.03.2000 No. 31 n, of 18.09.2006 No. 116n, of 26.03.2007 No. 26n, as amended , introduced by the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of 08.23.2000 No. GKPI 00-645) |
|
|
Organization's accounting policy |
||
|
Accounting for construction contracts |
||
|
Accounting for assets and liabilities, the value of which is denominated in foreign currency |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 No. 154n (as amended by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 25, 2007 No. 147n) |
|
|
Organization's accounting statements |
||
|
Accounting material production stocks |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of June 9, 2001 N ° 44n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 27.11.2006 No. 156n, from 26.03.2007 No. 26n) |
|
|
Fixed asset accounting |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of March 30, 2001 No. 26n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of May 18, 2002 No. 45n, of 12.12.2005 No. 147n, of September 18, 2006 No. 116n, of November 27, 2006 No. 156n) |
|
|
Events after the reporting date |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 25, 1998 No. 56n (as amended by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 20, 2007 No. 143n) |
|
|
Contingent facts of economic activity |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 28, 2001 No. 96n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of September 18, 2006 No. 11 bn, of December 20, 2007 No. 144n) |
|
|
Organization income |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of May 6, 1999 No. 32n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 30.12.1999 No. 107n, dated 30.03.2001 No. 27n, dated 18.09.2006 No. 116n, dated 27.11.2006 No. 156n) |
|
|
Organization expenses |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of May 6, 1999 No. ЗЗн (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 30.12.1999 No. 107n, dated 30.03.2001 No. 27n, dated 18.09.2006 N ° 116n, dated 27.11.2006 N ° 156n) |
|
|
Information about related parties |
||
|
Segment information |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of January 27, 2000 No. 11n (as amended by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 18.09.2006 No. 115n) |
|
|
State aid accounting |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of October 16, 2000 N9 92n (as amended by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 18.09.2006 No. 115n) |
|
|
Accounting for intangible assets |
||
|
Accounting for expenses on loans and credits |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of October 6, 2008 No. 107n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 18.09.2006 N ° 115n, of 27.11.2006 No. 155n) |
|
|
Information on discontinued operations |
||
|
Accounting for research, development and technological work costs |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 19, 2002 No. 115n (as amended by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 18.09.2006 No. 116n) |
|
|
Accounting for income tax calculations |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 19, 2002 No. 114n (as amended by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 11.02.2008 No. 23n) |
|
|
Accounting for financial investments |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 10, 2002 No. 126n (as amended by orders of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 18.09.2006 No. 116n, of 27.11.2006 No. 156n) |
|
|
Information on participation in joint activities |
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 24, 2003 No. 105n (as amended by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of September 18, 2006 No. 116n) |
|
|
Changes to accounting estimates |
||
|
Long-term investment accounting regulations |
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 30.12.1993 No. 160 |
The above Regulations are based on legislative and regulatory acts governing the organization of accounting in Russia and taking into account some international financial reporting standards, bringing Russian accounting closer to them.