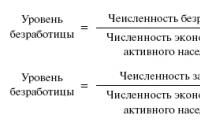
Earnings from past years of posting. How to take into account the profit of previous years, revealed in the reporting year. Last year's expenses identified in the reporting period: accounting
Debit 20 Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for property tax of organizations"
- 30,000 rubles. - reflects the additional assessment of corporate property tax for the 1st quarter.
How to correct significant errors of the past in accounting
Significant errors of the previous year, discovered before the approval of the annual accounts for that period, using the appropriate accounts for accounting for costs, income, settlements, etc.
If significant errors of past years are identified, the reporting for which has been signed and approved, using account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” (subparagraph 1, clause 9 of PBU 22/2010).
There are two possibilities.
Option 1. When, as a result of an error, the accountant did not reflect any income or overestimated the expense, make the entry:
Debit 62 (76, 02 ...) Credit 84
- the erroneously unreported income (excessively reflected expense) of the last year was revealed.
Option 2. If, as a result of an error, the accountant did not reflect any expense or overestimated income, make the following entry:
Debit 84 Credit 60 (76, 02 ...)
- an erroneously unreported expense (excessively reflected income) of the last year was revealed.
But what to do when mistakes were made not only in accounting, but also in tax accounting?
Then in you will have to make the necessary additional charges. For example, what kind of entry should be made for income tax if the tax base has been understated:
- additional tax on profit of the last year was charged according to the revised declaration.
In when, as a result of an error, taxes were overpaid, make entries based on those fixesthat you will do in tax accounting. Three situations can arise here.
1. If you submit an updated tax return for the year in which the error was made, then make a note:
Debit 68 subaccount "Income tax" Credit 84
- the income tax for the last year was reduced according to the revised declaration.
2. Correcting errors in tax accounting for the current period, make the following entry in accounting:
Debit 68 subaccount "Income tax" Credit 99
- reflected a permanent tax asset due to the fact that the tax accounting of the current period recognized expenses (reduced income) related to the previous year.
3. When it was decided not to correct an error in tax accounting, then there is no need to make additional entries. Since in accounting, the correction of significant errors does not affect the accounts of the financial results of the current period.
How to correct minor mistakes of the past in accounting
Correct minor errors in accounting. Profit or loss that will arise as a result of adjustments, reflect on account 91 "Other income and expenses". It does not matter whether the statements were approved by the time the error was identified or not. This conclusion follows from paragraph 14 of PBU 22/2010.
If, as a result of an insignificant error, the accountant did not reflect any income or overestimated expenses, make the entry:
Debit 60 (62, 76, 02 ...) Credit 91-1
- an erroneously unreported income has been identified (excessively reflected expense).
When, as a result of a minor error, the accountant did not reflect any expense or overstated income, make a note:
Debit 91-2 Credit 02 (10, 41, 60, 62, 76 ...)
- an erroneously unreported expense (excessively reflected income) was detected.
The correction of minor errors in accounting affects the accounts of the financial results of the current year, in the tax one this does not always happen. So, there will be permanent differences that need to be reflected in the accounting according to the rules of PBU 18/02.
There are two possibilities. When income tax was understated or overstated due to minor errors.
Option 1 - income tax is understated... In this case, corrections are made in tax accounting and an updated tax return is submitted for the period in which the error was made. At the same time, additional income tax is charged. However, in accounting they do it ... In this case, accounting needs to reflect permanent tax asset :
Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations of income tax" Credit 99 subaccount "Permanent tax assets"
- reflected a permanent tax asset.
An example of correcting a minor error (unreported income) in accounting and tax accounting. The mistake was made last year, the reporting for which was signed and approved
In March 2016, an accountant of Alpha LLC discovered an error in the calculation of income tax for 2015 - the proceeds from the sale of goods in the amount of 250,000 rubles were not taken into account. Income at Alpha is recognized in the same way both in tax and in accounting. As a result, the organization underpaid tax, the amount of which amounted to 50,000 rubles. (250,000 rubles × 20%).
The accountant filed an updated income tax return for 2015 and made the following entries:
Debit 62 Credit 91 subaccount "Other income"
- 250,000 rubles. - reflected income (proceeds from sales) of the previous tax period, identified in the reporting year;
Debit 99 subaccount "Income tax surcharge due to the detection of errors"
- 50,000 rubles. - additional tax on profit of the last year was charged according to the revised declaration;
Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations of income tax"
Credit 99 subaccount "Permanent tax asset"
- 50,000 rubles. - a permanent tax asset is reflected in the amount of proceeds from the sale of 2015, which is shown in accounting in 2016 income, and in tax accounting - in 2015 income.
For the first quarter of 2016, the amount of tax payable is 170,000 rubles. Thus, the total income tax debt to the budget amounted to 220,000 rubles. (170,000 rubles + 50,000 rubles), including 170,000 rubles. - current income tax and 50,000 rubles. - surcharge due to an error of the previous period. Alpha's accountant makes the following entry:
Debit 99 sub-account "Contingent income tax expense"
Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations of income tax"
- 220,000 rubles. - reflected the conditional income tax expense.
Option 2 - income tax is too high... In this case, the accountant makes his own decision , by what period to make an edit or even not to do it at all.
If he corrects the error by recalculating the tax of the current period, then he will make changes in both accounting and tax accounting at the same time. There will be no difference. They will arise only if the accountant decides to submit an updated declaration for the past period, or not to make an amendment at all. Then tax profit the current period will be greater than the one that will be obtained in accounting. So, there will be permanent tax liability ... Reflect it in accounting as follows:
- reflected a permanent tax liability.
This follows from paragraphs 4, 7 of PBU 18/02.
An example of correcting a minor error (unreported expense) in accounting and tax accounting. The mistake was made last year, the reporting for which was signed and approved. In tax accounting, an error is corrected in the period in which it was made
In March 2016, the accountant of LLC Alpha discovered an error in the calculation of income tax for 2015 - expenses (cost of goods sold) in the amount of RUB 150,000 were not taken into account. Expenses are equally recognized in tax and accounting. As a result, the organization overpaid the tax, the amount of the overpayment amounted to 30,000 rubles. (150,000 rubles × 20%).
Alpha's accountant filed a revised income tax return for 2015 and made the following entries:
Debit 91 subaccount "Other expenses" Credit 41
- 150,000 rubles. - reflects the expenses (cost of goods sold) of the previous tax period, identified in the reporting year;
Debit 68 subaccount "Calculations of income tax" Credit 99 subaccount "Overpayment of income tax on the revised declaration"
- 30,000 rubles. - reduced income tax for the last year according to the revised declaration;
Debit 99 subaccount "Permanent tax liabilities" Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations of income tax"
- 30,000 rubles. - a permanent tax liability is reflected in the amount of expenses in 2015, which is shown in accounting in expenses in 2016, and in tax accounting - in expenses in 2015.
For the first quarter of 2016, the amount of tax payable to the budget is 110,000 rubles. Balance sheet profit is less than tax profit due to expenses recorded for taxation in the revised tax return of the previous year. The tax calculated on the balance sheet profit is 80,000 rubles. (110,000 rubles - 30,000 rubles). The accountant makes the following entry:
Debit 99 subaccount "Conditional expense for income tax" Credit 68 subaccount "Calculations for income tax"
- 80,000 rubles. - reflected the conditional income tax expense.
Taking into account the tax overpayment for 2015, 80,000 rubles must be transferred to the budget. (110,000 rubles - 30,000 rubles).
Attention:there is an opinion that all expenses that are not taken into account when calculating taxes on profit should be reflected in accounting as part of others. This is not true. For a mistake officials will be fined ... If, in the end, taxes are also lowered, then the organization itself will be punished, and the amount of fines will increase ... But there is a way out.
If during the audit they find a similar error of past years, due to which reporting and taxes are distorted, then it will not be possible to avoid responsibility. You will mitigate the consequences if by yourself recalculate taxes and submit the correct information , pay interest.
As for the mistakes of the current year, everything is fixable. If you correctly qualify the costs, then you will successfully generate reports and calculate taxes. Erroneous entries .
Remember, expenses are taken into account depending on their purpose and the conditions under which they are incurred. So, for example, in accounting, costs are attributed not only to other costs, but also to costs for ordinary activities (paragraph 4 of PBU 10/99).
Alpha pays compensation to an employee when his car is used for business purposes. The compensation is 5,000 rubles. per month. But when calculating income tax, only 1200 rubles are taken into account. (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 8, 2002 No. 92).
Mistake!
Debit 20 Credit 73
- 1200 rubles. - compensation was charged to an employee for a personal car within the norms;
Debit 91-2 Credit 73
- 3800 rubles. - compensation was charged to an employee for a personal car in excess of the norms.
Correctly like this:
Debit 20 (26, 44 ...) Credit 73
- 5000 rubles. - the employee has been compensated for his personal car.
Here's how to fix the error:
Debit 91-2 Credit 73
- 3800 rubles. - canceled compensation to an employee for a personal car in excess of the norms;
Debit 20 Credit 73
- 3800 rubles. - additional compensation was charged to the employee for a personal car.
An error was made in the accounting of a small business
Significant accounting errors of past years small businesses , can be corrected in the same order as ... That is, without retrospective recalculation of indicators accounting statements (clause 9 of PBU 22/2010, part 4 of article 6 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
An example of correcting a significant error in accounting and reporting (overly reflected expense) by a small business. The mistake was made last year, the reporting for which was signed and approved
Alpha LLC is a small business. In March 2016, after the approval of the 2015 financial statements, Alpha's accountant revealed an error made in the 1st quarter of 2015.
The accounting reflects the cost of work performed by the contractor in March 2015 - 50,000 rubles. (without VAT). The act also indicates the amount of 40,000 rubles. (without VAT). The work performed was paid to the contractor in full (40,000 rubles) in March 2015. Thus, as of December 31, 2015, in the accounting of Alpha formed accounts payable in the amount of unnecessarily written off expenses - 10,000 rubles.
Alpha's accounting policy states that significant errors of previous years, revealed after the approval of the financial statements, are corrected without retrospective recalculation.
March 2016:
Debit 60 Credit 91-1
- 10,000 rubles. - reflects the cost of the contractor's work, erroneously attributed to expenses in the 1st quarter of 2015.
Since the 2015 statements have already been approved, no corrections have been made to them.
Corrections are made in accounting for 2016. In tax accounting, corrections are made in the period of the error. In this regard, Alpha's accountant filed a revised income tax return for 2015.
Alpha is a small business, therefore PBU 18/02 does not apply. This means that the discrepancy between the accounting and tax accounting the accountant won't have to.
Impact of past errors on current reporting
Correction of significant errors of the last year, revealed after the approval of accounting records, affects the balance sheet and other forms of the current year. Only when it is impossible to establish a connection between an error with a specific period, as well as to determine its impact on all previous periods, no correction will have to be made.
So, in the current reporting, you need to recalculate the comparable indicators of previous periods. Do it as if you never made a mistake. This is called retrospective recalculation. This follows from subparagraph 2 of paragraph 9 of PBU 22/2010.
An example of the correction in accounting and reporting of a material error (overly reflected expense) by an enterprise that is not a small company. The mistake was made last year, the reporting for which was signed and approved
In March 2016, after the approval of the statements for 2015, the accountant of LLC Alpha revealed an error made in the 1st quarter of 2015.
The accounting reflects the cost of the work performed under the act received from the contractor in March 2015, in the amount of RUB 50,000. (without VAT). In fact, the act indicates the amount of 40,000 rubles. (without VAT). The work performed was paid to the contractor in full (40,000 rubles) in March 2015. Thus, as of December 31, 2015, accounts payable in the amount of overwritten expenses - RUB 10,000 were generated in Alpha's accounting records.
The accountant reflected the overly written off expenses in the accounting as follows.
March 2016:
Debit 60 Credit 84
- 10,000 rubles. - reflects the cost of the contractor's work, erroneously attributed to expenses in the 1st quarter of 2015;
Debit 84 Credit 68 subaccount "Income tax"
- 2000 rubles. (RUB 10,000 × 20%) - additional income tax was charged.
Since the 2015 financial statements have already been approved, no corrections are being made.
Therefore, the result of the corrections was reflected by the Alpha accountant in the statements for 2016 in the sections where the indicators of 2015 are recorded. At the same time, he corrected the data as if there had never been an error (if expenses in the amount of 40,000 rubles were initially reflected). In the column for comparative indicators of 2015 in the lines of cost and profit (Statement of financial results approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n), the accountant reflected the amount in 10,000 rubles. different from the one that stands for the same lines in the reporting of 2015 for the corresponding period. In the balance sheet for 2016, the opening balances as of January 1, 2016 were recalculated by the accountant based on the cost of the work performed specified in the act, equal to 40,000 rubles, and not 50,000 rubles. Income tax increased by 2,000 rubles.
In addition, the Alpha accountant filed a revised declaration for income tax for 2015.
A significant mistake could have been made more than two years ago. In this case, you need to adjust the opening balances for the corresponding reporting items at the beginning of the earliest of the presented years. This is stated in paragraph 11 of PBU 22/2010.
If it is impossible to determine the impact of a material error on one (or more) of the previous reporting periods presented in the financial statements, the opening balance is adjusted at the beginning of the earliest of the periods for which recalculation is possible. This situation can arise if, to determine the impact of the error on the previous reporting period:
- complex and (or) numerous calculations are required, during which it is impossible to extract information about the circumstances that existed at the date of the error;
- it is necessary to use the information obtained after the date of approval of the financial statements for the previous reporting period.
This procedure is spelled out in paragraphs 12, 13 of PBU 22/2010.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia clarified that the organization has the right to include in the tax base of the current reporting period the amount of the detected error, which led to the excessive payment of tax in the previous reporting period, only if profit is made in the current reporting period. If, according to the results of the current reporting period, a loss is received, then it is necessary to recalculate the tax base for the period in which the error occurred ().
Recall that if errors are found in the calculation of the tax base relating to past tax periods, in the current tax period recalculation of the tax base and the tax amount is performed for the period in which these errors were made ().
Representatives of the Ministry of Finance of Russia emphasized that this is possible in two cases: when it is impossible to determine the period of mistakes (distortions) and when the mistakes made have led to excessive tax payments.
In which tax period it is necessary to reflect the unaccounted income of the previous tax period, learn from the material "Accounting for income of previous years identified in the reporting (tax) period
"
in "
Encyclopedias of solutions. Taxes and fees"
Internet versions of the GARANT system. Get free access for 3 days!
Thus, a taxpayer who made mistakes that led to excessive tax payment in the previous tax period has the right to adjust the tax base for the tax period in which errors were revealed.
Failure to reflect, for taxation purposes, the profits of organizations of expenses that arose in previous tax periods, but were identified in the current reporting period as a result of obtaining primary documents, is a distortion of the tax base of the previous tax period, therefore, these transactions are subject to the provisions.
In turn, the tax base for calculating profit tax is the monetary expression of profit determined in accordance with taxable ().
If in the reporting period the taxpayer incurred a loss, then in this reporting period the tax base is recognized as zero (). In this regard, recalculation of the tax base of the current reporting period is not possible.
Consequently, expenses related to past tax periods identified as a result of obtaining primary documents in the current reporting period can be taken into account in the tax period of their discovery, subject to the conditions established taking into account the provisions.
As an example, we can cite the situation when the primary documents on communication services provided in October of the previous year were received by the organization only in February of this year, after the annual accounting and tax reports for the previous year were submitted. The amount of the identified unrecorded expense resulted in excess income tax payment in previous year... Accordingly, a correction in tax accounting can be made in the current tax period by reflecting the unaccounted expense in the tax reporting for the first quarter of the current year.
The financiers also drew attention to the fact that an application for offset or refund of the amount of overpaid tax, including as a result of recalculation of the tax base that resulted in excessive payment of tax, can be submitted within three years from the date of payment of tax ().
If only the current income tax is reflected in the Profit and Loss Statement, then financial results will amount to 231,000 rubles. (300,000 rubles - 9,000 rubles - 60,000 rubles), but this does not correspond to the data accounting... Therefore, two amounts must be reflected in the Profit and Loss Statement: - on line 150 - 60,000 rubles. in parentheses; - on a free line below - 2160 rubles. (the amount of excessively accrued income tax for the previous, 2007, subject to refund). Then the net profit (line 190) will be 233,160 rubles. And this amount corresponds to the accounting data (account balance 99). Thus, the indicator of line 190 of the Profit and Loss Statement gives a real idea of \u200b\u200bthe amount of net profit received by the organization. Profit and loss statement for 2009 (thous.
Operations under pbu 18/02 when identifying profits and losses of previous years
And it should equal the profit (loss) revealed for the reporting period on the basis of accounting for all business operations of the organization. Recommendations for filling out Form No. 2 in the situation under consideration are given in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 10, 2004 No. 07-05-14 / 328.
It states that the amount of additional income tax payments for previous years should be reflected in the Profit and Loss Statement in a separate line - after the current income tax. Example 83 In April 2009, when reconciling settlements with a supplier, an accountant discovered that in November 2007
the printer received on the invoice worth 9000 rubles was not capitalized. (No VAT). Based on the accounting statement in April 2009, the following entries are made in accounting: D-t accounts 91 - K-t account 60 - 9000 rubles. - the cost of the purchased printer put into operation in 2007 is included in other expenses.
Losses of previous years identified in the reporting period
On the fact of the revealed discrepancies, the accountant of Veksel LLC filed an updated tax return for 2014. According to the information provided in the primary declaration, the taxable profit of OOO Veksel was RUB 83,000.
Attention
In the revised declaration, the Veksel LLC accountant showed a loss at the end of 2015 in the amount of RUB 13,750. In the accounting of OOO Veksel, the following entries were made: Dt CT Description Amount Document 91 76 Reflection of the identified expenses of the last year 118,000 rubles.
Important
Revised tax declaration 99 68.04 Reflection of PNR in the amount of 24% of the identified expenses in 2014 (118,000 rubles * 24%) 28 320 rubles. Revised tax declaration 76 91 Reflection of identified income in 2014 74,000 rubles.
Revised tax declaration 68.04 99 Reflection of PNA from the amount of revealed income in 2014 (74,000 rubles * 24%) 17,760 rubles.
How to take into account the profit of previous years, revealed in the reporting year
For tax purposes, the printer must be expensed as a 2007 expense. When calculating income tax for 2009, this amount is not included in expenses.
Info
Suppose that at the end of 2009, the organization received a profit from the sale of goods (works, services) in the amount of 300,000 rubles. both in accounting and tax accounting. The organization did not have any other income and expenses (apart from the identified expenses of previous years).
In this situation, the amount of income tax for 2009 will be 60,000 rubles. (300,000 rubles. X 0.20), the amount of overpayment for income tax for 2007 - 2,160 rubles. (9,000 rubles x 0.24). In accounting for 2009 we have the following final entries: D-t account 90 - K-t account 99 - 300,000 rubles. - reflected the profit from sales of the current year; D-t account 99 - K-t account 91 - 9000 rubles. - the total amount of other expenses of the current year is reflected.
How to take into account the profit of previous years in 2017
Revised tax declaration 68.04 99 Reflection of the overpayment of income tax according to the revised declaration (RUB 83,000 x 24%); RUB 19,920 Revised tax declaration 09 99 Reflection of IT from the amount of loss in tax accounting in 2014 that arose upon the filing of the revised declaration (RUB 13,750 x 24%). RUB 3,300 Revised tax declaration Loss coverage from reserve capital Let us assume that LLC Prospekt has formed reserve capital in the amount of RUB 314,850. At the end of 2015, LLC Prospect received a loss in the amount of RUB 118,740.
By the decision of the shareholders, the loss was covered by the reserve capital. The accountant of Prospect LLC reflected this transaction in the accounting as follows: Dt Kt Description Amount Document 84 99 Reflection of uncovered loss at the end of 2015 118,740 rubles. Profit and loss statement 82 84 Coverage of the amount of loss at the end of 2015 at the expense of the reserve fund 118,740 rubles.
Postings to reflect a loss in accounting
In this regard, let us pay attention to the procedure for filling out the Profit and Loss Statement (Form No. 2), namely, its lower part, where information on tax liabilities for income tax is indicated. The current income tax, which is reflected in line 150 of the Profit and Loss Statement, must be equal to the amount of income tax specified in the tax return for the relevant reporting (tax) period.
Therefore, the amount of income tax indicated in line 150 should not include the amount of tax additionally assessed (reduced) due to the discovery of errors relating to previous tax periods. At the same time, it is still necessary to reflect income tax on income (expenses) of previous years in the Profit and Loss Statement.
Otherwise, the overall financial result of the current period will be distorted.
Earnings of previous years transactions identified in the reporting period
Back to questions Print the correspondence March 8, 2016 at 20:14 I am again with PBU 18/02. Since 2016, according to the accounting policy of the enterprise, expenses / income of previous years are attributed to 91 accounts, respectively.
We close the profit on a monthly basis. In January 2016, 40,000 income was accrued, including entries for an increase in income for 2015 in the amount of 15,000 (excluding VAT) rubles, expenses of 30,000 were accrued, including expenses for 2015 in the amount of 20,000. year, a loss was received. In January 2016, in connection with the receipt of documents for 2015, the reserve for future expenses for 2015 was repaid in the amount of 2,000 rubles, and in January 2016, a vacation reserve was created in the accounting office in the amount of 5,000 rubles. (In tax accounting, the vacation reserve is not charged).
For example, in May 2018, an entity discovered that it had not reflected labor costs in its income tax expense in November 2017. She will need to file an updated 2017 tax return.
Although, if at the end of 2017, income tax was payable, then it will be possible to take into account salary costs in the declaration for the half of 2018. This is due to the fact that the non-reflection of the salary in the expenses of 2017 led to an excessive payment of the tax for 2017. And in this case, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation gives the taxpayer the right to take into account the costs either in the period to which they relate, or in the period when an error is discovered. Subscribe to our channel in Yandex.
Losses of the current year Suppose that at the end of 2015, OOO Flagman is reforming the balance sheet, determining the financial result. The turnover balance sheet for the last day of 2015 looks like this: Accounts Account name Amount for Dt Amount for CT 99 Profits and losses 1,389,000 rubles. 99.01 Profit / loss of taxation 1 874 000 rubles. 99.01.1 Profit / loss from sales 1,915,000 rubles. 99.01.2 Balance of other income and expenses 41,000 rubles. 99.02 Income tax 713,000 rubles. 99.02.1 Conditional expense / income withholding tax 695,000 rubles. 99.02.2 Permanent tax liabilities (assets) 18,000 rubles. 99.03 Tax sanctions 47,000 rubles. 99.09 Profit and loss balance - - After rolling up the account balances, the accountant of OOO Flagman determined the company's financial result as unprofitable.
Income of previous years identified in the reporting period postings in 1s
The main goal of any activity commercial organization - Receiving a profit. But it often happens when the expenses incurred by the enterprise exceed the income received, and the financial result of the organization is a loss.
You will learn how to reflect loss operations in postings and how to formalize losses of the reporting and previous periods from our article. Content
- 1 How to determine the loss at the end of the year
- 2 Reflection of losses in accounting
- 2.1 Losses of the current year
- 2.2 Postings for losses from previous years
- 2.3 Covering the loss through capital reserve
How to determine the loss at the end of the year The financial result - profit or loss - depends on the production and economic activity of an enterprise. To obtain the final result, one should take into account the main and other activities of the company.
In the activities of each company, there are situations when in the reporting time period the expenses of past periods are revealed, since only in theory the primary documents and the dates of the actual transactions are identical. In the course of work, it often happens in a different way: goods and services are accepted in one period, and supporting documents for them (invoices, invoices, remote control, acts) come from the seller in another. It turns out that the company is aware of the operations performed, but there is no reason to reflect them in tax and accounting. There are many other situations, the result of which is the discovery of expenses that were not reflected in previous periods or mistakes made. Let's figure out how to deal with this situation and recognize the costs.
How to reflect in tax accounting the expenses of the past periods identified in the reporting period
The term "expenses of previous years identified in the reporting period » is used both in tax and accounting, and is often replaced by the concept of “losses of previous years identified in the reporting period ». The tax authorities, considering such costs, require that the detected misstatements be reflected in the period when they occurred, but were not taken into account (Articles 54 and 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, the company adjusts the tax base of the previous period and submits a declaration with updated information. However, the RF Tax Code allows such expenses to be reflected in the current period if:
- it is impossible to establish the time of occurrence of the distortion (which in practice happens extremely rarely);
- the identified misstatements resulted in an overpayment of income tax.
Losses of previous years in such cases, the company can reflect in the accounting of the current year. For all other situations, the company will have to correct the information in the declaration.
How are the expenses of the last year revealed in the accounting year in accounting reflected
The accounting rules do not provide for any corrections in accounting and reporting for the past periods. Distortions and costs not reflected in time, admitted in previous years, are always reflected in accounting only in the period when they are found, and making any changes to accounting after the approval of the annual statements is strictly prohibited.
Therefore, in contrast to tax accounting, in accounting, the correction of distortions in the expenses of past periods is carried out according to a different algorithm. Clause 11 of PBU 10/99 recognizes losses of previous years discovered in the reporting period as other costs. If the errors are insignificant, then they are reflected in the accounting of the current year according to the debit of account 91, corresponding with accounts of materials, calculations, depreciation, etc.
Significant distortions (for example, those that may affect the share price or financial result, i.e., the decisions of users depend on the distortion (clause 3 of PBU 22/2010)) are reflected in the retained earnings account (84), fixing the write-off of past losses. years at the expense of profits. Note that the firm sets the criteria for materiality independently, fixing and approving them in the accounting policy.
Past expenses: transactions
Let's demonstrate the established procedure for correcting misstatements in accounting using examples:
- According to the act of reconciliation with the buyer on March 31, 2017, the company established that on 10.10.2016 the revenue was erroneously reflected (VAT does not apply): the amount of 1,300,000 rubles was recognized. instead of 500,000 rubles. According to the criteria accounting policies company, the error was recognized as insignificant. The accounting records will be as follows:
- D / t 91 K / t 62 for the amount of 800,000 rubles.
- If the misstatement made is material (again in accordance with the adopted accounting policy), then the correction entry will be as follows:
- D / t 84 K / t 62 for the amount of 800,000 rubles. profit on losses of previous years will decrease.
- All transactions are recorded in the month that errors were found, i.e. in our example, the records will be dated March 31, 2017.
- After the closure and approval of the statements for the goods received on December 15, 2016, in April, supporting documents for the costs (recognized as immaterial for the UP) were received in the amount of 500,000 rubles. In April, you need to make the wiring:
- D / t 91 K / t 62 in the amount of 500,000 rubles, increasing other expenses of the current period.
"Financial newspaper", 2008, N 30
In practice, organizations often have to deal with issues related to errors in tax accounting, one of which is the accounting of income (expenses) of previous years, identified in the current period. This problem arises for various reasons: the documents were missed and were not posted in the previous year, the officials of the organization did not submit them to the accounting department on time, an arithmetic error was made, etc.
Practice of application by tax authorities of Ch. 25 "Tax on profit of organizations" of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in terms of income (losses) of previous years, revealed in the reporting (tax) period, indicates that income (losses) of previous years are included in non-operating income (expenses) of the reporting (tax) period in which they are identified, only if the period to which the said incomes are not known, otherwise, if the specified period is known, then according to Art. 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, recalculation is made for the period in which an error (distortion) was made in determining the tax base. This means that the taxpayer must submit a revised declaration in the form that was valid in the period in which an error (distortion) was made in determining the tax base.
Thus, if it is impossible to determine the specific period of errors (distortions) in calculating the tax base based on the incomes of previous years identified in the reporting (tax) period, then these incomes are reflected as part of non-operating income, i.e. the tax liabilities of the reporting period, in which errors (distortions) were revealed, are adjusted.
It should be noted that the incomes of previous years, revealed in the reporting (tax) period, are reflected in line 101 in Appendix No. 1 to sheet 02 of the tax return on corporate income tax, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05.05.2008 No. 54n.
The following question is legitimate here: in what cases this line is filled in.
There are two such cases: the transition from the simplified taxation system to the general regime and the transition from the cash method to the accrual method.
Organizations that used the simplified taxation system, when switching to the calculation of the tax base for corporate income tax using the accrual method, recognize as income the repayment of debt (payment) to the taxpayer for goods delivered during the period of application of the simplified taxation system (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of article 346.25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 30, 2006 N 03-11-04 / 2/252, it is clarified that organizations that have switched from the simplified system to the general tax regime take into account, when determining the tax base for income tax, the amounts owed by buyers (customers) for the goods (works, services) on the date of transition to the general taxation regime (in the first reporting (tax) period of application general regime taxation) regardless of the time of repayment of this debt. This is due to the fact that according to paragraph 1 of Art. 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for taxpayers who use the accrual method when calculating corporate income tax, income is recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which they took place, regardless of the actual income money, other property (works, services) and (or) property rights.
Organizations that previously accounted for income on a cash basis, when switching to the payment of corporate income tax using the accrual method, are required to reflect the amount accounts receivable for sold but not paid for goods (work, services), property rights as part of income from sale as of the date of transition.
The procedure for recognizing income under the accrual method is established by Art. 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in accordance with paragraphs. 6 clause 4 of which the date of receipt of income of previous years is the date of identification of income (receipt and (or) discovery of documents confirming the existence of income) - Resolution of the FAS of the Volga District of 06.06.2006 on case N A65-30940 / 2005-CA2-34, FAS Of the Ural District of 09/06/2005 in case No. Ф09-3842 / 05-С7.
It should be noted that in past years, the position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia was such that corrections in tax reporting can only be deposited in the previous three years. This position was justified by the fact that according to Art. 87 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax authorities can audit an organization only for three calendar years preceding the year of the audit (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.05.2005 N 03-03-01-04 / 1/236).
To date, the position of tax authorities has changed. Now they do not dispute the taxpayer's right to submit revised declarations for periods exceeding three years, since Art. 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the right of a taxpayer to file a revised tax return for any period.
In the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 12.12.2006 N ChD-6-25 / 1192 @ it is indicated that in such a situation tax authority is obliged to accept the revised tax declaration (calculation), and the application submitted by the taxpayer for offsetting the amount of overpaid tax may be considered taking into account the supporting documents submitted by the taxpayer.
Let us consider an example of the situation of identifying income from previous years.
As of May 1, 2007, a reconciliation of settlements with the supplier was carried out, the accountant discovered that in April 2006 the fixed asset (monitor) worth 10,000 rubles was not capitalized. on the invoice (to simplify calculations, VAT is not taken into account).
In May 2007, an accounting statement is drawn up, on the basis of which the following entry is made:
Debit 91, Credit 60 - 10,000 rubles. - reflects the cost of the acquired fixed assets, put into operation in 2006.
For profit tax purposes, the cost of fixed assets should be included in expenses for 2006. When calculating income tax for 2007, this amount is not included in expenses.
The profit of the organization in 2007 from the sale of goods (works, services) amounted to 200,000 rubles. both in accounting and tax accounting.
Income tax for 2007 will amount to 48,000 rubles. (200,000 x 0.24); the amount of the overpayment of income tax for 2006 will amount to 2,400 rubles. (10,000 x 0.24).
Accounting for 2007 will have the following totals:
Debit 90, Credit 99 - 200,000 rubles. - reflected the profit from sales of the current year;
Debit 99, Credit 91 - 10,000 rubles. - the total amount of other expenses of the current year is reflected.
If the organization applies the Regulation on accounting "Accounting for calculations of income tax", PBU 18/02, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 N 114n, then the following entries are made in the accounting:
Debit 99, Credit 68 - 45 600 rubles. - conditional income tax expense for the current 2007 was charged [(200,000 rubles - 10,000 rubles) x 0.24];
Debit 99, Credit 68 - 2400 rubles. - a permanent tax liability has been accrued for the 2006 expenses identified in the reporting year (RUR 10,000 x 0.24);
If the organization does not apply PBU 18/02 when conducting accounting, then instead of the last three entries, only two are made:
Debit 99, Credit 68 - 48,000 rubles. - income tax was charged for this year according to tax accounting data;
Debit 68, Credit 99 - 2400 rubles. - reduced income tax for 2006
A. Kantrov
LLC "Capital Auditor"