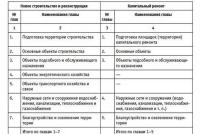
What debt is to be written off. Accounts payable and receivable write-off transactions. Write-off of overdue receivables - transactions
This follows from the provisions of Article 196 and paragraph 2 of Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Example of determining the term limitation period... The limitation period was not interrupted
LLC "Trading Firm Hermes" on January 13, 2014 shipped goods to CJSC "Alpha". Under the contract, payment must be made no later than 10 calendar days after shipment, that is, no later than January 23, 2014. However, in set time payment from Alpha has not been received.
The limitation period must be calculated from January 24, 2014 to January 24, 2017 inclusive (provided that the limitation period was not interrupted).
The limitation period can be interrupted when one of the parties brings a claim or by the actions of the debtor, indicating recognition of the debt. In the first case, the limitation period is interrupted on the day the court accepted the statement of claim. In the second case, when the debtor recognized the debt and sent a letter or reconciliation statement. This is stated in article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
When filing a claim, the limitation period will be interrupted only if the procedure for going to court (to a judge) established by law is observed. In particular:
The claim was filed with the court (judge), which is authorized to consider this category of cases in this territory (the jurisdiction and jurisdiction of the case are observed);
The claim was drawn up in accordance with all the rules;
The state duty for filing a claim has been paid.
This follows from clause 15 of the resolution of November 15, 2001, Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 15, Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 18.
If the court leaves the claim without consideration, then the limitation period is not interrupted (Article 204 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
After the interruption, the course of the limitation period begins anew. In this case, the time elapsed before the break, in new term do not count the statute of limitations (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, there is a limitation: the limitation period cannot exceed 10 years from the date of violation of the right, even if the term was interrupted. The exceptions are cases established by law dated March 6, 2006 No. 35-FZ on countering terrorism. This is stated in paragraph 2 of Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An example of determining the limitation period. The limitation period was interrupted
LLC "Trading Firm Hermes" on January 13 shipped goods to CJSC "Alpha". According to the contract, payment must be made no later than 10 calendar days after shipment, that is, no later than January 23rd. However, the payment from "Alpha" was not received in due time.
On January 25, Hermes sent a letter of claim to Alpha. On February 1, the parties drew up a reconciliation report. This means that Alpha has recognized its debt. In this case, the limitation period begins to count again - from February 2.
Situation: what actions of the debtor testify to the recognition of the debt and are the basis for considering the limitation period as interrupted ?
The legislation does not establish a list of actions of the debtor, which indicate that he has recognized the debt. And which can serve as a basis for interrupting the limitation period (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
However, an approximate list of such actions is named in the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 12, 2001 No. 15, of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of November 15, 2001 No. 18. It, in particular, includes:
Partial payment of debt;
- payment of interest for late payment;
- an appeal to the creditor with a request for a deferred payment;
- submission of an application for offset of mutual claims;
- amendment of the contract, from which follows the recognition by the debtor of the debt;
- signing of the debt reconciliation act.
For example, three years have passed since the date on which the obligations were due. But during this period, the parties signed a debt reconciliation act. This act is the basis for interrupting the limitation period (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 19, 2011 No. 03-03-06 / 1/426). Therefore, the three-year period should be counted from the day on which the last reconciliation act is dated.
There are exceptions to this rule - these are events due to which the receivable has become unrealistic to collect. A similar position is set out in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. ШС-37-3 / 16955.
The contract may provide that the obligation can be performed in parts (in the form of periodic payments). In this case, if the debtor has performed actions that indicate the recognition of only some part of the obligation, they are not grounds for interrupting the limitation period for other parts of the obligation. This is stated in clause 20 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 12, 2001 No. 15, of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of November 15, 2001 No. 18.
Documenting
The fact of occurrence accounts receivable must be documented (part 1 of article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Determine the amount of overdue receivables based on the results of the inventory and reflect it in the act, for example, in the form No. INV-17. Carry out the inventory by order of the head (f. INV-22).
To write off receivables, the manager must issue an appropriate order. The basis for this will be an inventory act and an accounting statement.
This is stated in paragraph 77 of the Regulations for the maintenance accounting and reporting, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Moscow dated December 13, 2006 No. 20-12 / 109630.
Attach documents confirming its occurrence to the act of inventory of accounts receivable, for example:
Agreements that specify the terms of repayment of obligations by counterparties;
- consignment notes;
- acts of work performed (services rendered);
- acts of inventory of accounts receivable at the end of the reporting (tax) period.
This procedure follows from the letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 8, 2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/11347 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 13, 2011 No. 16-15 / 035618.1.
Accounting
Write off the amount owed at the expense of the doubtful debts.
In accounting, write off accounts receivable at the expense of a reserve for doubtful debts by posting:
Debit 63 Credit 62 (58-3, 71, 73, 76 ...)
- the accounts receivable were written off at the expense of the created reserve.
The reserve can only be used within the limits of the reserved amounts. If during the year the amount of expenses for writing off the debt exceeds the amount of the created reserve, reflect the difference as part of other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
When writing off the difference, make the posting:
Debit 91-2 Credit 62 (58-3, 71, 73, 76 ...)
- written off accounts receivable not covered by the provision.
Writing off accounts receivable, for which the limitation period has expired, or other debts that are unrealistic for collection, is not cancellation of the debt. Therefore, within five years from the date of write-off, reflect it off the balance on account 007 "Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss" (Instructions to the chart of accounts):
Debit 007
- written off accounts receivable are reflected.
During this period, watch out for the possibility of its recovery when the property status of the debtor changes (clause 77 of the Regulations on accounting and reporting).
An example of the reflection in the accounting of written off receivables
Alfa CJSC conducts an inventory of accounts receivable on a quarterly basis and makes contributions to the reserve for doubtful debts in accounting.
The unused balance of the reserve for doubtful debts for the II quarter amounted to 45,400 rubles.
According to the results of the inventory as of September 30, the organization registered:
1) doubtful accounts receivable of organizations:
LLC "Trading Firm Hermes" - 170,700 rubles;
2) indebtedness to OJSC "Manufacturing firm Master" in the amount of 45,400 rubles. In the third quarter, the debt of "Master" was recognized as unrealistic for collection in connection with the liquidation of the debtor organization (confirmed by an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities). The amount owed was fully taken into account when forming the reserve.
Based on the results of the inventory as of September 30, Alpha's accountant included Hermes's debt in the doubtful debt reserve in the amount of 170,700 rubles.
The Master's debt was completely written off at the expense of the reserve.
In the accounting of Alpha, the reserve was formed in the amount of 170,700 rubles.
Taking into account the balance of the reserve as of June 30 and the written off debt of "Master", the additional amount of expenses for the formation of the reserve in the third quarter was:
RUB 45 400 + 170 700 rub. - 45 400 rubles. \u003d RUB 170,700
On September 30, Alpha's accountant made the following entries:
Debit 63 Credit 62
- 45 400 rubles. - written off accounts receivable at the expense of the reserve;
Debit 91-2 Credit 63
- 170,700 rubles. - reflects the cost of creating a reserve for doubtful debts.
Indebtedness of citizens
The written off bad accounts receivable of citizens (for example, buyers who did not pay for the goods shipped to them) are recognized as their other income (letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 8, 2012 No. 03-04-06 / 4-27). With respect to such income, the organization is recognized as a tax agent for personal income tax.
Each company in its current activities must monitor the status of settlements with counterparties, controlling the timing and amount of mutual debts. This directly affects the "cleanliness" of the balance sheet of the enterprise. But there are situations when it is impossible to repay the debt and it is necessary to write off accounts payable or receivable. What an accountant should do, how to carry out such operations, what transactions are formed, what documents to be guided by - we will consider all this further.
To write off any type of debt, you need good reasons, supported by appropriate documents. These, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are:
- End of the limitation period;
- Liquidation of a counterparty;
- Unreality of collection.
To "part" with the company's debt, it is necessary to draw up a number of documents for each obligation:
- The act of inventory of mutual settlements with counterparties (form INV-17);
- Order of the bailiff to terminate enforcement proceedings - in case of unrealistic collection;
- Extract from the state register legal entities with a record of the completion of the liquidation procedure of the enterprise (Article 49, Article 63 of the State Committee for the Russian Federation) - in case of liquidation of the counterparty;
- The order of the head of the write-off, signed on the basis of the listed documents.
At the same time, KZ is taken into account as non-operating income, in addition to debt to government agencies and extrabudgetary funds (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 18; Article 251, clause 21), DZ - as part of non-operating expenses or refers to the account. 63 "Provisions for doubtful debts".
Important: when writing off DZ due to unrealistic collection due to the debtor's lack of property, it is necessary to take into account such debt for 5 years beyond the balance on account 007 to control the likelihood of its recovery when the debtor's financial condition improves.
Get 267 1C video tutorials for free:
We write off accounts receivable
We draw up the results of the inventory and identify the remote sensing with expired prescription. The documents confirming its existence and limitation period are:
- Agreement and documents on payment to it;
- Documents confirming the delivery (provision of services) - acts, invoices;
- Reconciliation report (if any);
- Mutual official correspondence confirming the fact of reclaiming the debt (claim). It is necessary to support copies of letters with a document confirming the fact of receipt of the letter by the counterparty (for example, a notification of delivery).
It is important to take into account that if there is a reconciliation act for a certain date, the period begins to be calculated from the beginning.
Documents for confirming the impossibility of recovery: the order of the bailiff or an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities:
Receivables write-off - transactions
In accounting, the reflection procedure is as follows:
1) If the reserve was created (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34-n):
- Dt 63 Kt 62 (60,76,71,73,70) - accounts receivable were written off;
2) If the reserve was not formed or its size does not cover the amount of the debt:
- Dt 91.2 Kt 62 (60,76,71,73,70) - accounts receivable were written off;
- Dt 007 - we reflect the written off debt off the balance sheet.
The amount of the provision is determined separately for each doubtful amount of debt. Formation of the reserve since 2011 became the responsibility of enterprises.
In tax accounting, a reserve is used to cover losses from the write-off of DZ (Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If it is not created or insufficient, then the debt is attributed to non-operating expenses in the period when the limitation period ended or the impossibility of collection was confirmed. (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2011 No. 16-15 / 035618.1).
We write off the creditor
Every year, the company is obliged to make an inventory, including accounts payable, before reporting. If a short circuit with an expired statute of limitations is identified, it is written off on the basis of an order to the income of account 91 both for accounting purposes and for tax accounting... It should be remembered that, by analogy with DZ, the presence of a signed reconciliation act or receipt of an official claim from a supplier extends the limitation period:

Accounts payable write-off - transactions
For both tax and accounting, payables (KZ) are written off uniformly, with the following entries:
- Дт 60 (76,70,71,73) Кт 91.1 - written off accounts payable is reflected.
However, in tax accounting, KZ is written off in the period when the period has expired, regardless of the date of its identification.
To write off overdue creditors, a package of documents is required:
- Agreement;
- Acts of services rendered or invoices from the supplier;
- Act of reconciliation;
- Official complaint correspondence.
After collecting and analyzing the package of documents, making sure that the deadline has expired, you need to write off the KZ and reflect it as taxable income in order to avoid comments from the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate.
Debt inventory deadlines are set accounting policies, but it must be carried out at least 1 time in reporting period (year).
1. How to document the write-off of receivables and payables.
2. How to reflect the write-off of debt in accounting and tax accounting.
3. Peculiarities of writing off and including in expenses of bad accounts receivable.
Debts and creditors' debts for which the limitation period has expired, as well as other debts recognized as uncollectible, are subject to mandatory write-off. In accounting, timely writing off of bad debts ensures reliability accounting statements, since the indicators of receivables and payables are integral parts of the assets and liabilities of the organization. In tax accounting, by writing off unrealistic debts for collection, it is adjusted the tax base, which affects the correctness of tax calculation. At first glance, debt cancellation is not a big problem, but this is only at first glance. When an accountant is faced with the specific task of writing off bad debts, many questions arise: how to arrange, how to reflect in the accounting, how this operation will affect the calculation of income tax, VAT, simplified taxation system, etc. In this article, I propose to understand these and other practical aspects of writing off receivables and payables.
Documentary registration of writing off bad debts
- In addition, on the fact of writing off the debt in accounting, an accounting statement is drawn up, which serves as confirmation of the completion of this operation.
The tax legislation does not contain requirements for documenting the write-off of receivables and payables, the main condition is that there are grounds for recognizing such debt as hopeless (contracts, invoices, acts, extracts from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities for liquidated counterparties, etc.).
! Note: When writing off debt due to the expiration of the limitation period, the write-off for tax accounting purposes must be made in the reporting period when the specified period has expired, and not when the organization carried out an inventory and issued an order (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/38). Thus, it is in the interests of the organization itself to conduct a timely inventory of debt (at least as often as on the last day of each reporting period for income tax), so as not to make adjustments to the tax returnsand also so that the data on debt write-off in tax and accounting are the same.
Write-off of receivables
Tax accounting
Reflection of the write-off of bad accounts receivable in tax accounting largely depends on the cause of its occurrence. The most common are buyers 'debts for shipped but not paid for products (works, services), and suppliers' debts for listed advances that are not closed by deliveries. Let's see how debtor debt write-off affects the calculation of income tax, VAT and STS:
|
The nature of the debt |
Income tax | VAT | |
| Buyer's debt for sold goods, works, services | Written off debt is included in expenses in full (including VAT) (Letters dated 07.24.2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/29315, dated 03.08.2010 No. 03-03-06 / 1/517) 1. If the reserve for doubtful debts for tax purposes was created: - the written off debt reduces the amount of the reserve (regardless of whether this debt participated in the formation of the reserve or not) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 17, 2012 No. 03-03-06 / 2/78, subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - the written off debt is included in the non-operating expenses (in terms of the excess of the amount of the created reserve) 2. If the reserve for doubtful debts for tax purposes not created: - written off debt is included in non-operating expenses (subparagraph 2, paragraph 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
Debt write-off does not entail VAT adjustments, since the tax was charged on the date of sale (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
Written off debt is not included in expenses, since the sale amount was not previously included in income, since it was not paid (Clause 1 of Art. 346.17, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 22, 2013 No. 03-11-11 / 28614) |
| The seller's debt on the previously listed advance (prepayment) | Written off debt is included in non-operating expenses, regardless of the fact that a provision for doubtful debts has been created in tax accounting, since prepayment receivables to the supplier are not recognized as doubtful for tax accounting purposes and, accordingly, does not participate in the formation of the provision. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 30, 2011 No. 07-02-06 / 115) |
VAT from the advance paid, previously accepted for deduction, must be restored in the period of writing off receivables (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 11.04.2014 No. 03-07-11 / 16527) |
Written off debt is not included in expenses (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated 30.03.2012 No. 03-11-06 / 2/49, dated 12.12.2008 No. 03-11-04 / 2/195) |
As can be seen from the table, the procedure for including written off receivables in expenses when applying the general taxation system depends on whether the organization created in tax accounting or not. If the reserve was created, then the bad debt is written off at the expense of the reserve, and is not included in non-operating expenses. Wherein it does not matter in tax accounting whether such debt was involved in the formation of the reserve or not.
Accounting
For accounting purposes, bad debts of debtors are included in other expenses as of the date of the inventory of debts and are reflected in account 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses”. At the same time, the debt written off due to the debtor's insolvency after the expiration of the limitation period must be recorded on the off-balance sheet account 007 “Debt written off at a loss by insolvent debtors” for five years in order to track the prospects for its repayment.
Unlike tax accounting, it is on the right, but the responsibility of the organization in the presence of doubtful receivables. Therefore, if the reserve for doubtful debts was created, then the bad accounts receivable are written off at the expense of it, and not referred to other expenses. However, one must remember that in accounting, only the debt that participated in its formation can be written off at the expense of the reserve.
| Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
|
1. If the reserve for doubtful debts in accounting was not created or if the receivable to be written off did not participate in its formation |
||
| 91-2 | 62, 60, 76, etc. | Bad receivables written off to other expenses |
| 007 | ||
|
2. If the reserve for doubtful debts in accounting has been created and accounts receivable to be written off were taken into account when it was formed |
||
| 63 | 62, 60, 76, etc. | Bad receivables were written off at the expense of the allowance for doubtful debts |
| 007 | The amount of debt written off is shown off the balance sheet | |
Writing off accounts payable
Writing off accounts payable with an expired limitation period, as well as writing off accounts receivable, is reflected in tax accounting when applying the general taxation system and the simplified tax system, depending on the reason for its occurrence: debt on received but not paid goods (works, services) or debt on advances received from buyers.
| The nature of the debt | Income tax | VAT | STS |
| Debts to the supplier for the received goods, works, services | (Clause 18, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
VAT previously accepted for deduction (when posting goods, works, services) is not restored (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated June 21, 2013 No. 03-07-11 / 23503) |
Written off debt is included in the income of the organization (Clause 1 of Art. 346.15, Clause 18 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07.08.2013 No. 03-11-06 / 2/31883) |
| Amount owed to the buyer on the received advance payment (prepayment) | Written off debt is included in non-operating income in full (including VAT) (Clause 18, Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
VAT paid earlier on the received advance is not deductible (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 07.12.2012 No. 03-03-06 / 1/635) |
The written off amount of debt is not included in income, since it was previously accounted for (at the time of payment from the buyer) clause 1 of Art. 346.17 Tax Code |
! Note: In tax accounting, any written off accounts payable (due to the expiration of the statute of limitations and on other grounds) is subject to inclusion in non-operating income, with the exception of debts (clauses 3.4, 11, 21, clause 1 of article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- before the budget for the payment of taxes, fees, penalties and fines;
- to state extra-budgetary funds for the payment of contributions, penalties and fines;
- in front of a participant owning more than 50% authorized capital organizations (except for debt on payment of interest on loans);
- to an organization, in the authorized capital of which your organization's share of participation is more than 50% (excluding debt on payment of interest on loans);
- to any member of your organization, if the document confirming debt forgiveness says that this is done to increase the net assets of your company;
- to members of the organization for unclaimed dividends.
Accounting
In accounting, written off accounts payable is included in other income of the organization and is reflected in account 91 "Other income and expenses", subaccount 91-1 "Other income".
Difficult situations when writing off accounts receivable
Bad accounts receivable, as we found out, are included in expenses for tax purposes, so you need to be careful about writing it off. Often the accountant has doubts about the "hopelessness" of the debt and the legality of attributing it to expenses. With the most frequent questions writing off accounts receivable, I propose to understand.
- Is it possible to include in expenses the amount of debt with an expired statute of limitations if the debtor is in the process of bankruptcy?
According to the position of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, such debt is not included in non-operating expenses if the proceedings against the debtor are not completed, and the creditor is included in the register of creditors. In this case, the expiration date of the statute of limitations does not matter. A taxpayer can write off accounts receivable only after the court has declared the debtor bankrupt and excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04.03.2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/6313, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 23.09.2013 No. 03-03-06 / 2/39363, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04.03.2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/6313)
- Is it possible to take into account in the expenses the amount of bad debts, the measures for which were not taken to collect?
In accordance with court decisions and clarifications of the Ministry of Finance, bad accounts receivable with the expired statute of limitations can be included in expenses for tax purposes, regardless of whether measures were taken to claim it or not. (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District of 14.09.2012 on case No. A40-85915 / 11-91-367, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 21.02.2008 No. 03-03-06 / 1/124, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia of 25.11.2008 No. 03- 03-06 / 2/158)
- Does the expense include the amount of accounts receivable if the debtor is recognized as an invalid legal entity and is excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities by decision tax authority (if during the previous twelve months reports were not submitted, transactions were not carried out on the current account)?
Until 09/01/2014 - not included, since the exclusion of the debtor from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities is not his liquidation and such a basis for writing off accounts receivable is not provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 27.02.2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1/5556, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07.07.2008 No. 03-03-06 / 1/309, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 11.12.2012 No. 03-03-06 / 1/649)
From 09/01/2014 - it is included, since from that date Law No. 99-FZ of 05/05/2014 came into force, in accordance with which the Civil Code of the Russian Federation was supplemented by Art. 64.2. In accordance with this article, the exclusion of an inactive legal entity from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities is actually equivalent to its liquidation.
- At what point can a receivable be written off as non-operating expenses if a reconciliation of settlements with the debtor was carried out?
The signing of the statement of reconciliation of settlements is the basis for interrupting the limitation period, therefore, receivables can be written off and accounted for in expenses only after three years have passed since the date of signing the last statement of reconciliation of settlements. (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06.12.2010 No. ShS-37-3 / 16955)
- Can bad accounts receivable be included in expenses if there is a counter payable for this counterparty?
So, we examined the procedure for writing off receivables and payables in accounting and tax accounting. Once again I want to remind you that writing off bad debts is the responsibility of the organization and affects both the indicators of the financial statements and the calculation of taxes. Therefore, it is necessary to write off counterparties that are unrealistic to collect debts in a timely and prudent manner, in which, I hope, the material in this article will help you.
Do you find the article useful and interesting - share with colleagues on social networks!
There are comments and questions - write, we will discuss!
Yandex_partner_id \u003d 143121; yandex_site_bg_color \u003d "FFFFFF"; yandex_stat_id \u003d 2; yandex_ad_format \u003d "direct"; yandex_font_size \u003d 1; yandex_direct_type \u003d "vertical"; yandex_direct_border_type \u003d "block"; yandex_direct_limit \u003d 2; yandex_direct_title_font_size \u003d 3; yandex_direct_links_underline \u003d false; yandex_direct_border_color \u003d "CCCCCC"; yandex_direct_title_color \u003d "000080"; yandex_direct_url_color \u003d "000000"; yandex_direct_text_color \u003d "000000"; yandex_direct_hover_color \u003d "000000"; yandex_direct_favicon \u003d true; yandex_no_sitelinks \u003d true; document.write ("");
Legislative and Regulatory Acts
1. tax code RF
2. Civil Code of the Russian Federation
3. Regulations on accounting and bookkeeping in Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of July 29, 1998 No. 34n
4. Chart of accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations and Instructions for its use, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of October 31, 2000 No. 94n
You can familiarize yourself with the codes and orders of the Ministry of Finance at http://pravo.gov.ru/
5. Letters of the RF Ministry of Finance
Letters of the RF Ministry of Finance can be found at the official http://mfportal.garant.ru/
The concept of receivables constantly accompanies economic activity companies.
Dear Readers! The article talks about typical ways of solving legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how to solve exactly your problem - contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and WITHOUT DAYS.
It is fast and IS FREE!
It is important for an accountant of business entities to determine which counterparties' debts can be written off and how to document this procedure.
Debt concept
Counterparty debt in the simplest sense implies the presence of unpaid company invoices by partners, despite the shipment or work. Thus, organizations are implementing a commodity credit mechanism that allows the transfer of goods and services with a deferred payment.
Unfortunately, not every counterparty is reliable, and not every transaction is safe. As a result, a doubtful or hopeless debt is formed in the organization. After a certain period of time, Russian organizations have the right to write off unrealistic debt receivable.
In order for the accountant to have the opportunity to confirm the possibility, due to the requirements of the law, to write off the debtor's debt, he should prepare a package of documents:
- a contract confirming interaction with a partner and the transfer of values \u200b\u200bto him;
- signed reconciliation of settlements;
- (can be either a separate document or an annex to the signed agreement).
In order for the company to come to a conclusion whether the receivables available in the company correspond to the bad ones, it is necessary to consider how the normal receivables differ from the doubtful and bad ones.
Accounts receivable are recognized as normal if the maturity date has not yet come and the partner fulfills its financial obligations in full.
All deviating from normal events are classified as doubtful, and if we consider the situation in a negative way, then to debts, which are not possible to collect.
Nevertheless, if the organization still has an unlikely receivable debt, the most reasonable in this situation would be to form a protective fund that would minimize the negative consequences of the appearance of insolvent debtors.
What is to be written off

It is necessary to include accounts receivable in the composition of expenses, relying on the regulatory framework, in particular, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Only the debt that belongs to the category of hopeless, unrealistic to receive can be attributed to the losses of the organization.
This group of receivables includes such debts as:
- expired debt;
- the debt of a liquidated company in the event that there is an entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities on the termination of activities (if the debtor is an entrepreneur, then the write-off is made only after the information is entered into the USRIP);
- debt that is impossible to collect and this is confirmed by the bailiffs.
First of all, when an unlikely or unrealistic receivable debt appears in the company, the presence of a reserve fund for doubtful debts is checked. Having formed such a fund, the company can protect itself in the event of the appearance of unscrupulous counterparties.
In most cases, debtors are covered by the above reserve. When the amount of debt exceeds the fund accumulated by the company, then the resulting difference must be attributed to other costs of the company.
The limitation period established by law is recognized as equal to three years. Accordingly, after three years from the date of the appearance of the debt, the outstanding debt becomes uncollectible.
Documenting the write-off for losses of unreal receivables
Due to the fact that tax officials are extremely careful in checking the written off debt, the organization should take care of the registration of all operations performed by the established documents.
Tax law establishes the need to revise liabilities, both incoming and outgoing, systematically, and not only during the reporting period. Based on the results of the audit of debts, the authorized employees must draw up an inventory act and fill out the corresponding document.
After the audit, the information is transferred to the head of the company for review. It is he who decides to start the procedure for writing off a bad debt and issues an order justifying this action.
The basis for the write-off is the inventory act and the accounting statement. The certificate must disclose all information about the debt being written off, from the contract concluded between the counterparties and ending with the cause of the unrealistic debt to be received.
In addition to the above documents, the accountant should supplement the package of documents with signed reconciliation acts, invoices, invoices and other documentation characterizing the relationship between the company and its debtor.
Formation of a reserve in the company's accounting

The formation of a reserve will allow the company to see the actual situation in the area of \u200b\u200boutstanding debt and will allow, if any, to recognize in expenses the amount of debt to those companies that operate on an accrual basis. The possibility of creating a reserve for doubtful debts is regulated by Russian tax legislation. According to the established requirements, the formation of the fund can be carried out as a current tax period, and after its immediate end.
Recent changes in tax law state that the created reserve should not exceed ten percent of the amount of income of the previous period (reporting or tax, depending on in which of these periods the fund is formed).
As for the accounting of the organization, the formation of the reserve must be attributed to the operating costs created at the expense of the profit received by the organization.
In the process of creating a fund to cover debts with a low probability of receiving, the accountant needs to make the following entry:
Dt 91 Cr 63
It is important to note that in the event that a company has decided to create a reserve for doubtful debts, it is obliged to fix this in its accounting policy.
Tax accounting
Debt write-offs of counterparties should be reflected in both accounting and tax accounting. On the basis of the Order of the Ministry of Finance, only firms that apply common system taxation and calculate income tax using the accrual method. Thus, there is no such opportunity for entrepreneurs and firms operating with the use of special taxation systems, such as “simplified” or “imputed”.
The method of writing off such debt depends on whether the company has created a reserve to cover doubtful debts... If available, the debt offset should be the funds of this reserve. If there is no fund in the company, then it is necessary to write off the debt for the organization's non-operating expenses. The same costs include the difference between the amount of the counterparty's debt and the accumulated reserve for doubtful debts.
When determining the period of possible attribution of bad debts to costs, companies should proceed from the time of the earliest event: liquidation of the counterparty, expiration of the statute of limitations or the inability to pay off debts by decision of bailiffs.
Each document confirming the validity of deregistration of debt in the register for the Federal Tax Service must be kept for at least four years.
Tax legislation determines the need to recover VAT in the event that the advance paid to the supplier is recognized as a bad debt.
There is one more peculiarity when writing off the amount of a hopeless debt to be collected... When the debtor of the organization is individual, during the period when the amount of the company's debt is attributed to extraordinary expenses, the accountant is obliged to transfer personal income tax to the treasury. According to the tax authorities, in this situation, the citizen receives economic benefits, and the organization takes on responsibilities tax agent... If the debtor was also an employee of the organization, then the company must pay insurance premiums for him.
Write-off procedure

In order for the accountant to determine the sequence of actions when writing off debts in accounting, it is necessary to clarify the existence of a reserve to cover debts that are doubtful for collection.
If such a fund was nevertheless created, then the debt must be written off as follows:
Dt 63 Cr 62 (76 or other settlement account) - writing off the amount of debt by means of the formed fund.
If the amount of the reserve is not enough to cover the debt, the accounting write-off is made by posting:
Dt 91 Kr 62 (76 or another account of settlements with debtors).
If the company has not created a provision for covering debts, the accounting will consist of the following entries:
- Dt 91 Kr 62 (or another account for accounting for settlements with debtors) - the product of writing off the amount of debt with reference to non-operating expenses;
- Дт 007 - accounts receivable are included in the company's balance sheet.
Written off debts should be reflected in off-balance sheet account 007 for five years. After the expiration of this period, the amount of debt is written off completely.
Thus, it should be noted that the mechanism for writing off the debt of a counterparty that is hopeless to collect does not cause significant difficulties for the accounting service. Nevertheless, the employees of the Federal Tax Service very tightly control the legality of writing off debtors' debts and often charge additional income tax or oblige the organization to transfer a fine to the treasury.
Please note that write-offs can only be made if there is an order from the head and an audit of the amount of debt is carried out.
By and large, it is possible to write off accounts receivable at a loss, observing the statute of limitations, except for cases when the partner has ceased its activities and an entry about this is made in the register of legal entities or entrepreneurs.