The write-off of receivables due to the customer's insolvency is reflected. Writing off debts with expired statute of limitations. Full cancellation of debts on loans to individuals
If the debt of the counterparty or individual has become hopeless, it must be written off. Let's look at examples with postings how to write off receivables from previous years.
Attention! These documents will help you write off receivables in accordance with all legal requirements:
It is convenient to work with documents in. It is suitable for organizations and individual entrepreneurs. The program will automatically generate and print all the necessary primary items. It also includes unloading transactions in 1C, automatic generation of any reports and much more.
When is a receivable
Cases of occurrence accounts receivable are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.When a receivable occurs
|
Formed |
The reasons |
|
At the buyer |
Items paid upfront were not shipped by the supplier |
|
At the customer |
The works or services paid for in advance were not performed by the contractor |
|
At the supplier |
The goods delivered were not paid by the buyer |
|
At the performer |
The work or services performed were not paid by the customer |
|
At the lender |
The loan received was not returned to the lender |
|
At the employer |
The employee did not report on the amounts received earlier for the report |
When write off receivables
Let's consider the cases when it is necessary to write off receivables (see below for postings). We also note that write-off operations are done separately in terms of each obligation.
- When the debt has become unrealistic for collection (in particular, upon liquidation of the debtor counterparty).
- Expiration of the limitation period.
The term is equal to 3 years (see table 2). Moreover, it can be interrupted, but it cannot be more than ten years from the moment of violation of the law.
table 2... Commencement of the statute of limitations
Interruption of the term is possible in the case when the creditor filed a claim (the court accepted the application) or the debtor recognized the debt (sent the creditor a letter or a reconciliation statement).
Also, the term will be interrupted if the parties have made changes to the agreement, according to which the debtor recognizes a debt.
The term is also interrupted in the event that the counterparty has partially repaid the amount of debt, but does not sign the reconciliation report.
The debtor's actions giving grounds for interrupting the statute of limitations, see post. Plenum of the Supreme Court of 12.11.2001 No. 15 and Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of 15.11.2001 No. 18.
The following actions of the debtor will lead to the interruption of the term:
- the counterparty signed the reconciliation report;
- partially paid off the debt;
- paid interest due to the creditor for the delay in payment;
- asked for a grace period;
- submitted to the creditor a statement on offset of mutual claims.
If the term is interrupted, the three-year report starts over.
What documents to write off accounts receivable
Law No. 402-FZ provides for the obligation to confirm the occurrence of a receivable. The amount of debt is established by taking an inventory. She is appointed by order of the director of the company in the form No. INV-22. Based on the results of the conduct, an act is drawn up in the form No. INV-17.
Based on the above documents and accounting records, the director issues an order to write off accounts receivable.
For confirmation you will also need:
- contracts that contain clauses on the dates of repayment of obligations by debtors;
- waybills;
- acts of services rendered and work performed;
- inventory acts of receivables at the end of the reporting and tax period.
You can prepare any of the above documents in a special online service from BuchSoft
Issue an accounting primary
Accounts for writing off receivables
There are two options for carrying out transactions to write off accounts receivable in accounting:
- Using account 63 "Reserve for doubtful debts" at the expense of the previously created reserve (but only within its amount).
- By applying account 91.2 "Other expenses" in case the company did not form a reserve or its amount was insufficient and an excess was formed.
Write-off of expired receivables (transactions)
When using account 63 "Reserve for doubtful debts" make the entry:
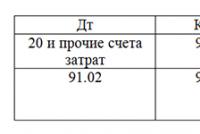
D 63 K 62 (58-3, 71, 73, 76 ...).
For the excess amount or when the firm did not create a provision:
D 91-2 K 62 (58-3, 71, 73, 76 ...).
Note: the reflection of the above transactions in the accounting is not the cancellation of a receivable that has expired.
Within five years after the transactions, the company must reflect the receivables behind the balance sheet on the debit of account 007 "Written off at a loss debt of insolvent debtors":
D 007
In this case, you need to monitor the possibility of debt collection and changes in the property status of the debtor counterparty.
Example of writing off uncollectible receivables (transactions)
Let's consider a specific example of a debtor write-off transaction
Example
The company carried out an inventory of settlements with buyers, suppliers and other debtors and creditors. As a result, she created a reserve for doubtful debts in the amount of 250,000 rubles. The firm is a creditor to LLC Gamma. The amount of the debt is 270,000 rubles (including VAT 32,796.61 rubles).
In October of the same year, the limitation period for this amount expired. The firm has decided to write off expired debt at the expense of the reserve. Write-off transactions in accounting:
Features of writing off bad accounts receivable from an individual
The amount of accounts receivable that the company has written off from an individual is his income. The company acquires the status of a tax agent. Together with him, she has a duty to keep from such income
Each company has the right to resort to writing off accounts receivable that cannot be collected, even without going to court. Let's take a look at the process of writing off expired receivables step by step.
In this article, you will learn the procedure for writing off receivables:
Due to a decrease in sales volumes, a lack of working capital, counterparties are not always in a hurry to pay off their debts. As a result, significant amounts of receivables with expired statute of limitations are accumulated in the accounting of the creditor company. At the same time, the analysis of the activities of the debtor organization indicates that even if a positive court decision is received, the recovery of the awarded amounts will be extremely difficult or even impossible.
To collect receivables in court, the creditor spends additional material resources:
- state duty for filing a statement of claim in court;
- payment for legal services to represent the interests of the company in court;
- support of enforcement proceedings for collection of receivables.
However, in fact, the court's decision has not been executed due to the lack of property of the debtor. At the same time, each company can write off a hopeless one, that is, to collect accounts receivable from legal entities for which the limitation period has expired, even without going to court.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia has repeatedly spoken about the possibility of writing off receivables with an expired limitation period, regardless of the fact of its reclamation from the debtor (letters dated 13.01.2009 No. 03-03-06 / 1/3, dated 25.11.2008 No. 03 -03-06 / 2/158, dated February 21, 2008 No. 03-03-06 / 1/124). In practice, the most popular reason for writing off receivables is the expiration of the limitation period. In order to properly write off a debt with an expired limitation period, it is necessary to take a number of successive steps.
Step 1. Determine if the limitation period for writing off receivables has expired
On the basis of paragraph 2 of Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, any debt to your company is recognized as hopeless if the limitation period has expired. In accordance with Article 195 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the limitation period is the term for protecting the violated right.
By general rule for obligations with a specific deadline, the limitation period is three years and begins to be counted from the day following the last day of the debtor's fulfillment of his obligations (Article 196, Clause 2, Article 200 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Meanwhile, for some obligations, special terms have been established that differ from the general three-year term. Therefore, before writing off receivables, it is necessary to analyze the nature of the liability that has arisen, according to which the debt is to be written off.
In addition, before writing off receivables, you should check the presence / absence of documents that may indicate the interruption of the limitation period. In particular, the signing of reconciliation acts with the counterparty and other documents confirming the recognition by the debtor of the obligation that has arisen, for example, the recognition of a claim, changes in the terms of the contract, interrupt the course of the limitation period.
Step 2. Prepare documents confirming the write-off of overdue receivables, carry out an inventory
So that the controllers do not have any claims to the amounts of the written off receivables, it must be remembered that the date of the receivable and the expiration date of its limitation must be documented, and the debt itself must be written off on the basis of the order (instruction) of the head of the organization.
For documentary confirmation of the date of origin of the receivable, one civil contract is not enough. The debt must also be confirmed by primary accounting documents, such as acts of services rendered, work performed, invoices, acts of acceptance and transfer of goods, payment orders in the event of an advance payment, and other documents.
Accounts receivable must be confirmed by acts inventory of accounts receivable .
Step 3. Determine the period in which the receivables are to be written off
Consider writing off accounts receivable in tax accounting. Accounts receivable are recognized as uncollectible and are subject to write-off in the tax (reporting) period in which the limitation period expired. According to the explanations of the financial department, accounts payable for which the limitation period has expired is taken into account as part of non-operating income on the last day of the reporting period in which this period expires (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06 / 1 / 38).
For the purpose of income tax hopeless accounts receivable , identified on the basis of the inventory, will be extremely difficult to take into account in a later period. Judicial practice proceeds from the fact that the taxpayer has no reason to write off receivables if the taxpayer did not write off the debt as of the date of expiration of the statute of limitations (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 15.06.2010 No. 1574/10).
Therefore, an inventory of accounts receivable should be carried out at the end of the reporting (tax) period in which such a debt will be written off.
In accordance with the Regulation on accounting and accounting statements in Russian Federation, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of July 29, 1998 No. 34n, the procedure for conducting an inventory, including the number of inventories in reporting year, the dates of their holding, the list of property and obligations checked for each of them, is determined by the head of the organization, except for cases when the inventory is mandatory.
Thus, taking into account these provisions and on the basis of the order of the head, an inventory of accounts receivable is carried out at any time, for example, immediately before writing off, which is confirmed by an inventory of accounts receivable.
Step 4. We analyze the circumstances that can significantly affect the write-off of expired debt
Formation of a reserve for doubtful debts
There are several methods for creating a provision for accounts receivable:
- percentage of sales method;
- aging method;
When using the first method, a percentage of revenue is included in the reserve - for example, 1.5% per month.
In the second case, all debt is distributed according to the number of days of delay and the probability of non-repayment is estimated in percentage terms.
Moreover, if there are few counterparties, you can take into account the debt for each counterparty / contract.
Cases when the creditor cannot get the debtor to pay off the debt or collect the amounts either by contract, by collection or by court, are common.
In such situations, the creditor is left with nothing but the outstanding debt in financial results... However, to carry out such an operation, it is necessary observe carefully accounting and tax regulations.
What debt is to be written off
 Accounts receivable is the sum of the debts owed by different persons to one person. Typically, such relationships arise between enterprises. Less often - one of the parties is an individual.
Accounts receivable is the sum of the debts owed by different persons to one person. Typically, such relationships arise between enterprises. Less often - one of the parties is an individual.
Such debt is subdivided into normal and overdue. If the company has delivered goods, services, work within the framework of an advance payment agreement, normal accounts receivable appear in the supplier's accounting department. Payment terms are not violated, the buyer is still complying with the agreement.
If the due amounts are not paid on the contract date, there is a delay, the debt becomes overdue.
Types of overdue debt according to article 266 of the Tax Code:
- doubtful - when the creditor has not provided himself with property guarantees, for example, a pledge or surety, i.e. from the point of view of the lender, there are potential risks of non-receipt of payment;
- hopeless - the debt is recognized as unrealistic for repayment and is written off.
When debt becomes bad:
- expiration of the statute of limitations and the term of collection by bailiffs;
- issuance of a decision of the authority canceling debt obligations;
- the termination of the debtor's existence - and the bankruptcy procedure.
The statute of limitations for civil law is three years from the moment of detection of delay or the last action on the part of the debtor to settle the relationship.
The accounting regulations provide an explanation that overdue receivables are written off separately for each case and on the basis and order of the company's executive body.
The write-off is made:
- reserves for doubtful debts;
- in the financial result;
- expenses - for non-profit companies.
If the subject himself has debts to other persons, accounts payable, it is recommended to write off receivables in the amount of their own debts.
Why do you need to write off? Any debt on the balance sheet refers to the income of the person and increases the size of the taxable base. When it comes to enterprises, debts make up a considerable, and sometimes significant amount and can significantly affect the financial result and the amount of tax. Such a situation is unattractive to the enterprise, so it will seek to get rid of bad debt records.
 The Tax and Civil Codes approved the deadline for the claim - within three years from the date of discovery.
The Tax and Civil Codes approved the deadline for the claim - within three years from the date of discovery.
For the purpose of reconciliation, the accounting department generates a certificate of the amount of the company's accounts receivable and payable at the time of the start of inventory operations.
The help provides information:
- about debtors - separately about each of them (full name, contacts, specifics of relations);
- the amount of debts (time and circumstances of education);
- list of supporting documentation.
The help is attached to and serves as a foundation for the review team when analyzing settlements with customers and suppliers.
What to check:
- score 60 - advances to suppliers and contractors and debts to them;
- score 62 - advances from buyers and their debts;
- accounts 66 and 67 - debts on loans and credits;
- score 68 - overpaid amounts and debts for taxes and fees;
- score 69 - overpaid amounts and debts on insurance premiums;
- score 70 - payments to employees and overpayments, accrual and non-payment of labor remuneration;
- - payments to accountable persons, not certified by reports, and expenses of accountable persons in excess of the amounts issued;
- - debts of employees and employees for other reasons;
- score 75 - debts of founders for the maintenance of their shares, arrears in dividends;
- - amounts between debtors and creditors.
 The results of the inventory are indicated in the act on. Also, the document contains information about part of the debts recognized by debtors, and part - not recognized by debtors. The share of the debt classified as uncollectible due to the term of claim prescription.
The results of the inventory are indicated in the act on. Also, the document contains information about part of the debts recognized by debtors, and part - not recognized by debtors. The share of the debt classified as uncollectible due to the term of claim prescription.
The amounts of bad debts with a delay in the claim period should be displayed on a separate line - for a reasonable write-off.
After consideration of the act, the management of the company issues an order to write off debts. The order form is free. By registering the document, the accounting department can actually write off debts.
When converting debt from buyers into expenses, you must take into account the factor. If the company operates according to the tax on delivery scheme, then, therefore, VAT was charged even when the goods or services were shipped and does not need to be added to the amount again. The opposite situation is if the company operates under the VAT payment scheme.
If the company has not formed reserves for doubtful debts, then debts are written off in the calculation of profit as part of non-operating expenses.
If the reserves have formed, then the write-off is carried out from the reserves account. The wiring for such an operation looks like this: Dt 63 Kt 62.
If the account contains only a part of the amount of bad debts, then this part is written off from the reserve, and the remainder is in non-operating expenses.
Examples of transactions: LLC "Vector" carried out an inventory of the debt in 2015, identified and assigned debts in the amount of 100,000 rubles to the reserves. The following year, one of the company's customers did not pay for the delivery and soon went through the liquidation procedure. An unrealistic debt was the amount of 200,000 rubles. The company operates under a VAT payment scheme. VAT on the amount is 30,000 rubles.
 Postings:
Postings:
- Dt 91-2 Kt 63 - formation of a reserve for 100,000 rubles;
- Dt 63 Kt 62 - write-off of the reserve in the full amount of 100,000 rubles;
- Dt 91-2 Kt 62 - writing off the remaining 100,000 rubles as expenses;
- Dt 76 Kt 68 - the calculation of value added tax in the amount of 30,000 rubles.
If it is possible to write off only a certain share of the total amount of the debt - for example, during the bankruptcy procedure of the debtor, the arbitration court recognized its fixed assets and turnover as insufficient to satisfy creditors and attributed only part of the funds to the return, and found part to be hopeless for recovery
Then the creditor writes off a certain amount that is unrealistic to be reimbursed and receives another part:
- Dt 51 Kt 62 - the debtor paid part of the debt;
- Dt 91-2 Kt 63 - write-off of the remaining part.
And if there are amounts in the reserves that were not included in the write-off process, if the amount of the reserve exceeds the real debt by the end of the year, this balance must be transferred to the company's income.
Within the tax accounting, which the company maintains for calculating income tax, the write-off procedure looks similar:
- debts refer to non-operating expenses in the absence of reserves;
- the presence of a reserve leads to writing off debts from the reserves account to the financial result;
- if after that any amount of debt remains, it is also written off to non-operating expenses.
The amounts written off continue to be present on the accounts of the creditor for 5 years - such a rate was established in case of stabilization of the debtor's financial situation and the appearance of an opportunity to repay the debt.
The write-off is recorded on the off-balance account - 007.
Read more about accounts receivable in this video.
In economic life legal entity often there are cases when the organization has long-term accounts payable (KZ): a perfect loan, shipment of goods by the supplier on credit, failure to pay on time wages employees of the enterprise.
Dear Readers! The article talks about typical ways of solving legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how to solve your problem - contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and WITHOUT DAYS.
It is fast and IS FREE!
If, for various reasons, the debt cannot be paid within the timeframe established by law, such debt goes to the overdue section. However, the debt cannot hang “forever” - if the lender organization has not claimed the debt in court within the time frame established by law, it must be written off.
To avoid additional charges in case of verification tax authorities it is necessary to write off accounts payable correctly, taking into account all regulatory documents.
Basic concepts
Writing off accounts payable is a procedure for recording debts for which the statute of limitations has expired, which has tax consequences.
The limitation period under the civil legislation of the Russian Federation is calculated for a period of three years (Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Interruption of the limitation period is possible if the creditor has brought a claim to the debtor organization. Also, the basis for interruption can be some actions of the borrower, talking about the recognition of the debt, for example, by a response letter to a claim recognizing the presence of non-payment, signing a reconciliation report with the lender or partial repayment of the debt. After the break, the limitation period will be recalculated, i.e. 3 years, the previous time is no longer taken into account.
Foundations
The main reason for writing off KZ is the expiration of the limitation period. There may be other reasons that the organization can refer to when writing off the debt.
The basis for writing off accounts payable will be the impossibility of fulfilling the obligation for objective reasons. For example, writing off accounts payable upon liquidation of a creditor () is the only opportunity to legally refuse to repay money to a non-existent legal entity.
In this case, it is necessary to wait for the exclusion of the inoperative creditor from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Debt payment is also impossible in a situation when the debtor is declared bankrupt.
Obligations can be terminated due to the release of the debtor by the creditor from the payment of the debt (). A similar situation in practice is possible between related, affiliated persons, or, for example, when a loan to an organization was provided by the founder. Such procedures are considered in civil law as a gift, if the economic benefit received by the party forgiving the debt is not proven.
The legislation presupposes the use of an act of a state body as a basis for writing off if, as a result of its issuance, it becomes impossible to fulfill the obligation (Art.).
Another reason for writing off a short circuit is the impossibility of its execution due to the onset of an event (force majeure), for which none of the parties can be responsible (Art.).
Finally, the reason for the termination of credit relations may be the death of the creditor (Art.), If we are talking about an individual.
All of the above grounds make it possible to write off bad accounts payable .
Basic Rules
The basic rule applied to writing off accounts payable is that the accounting of this operation is carried out exactly during the period when its limitation period expired.
If there is a violation of this provision, you will have to submit an updated declaration in the following reporting period.
Timing
The task of the organization's accountant is to correctly calculate the timing of the amounts to be written off. This is necessary in order not to make a mistake when calculating income tax.
Based established by law a three-year period for filing a claim, the accountant must check whether all the conditions for writing off the debt have been met, whether there has been an interruption, if the debtor organization in any way contacted the creditor: a letter of guarantee, a signed reconciliation statement, etc. If there were no contacts, the basis is taken from the date of the last payment or from the date of the end of the loan agreement.
Documenting
Write-off of KZ is carried out in the documents of accounting and tax accounting.
The procedure consists of preparation:
- inventory act;
- accountant's certificates;
- the order of the head of the institution to write off overdue accounts payable.
It is recommended to carry out an inventory regularly at the end of each reporting period. This will allow timely identification of the arisen debt. The peculiarity of the inventory at the enterprise is that in addition to the payable part, it is necessary to check the accounts receivable.
When carrying out an inventory, we pay special attention to settlements with financial institutions, extrabudgetary funds, customers of the enterprise and the amount of debt to the budget. As a rule, if, based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up in a standard form.
It should be noted that the quarterly inventory is the right of the economic entity, but not its obligation. The Federal Law "On Accounting" obliges to conduct an inventory once a year.
The next important step is to prepare an accounting statement that includes important information on overdue debts:
- contract number and date of its drawing up;
- links to primary documents: consignment notes, acts, invoices;
- justification of the expiration date by means of mathematical calculations;
- information about the creditor company.
The director of the organization is guided by these documents when signing an order to write off the debt.
Order to write off overdue accounts payable
A typical bad accounts payable write-off order might look like this.
The order is issued on the company's letterhead, in the header of which its details are indicated.
In the text of the order, referring to the accounting rules approved by the Ministry of Finance of Russia and articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the head of the organization justifies the need to write off the debt to a specific creditor on the basis of the inventory and accounting certificate. The amount written off is recognized as non-operating income. Control over the execution of the order is assigned to the chief accountant.
Procedure order
The short circuit write-off procedure takes place in four stages:
- Identification of the amount of overdue debt during the inventory at the end of the reporting period.
- Drawing up an accounting statement on the identified short circuit.
- Issuance by the director (head) of the company of an order to write off the debt on the basis of regulatory documents.
- Introduction by the accounting department of the corresponding changes in accounting and tax accounting.
In accounting, the write-off is carried out on the basis of the following entry:
Debit 60 - Credit 91-1
Taxation
Tax accounting requires a delay in the period when the limitation period expired. If this did not happen due to an accounting oversight, you will have to submit a "revised" declaration in the next period.
The grounds for fixing the amount of debt and the statute of limitations are exactly the same as in accounting:
- an order to conduct an inventory;
- inventory sheet in a standard form;
- accounting information;
- order of the head to write off the short circuit.
When calculating the single tax under the simplified tax system, regardless of its form (single tax on income, or income minus expenses), the debt is included in non-operating income. Income does not include debts that have arisen from the payment of fines and penalties, as well as mandatory insurance premiums.
If an organization pays UTII, it is obliged to keep separate records of income, expenses and business transactions. Therefore, for the purposes of calculating a single tax on imputed activities, the total amount of income received is not important and tax consequences do not occur.
The reporting period for income tax is a quarter. If taxpayers calculate monthly advance payments based on advance profit - every month.
Often, accountants have a question about how to pay VAT on the advance after the expiration of the KZ period. The Ministry of Finance clarifies this point by allowing the taxpayer to reduce VAT only in terms of material and production resources, works and services.
The grounds for writing off accounts receivable are important from the point of view of the prospects for optimizing the tax base of the enterprise. Consider their list and application features.
On what basis is it legal to write off a receivable?
When can a receivable be written off? It is legitimate to talk about three main scenarios for its cancellation:
- Writing off after the debtor has repaid the debt.
Such a write-off does not imply that the creditor has any additional rights or obligations in terms of taxation - if we are talking about the principal amount of the debt. Exceptions will be observed:
- when receiving income from interest - in this case, it is necessary to calculate and pay tax on it;
- when the debtor is an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur, and the interest rate on the loan is less than the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation: in this case, the creditor as tax agent you will need to calculate and pay tax on material outputs of the debtor.
- Write-off on the fact of forgiveness of the debt to the debtor.
Similarly, the creditor does not have any tax rights or obligations here, except for the need to calculate and pay tax on material output on a forgiven debt to an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur.
Debt forgiveness is regarded as a gratuitous transfer of property and therefore cannot be included in expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04.04.2012 No. 03-03-06 / 2/34, clause 4 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 15.07.2010 No. 2833/10 provides for the possibility of writing off the debt as an expense if the creditor company has a commercial interest in forgiving the debt. But in litigation with the Federal Tax Service, such an expense is not always possible to defend (resolution of the Fifteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated November 14, 2013 No. 15AP-13132/13).
- Write-off upon recognition of the debt as uncollectible.
Here's the situation in terms of tax consequences more interesting: the written off bad debt can be taken into account in non-operating expenses when forming the tax base on the tax base (subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under the simplified tax system, such a preference is not provided (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 13, 2007 No. 03-11-04 / 2/274).
It is possible to recognize a debt as hopeless if (clause 2 of article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- the statute of limitations has expired;
- the debt has been canceled due to the impossibility of its repayment;
- the debt was canceled by a decision of the authority;
- the debtor organization was liquidated;
- the bailiffs were unable to collect the debt at the expense of the debtor's property.
Let's consider the grounds for writing off accounts receivable in accounting due to the recognition of the debt as hopeless - with the prospect of its inclusion in expenses, in more detail.
When you can write off a debt as hopeless: the limitation period has expired
In general, the limitation period for accounts receivable is 3 years (Art. 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). It is counted from the moment the creditor finds out that the debtor has failed to fulfill its obligations under the loan agreement. That is, delays in relation to the date of fulfillment of obligations established by the contract and the documents drawn up as part of its execution - acts, invoices.
The limitation period is counted from zero if (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- there was a partial repayment of the debt;
- the debtor initiated reconciliation of the debt, applied to the creditor with a restructuring request (or took other actions indicating that he was going to repay the debt).
NOTE! If the debtor has recognized part of the debt, then this does not mean that he recognizes the debt in full, unless otherwise specified (Resolution of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces dated 09.29.2015 No. 43).
The term is also reset to zero if the creditor submits a lawsuit against the debtor (letter from the Ministry of Finance dated 09.21.2007 No. 03-03-06 / 2/18).
It should be borne in mind that if the creditor has its own debt to the debtor, then even a hopeless receivable cannot be written off, since in this case the debt and the receivable must be mutually offset (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04.10.2011 No. 03-03-06 / 1 / 620). Actually, this rule applies, whenever possible, to the following scenarios of debt as hopeless.
Debt cancellation under circumstances beyond the control of the parties: nuances
A debt can be canceled, that is, recognized as hopeless:
- Due to the factual circumstances that interfere with the fulfillment of obligations under the contract, which none of the parties can influence (clause 1 of article 416 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
As a rule, we are talking about force majeure - natural disasters, man-made disasters.
The occurrence of such circumstances can be confirmed by the official conclusion of the Ministry of Emergencies or another authority (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 02.07.2009 No. 03-02-07 / 1-336).
Don't know your rights?
- By virtue of the issuance of an act by the authorities, the provisions of which make it impossible for the debtor to fulfill the obligations, this is also considered as a circumstance that does not depend on the will of the parties to the contract.
A typical example is the revocation of a banking license from a credit and financial organization, which was the guarantor of the debtor under the transaction (while the debtor, for his part, was able to legally justify the impossibility of repaying the debt on his own).
Upon recognition of the relevant normative act as invalid, the obligation of the creditor again becomes relevant and subject to execution, unless otherwise established by an agreement between him and the creditor.
Writing off a debt upon liquidation of a debtor organization
Another criterion for recognizing a debt as hopeless is liquidation of a debtor organization without transferring his duties to other persons, for example:
- to another organization as a result of a merger or acquisition;
- to an individual (former founder, actual owner of the business) due to the onset of subsidiary liability.
The liquidation of an organization is considered complete only if the relevant information is entered in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Thus, an extract from the state register will be a voucher for writing off the debt.
The liquidation rule cannot be applied to debtors in the status of an individual entrepreneur, even by legal analogy, since the former entrepreneur in any case must fulfill the obligations undertaken during the period when he had the status of an individual entrepreneur.
Note that the exclusion of a legal entity from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities as an inoperative economic entity - as an actual type of liquidation (although it has a different legal nature) can also be the basis for declaring a debt hopeless (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 23.01.2015 No. 03-01-10 / 1982).
Impossibility of debt collection by bailiffs
Another reason for writing off accounts receivable is the inability to collect the debt through enforcement proceedings. In this case, the Bailiffs Service issues an act on the completion of the debt collection due to the impossibility of its implementation and returns the writ of execution to the creditor. On the basis of the relevant act and the writ of execution, the creditor company has the right to write off the receivable.
It should be borne in mind that before the expiration of the writ of execution - that is, within 3 years after its issuance by the court - the creditor can repeatedly initiate re-collection of the debt by transferring the list to the Bailiff Service, however, every time no earlier than 6 months after its return by the bailiffs (subparagraphs 4, 5 of article 46 of the law "On enforcement proceedings" dated 02.10.2007 No. 229-FZ).
Having considered on the basis of which it is possible to write off receivables, we will get acquainted with the nuances of documenting such a write-off.
Write-off of accounts receivable in accounting: documentary registration
To document the creditor's right to recognize a debt, you will need:
- Conducting an inventory of debts and drawing up an act on it.
The document can be drafted using unified form INV-17 or a form developed by the enterprise independently.
- Drawing up an act on writing off accounts receivable.
Attachments to it can be documents certifying the grounds for writing off the debt, for example, an act from the Bailiff Service.
- Formation of a certificate of debiting write-off, which will disclose:
- information about the amount of debt;
- reasons for debt cancellation.
No unified form for such a certificate has been developed, the enterprise can use its own.
- Issuing an order from the head to write off debt.
The order is issued on the basis of the above acts and a certificate.
Separately, it may be necessary to draw up an order on the formation of an inventory commission - if it has not been established by the time the procedure in question is carried out.
Debt write-off account: nuances
In the accounting registers, the write-off of receivables is reflected in the following groups of transactions:
- If there is a reserve for doubtful debts: correspondence Dt 63 Kt 62 shows debt write-off at the expense of the reserve.
- In the absence of a reserve or if the amount of debt is greater than it: correspondence Dt 91 subaccount "Other expenses" Kt 62 shows the inclusion of the written off debt in expenses.
The most important feature of debt write-off is that it is generally viewed as a temporary phenomenon. That is, with the expectation that the creditor will ever settle accounts with the firm. The legislator believes that a reasonable waiting period for such calculations is 5 years. As a result, the written off debt must be temporarily reflected off the balance sheet (clause 77 of the Accounting Regulations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 34n dated July 29, 1998).
For these purposes, additional entries are generated in accounting:
- Дт 007 - the amount of the written off debt is temporarily fixed off the balance sheet.
- When returning a debt by a creditor:
- if there is a reserve for doubtful debts: Дт 63 Кт 91 - that is, the reserve is restored;
- in the absence of a reserve for doubtful debts: Dt 62 Kt 91 ("Other income") - that is, the receivable is restored and included in income when the tax base is formed.
- Kt 007 - the repaid debt has been removed from off-balance sheet accounting.
A similar posting can be applied after 5 years, when the debt is already considered as irrecoverable.
Accounts receivable can be written off upon repayment, forgiveness of the debt or its recognition as hopeless. The third option is optimal for the lender from the point of view of taxation under DOS. It requires accounting and documentation of the circumstances that make it possible to talk about the emergence of an opportunity to write off the debt.