Summary reporting. Consolidated reporting: how it is formed, accounting principles Types of consolidated reporting
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists using the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
Coursework by discipline
"Accounting financial statements"
"Consolidated reporting"
Introduction
Chapter 1 The concept of consolidated financial statements
1.1 Concept and meaning of consolidated reporting
1.2 Regulation of consolidated reporting
Chapter 2 application and preparation of consolidated reporting
2.1 Purpose, scope and features of consolidated reporting
2.2 Drawing up and requirements of consolidated reporting
Chapter 3 Practical Part
Conclusion
List of references
INconducting
The concept of consolidated reporting emerged at the turn of the 20th century in the United States. The need for consolidation financial statements associated with the processes of concentration and centralization of capital, the creation of subsidiaries and dependent companies, branches and separate divisions.
The relevance of this topic lies in the fact that in modern conditions the most characteristic tendency of management is the acquisition by some organizations of blocks of shares in others, participation in the authorized capital of other organizations, the creation of financial and industrial groups of interconnected organizations, the conclusion of agreements on joint activities. And obtaining data on the financial position and financial results of a group of interconnected organizations is carried out using a system of indicators of consolidated reporting.
One of the promising areas of business development at present is the creation of groups of enterprises that are economically connected with each other, but at the same time remain independent legal entities - concerns or holding companies, in which one company, called the parent or parent company, controls one or several others. Thanks to the creation of concerns and holdings, enterprises that are part of them get the opportunity to access new technologies, expand the scope of their activities, develop business ties, attract new qualified workers, and acquire loans. Another positive point is that the formation of groups of enterprises can significantly strengthen the investment potential of such an economic association, increase profitability and the technological level of production. The creation of groups of enterprises opens up ample opportunities for a number of group operations to save financial resources, reduce tax losses, coordinate financial and material flows within the group. The balance sheets of individual enterprises cannot provide adequate information for analyzing the functioning of a group of enterprises - they can only be used when analyzing a single enterprise. To identify the results of the analysis of the state and activities of such associations as concerns and holdings, a special financial statements - the so-called consolidated financial statements or, as we call it, using a term adopted abroad, - consolidated financial statements.
The objectives of the course work are:
Consider this type of reporting as consolidated reporting;
Consider the preparation of consolidated statements;
To consolidate practical skills based on solving a cross-cutting problem;
From the tasks it follows that the purpose of the course work is to consolidate theoretical knowledge and learn how to fill out accounting forms.
This course work consists of three chapters. The first chapter discloses the essence of consolidated accounting reporting, its meaning and concepts, regulation and basic principles. The second chapter discusses the rules, principles, purpose, scope and features of consolidated reporting, as well as the cases in which it is not required, it is considered how consolidated reporting is prepared. The third chapter of the course work is a practical part, in which, on the basis of drawing up an annual accounting report on a cross-cutting example of a conditional enterprise - the Etalon plant, the main stages of the formation of accounting indicators are completed.
consolidated accounting statements
Chapter 1 The concept of consolidated financial statements
1. 1 Concept and meaning of consolidated reporting
The practice of doing business in economically developed countries indicates that the most important role in a market economy is played by joint stock companies (corporations), which are a form of business organization in the form of a set of enterprises (independent legal entities), whose capital is divided into shares (shares).
The advantages of this form of entrepreneurial activity are: limitation of the liability of the owners of the corporation by the amount of their net capital; convenience and speed in changing owners, unlimited activities in terms of scale and type. Unlike an individual private enterprise, a corporation has many owners, who in the overwhelming majority of cases are in no way connected with each other and have only a say in the fate of the firm. Therefore, the degree of independence of the corporation as a participant in economic relations is higher, and as a consequence, higher than the ability and ability to develop activities. It is no coincidence that corporations usually rapidly increase their capital and the scale of production and commercial activity, and in a competitive environment they crowd out smaller competitors.
In its most general form, a corporate group can be thought of as a combination of one parent company and several subsidiaries. In real life, the parent-subsidiary relationship can be multilevel.
Parent and subsidiary companies are defined differently in different countries. In particular, in our country, the corresponding concept is given by the first part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Parent - the holder of a controlling stake in subsidiaries or other entities that exercise control over them
Subsidiary enterprise (company) - an organization in respect of which the parent organization either:
Has the ability to determine the decisions made by this organization in accordance with the agreement concluded between them;
Has other ways of determining the decisions made by the subsidiary.
A subsidiary can be fully or partially owned.
Dependent company - an organization, a significant share of the capital of which 25-50% is owned by the parent organization.
An important feature of a group of companies is the control over the assets and operations of all companies in the group.
In accordance with the Regulation on accounting and reporting in the Russian Federation, if an organization has subsidiaries and dependent companies, in addition to its own accounting reports, consolidated financial statements are drawn up, including indicators of such companies located in the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad.
Consolidated financial statements are a system of indicators that reflect the financial position at the reporting date and financial results for the reporting period of a group of related organizations.
Own accounting report;
Consolidated financial statements, including indicators of reports of subsidiaries and dependent companies located on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad.
Organizations that have branches of a representative office and other structural divisions, including those allocated to a separate balance sheet, must include indicators of their activities in the accounting statements.
These organizations compile a single accounting report by arithmetic information of indicators of both their own activities and the activities of branches and representative offices.
There is a consolidated accounting statement of a group of related organizations. Such reporting combines the accounting statements of the parent organization, its subsidiaries, and also includes data on dependent companies that are legal entities under the laws of the place of their state registration.
Both a subsidiary and a dependent company develop an independent accounting policy.
The procedure for preparing consolidated financial statements is regulated by the Methodological Recommendations for the Preparation and Presentation of Consolidated Financial Statements, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 1996 No. 112.
The reporting data of the parent organization and subsidiaries are summarized in compliance with a number of rules.
First of all, you need to determine the date on which the consolidated financial statements are drawn up.
Combine the statements of the parent organization and subsidiaries drawn up for the same period and for the same reporting date. If the accounting statements of any subsidiary located outside the Russian Federation are drawn up on a different date, then this company forms interim statements as of the date of the consolidated financial statements. If it is impossible to form the interim financial statements of the subsidiary, the indicators for the specific reporting date of the “daughter” are included in the consolidated statements of the organization, but provided that the difference between the dates does not exceed three months.
Before drawing up the consolidated financial statements, it is necessary to reconcile and settle all mutual settlements of the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as settlements between subsidiaries.
If the parent organization, in addition to subsidiaries, other dependent companies, the set is achieved by combining the reporting indicators of the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as including data on the participation of the parent organization in the formation of the share capital or charter capital of dependent companies.
The reporting indicators of the subsidiary are included in the summary from the 1st day of the month following the month of the acquisition by the parent organization of the corresponding number of shares (stakes) or the emergence of another opportunity to influence the decisions of the subsidiary.
Similarly, they include data on associates in the consolidated financial statements.
Indicators of the subsidiary's reporting in foreign currency for inclusion in the consolidated financial statements are recalculated as follows:
At the rate of the Bank of Russia, the most recent quotation in the reporting period;
Income and expenses are translated using exchange rates at the dates of transactions or the average rate;
The difference from the recalculation of assets and liabilities, the amount of income and expenses in the consolidated balance sheet is reflected in the additional capital and disclosed in the notes to the consolidated balance sheet and the consolidated income statement.
The consolidated annual accounting statements of federal ministries and other federal executive bodies are submitted to the Ministry of Finance of Russia, the Ministry of Economy and the State Statistics Committee of Russia:
For joint-stock companies (partnerships), part of the shares, shares or contributions of which are fixed in federal ownership - no later than August 1 of the year following the reporting year.
These terms are stipulated by clause 93 of the Regulation on accounting and reporting in the Russian Federation.
The consolidated annual financial statements of an association of legal entities created by them on a voluntary basis are presented in the manner and terms provided for in the constituent documents of the association, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 94).
Consolidated financial statements are in millions or billions of rubles with one decimal place.
The usual consolidated accounting statements are presented to the founders (members) of the parent organization. This reporting is sent to other interested users in cases specifically established by law, or by decision of the parent organization.
The consolidated statements are signed by the head and the chief accountant of the parent organization. In the case when the accounting is conducted by a centralized accounting department, a specialized organization (audit firm) or a specialist accountant on a contractual basis, one signature is drawn up - the head of the centralized accounting department, a specialized organization or a specialist accountant.
By decision of the group members, the consolidated accounting statements may be included in the published statements of the parent organization.
There are a number of factors that need to be guided when deciding whether to compile consolidated financial statements.
The problem of non-inclusion of indicators of subsidiaries or dependent companies in the consolidated financial statements is positively resolved if a share of voting shares or a share in the authorized capital of companies is acquired for a short period with the aim of subsequent resale.
If the parent organization does not own more than 50% of the voting shares (50% of the authorized capital of a limited liability company) of the subsidiary and has not entered into an agreement that allows determining the decisions of the subsidiary, it is not necessary to prepare consolidated financial statements in the presence of two circumstances:
1. data on the subsidiary (dependent) company does not have a significant impact on the assessment of the financial position and financial performance of the group;
2. the inclusion of the financial statements of the subsidiary in the consolidated statements contradicts the requirement of rationality. This requirement implies economic accounting based on the conditions of economic activity and the size of the organizations.
The expediency of not including the indicators of subsidiaries in the consolidated statements must be confirmed by an independent auditor.
For the same reasons, indicators of dependent companies may not be included in the consolidated reporting.
1.2 Consolidated reporting regulations
Consolidated financial statements in accordance with the requirements of international regulatory documents are a combination of financial statements of two or more legally independent companies acting together economically and financially.
The adaptation of international financial reporting standards to Russian conditions makes the foreign experience gained in the field of preparing consolidated statements valuable for domestic organizations. In recent years, attention to this issue on the part of Russian accounting organizations has increased, regulatory documents and methodological instructions on this issue have appeared, the issue of adopting a law on consolidated reporting is on the agenda. At the same time, the continuing inconsistency and some inconsistency of the regulatory framework determine the increased interest in the methodological foundations of preparing consolidated statements by domestic organizations. Coverage of issues that predetermine further understanding of the problems of drawing up consolidated financial statements can be found in a number of Russian laws adopted in recent years.
First of all, along with the legal forms of commercial organizations in the Civil Code Russian Federation definitions of subsidiaries and affiliates are given. Studying the legal status of a joint stock company helps to uncover the system of participation of the companies included in the group.
In accordance with Art. 105 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a business company is recognized as a subsidiary if another (main) business company, due to the prevailing participation in its authorized capital, or in accordance with an agreement concluded between it, or otherwise has the ability to determine the decisions made by such a company. The subsidiary is not liable for the debts of the parent company. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not establish the share of the parent company in the authorized capital of the subsidiary, which allows it to determine the decisions of the subsidiary, while such parameters are indicated for dependent companies. In Art. 106 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a definition of a dependent economic company is given, which is recognized as such if the other (dominant, participating) company has more than 20% of the voting shares of a joint-stock company or 20% of the authorized capital of a limited liability company.
Other aspects of the definition of participation, dependence and control between companies are considered in the Law of the Russian Federation of March 22, 1991, No. 948-I "On Competition and Restriction of Monopolistic Activities in Product Markets."
In accordance with Art. 18 of this Law, the acquisition by a person (group of persons) of shares (stakes) with the right to vote in the authorized capital of a business entity, under which such person acquires the right to dispose of more than 20% of the said stocks (stakes), as well as the acquisition by a person of rights that allow a person to determine the conditions for running an economic entity his entrepreneurial activity or to exercise the functions of his executive body, is carried out with the prior consent of the federal antimonopoly body on the basis of a petition of a legal entity or individual.
Other issues of drawing up consolidated financial statements are supplemented and specified in the Federal Law of November 30, 1995 No. 190-FZ "On financial and industrial groups". In this Law, a financial and industrial group is defined as a set of legal entities acting as a parent company and subsidiaries, or having fully or partially combined their tangible and intangible assets on the basis of an agreement on the creation of a financial and industrial group for the purpose of technological or economic integration for the implementation of investment or other projects and programs aimed at increasing competitiveness and expanding markets for goods and services, increasing production efficiency, creating new jobs.
The procedure for maintaining summary (consolidated) accounting, reporting and balance sheet of a financial and industrial group was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 9, 1997 No. 24.
Until recently, the preparation of consolidated statements in the Russian Federation was regulated by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 28, 1995 No. 81 "On the procedure for reflecting in the accounting of certain transactions related to the introduction of part one of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation" and the Procedure for maintaining consolidated (consolidated) accounting, reporting and balance sheet of a financial and industrial group.
Both documents provided only initial information about the consolidated financial statements. The first dealt with the relationship between the parent (parent) company and the dependent (subsidiary) enterprise. The second provided for the preparation of consolidated statements by the central (parent) company, established by all parties to the agreement on the creation of a financial and industrial group and authorized to conduct business of the financial and industrial group.
In addition to these documents, the Ministry of Finance of Russia approved Order No. 112 dated December 30, 1996 "On Methodological Recommendations for the Preparation and Submission of Consolidated Financial Statements," which was amended and supplemented in 1999.
This order gives a more precise definition of consolidated financial statements and indicates the cases in which it is drawn up, considers the general procedure for the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements, the rules for combining the accounting indicators of the parent organization and subsidiaries in the consolidated financial statements, the rules for including data on dependent companies in consolidated financial statements, explanations to the consolidated balance sheet and consolidated income statement.
Consolidated financial statements are drawn up in the manner and volume established by PBU 4/99 "Accounting statements of the organization".
Consolidated financial statements are compiled according to the forms developed by the parent organization on the basis of accounting forms approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of June 22, 2003 No. 67n.
As a result of market transformations in the Russian Federation, the previous accounting system could not fully reflect the new financial and business operations of organizations. Changes in legislation, clarification of conceptual acts and methodology of accounting and reporting were required.
In the system of international financial reporting standards (IFRS) there are several standards devoted to the methodological aspects of preparing consolidated reporting.
Among them:
IFRS 25 "Investment accounting",
IFRS 27 "Consolidated Consolidated Financial Statements and Accounting for Investments in Subsidiaries"
IFRS 28 Accounting for Investments in Associates,
IFRS 31 "Financial Statements on Interests in Joint Ventures",
IAS 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation ",
IAS 39 "Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement"
Chapter 2 application and preparation of consolidated reporting
2.1 Appointment,scope and features of consolidated reporting
Consolidated financial statements are prepared in addition to the organization's own accounting statements if it has subsidiaries and affiliates.
The consolidated reporting includes indicators of such companies located in the country and abroad. If the constituent documents of associations of legal entities created on a voluntary basis provide for the compilation of consolidated financial statements, they are drawn up according to the rules established by the RF Ministry of Finance for the preparation of consolidated statements.
Currently, summary reports are prepared in the following cases:
When forming consolidated statements by federal ministries and departments and other organizations of the executive power in accordance with the Procedure for drawing up and submitting consolidated annual financial statements by federal ministries and departments and other federal executive bodies of the Russian Federation.
When reporting within one legal entity based on the reporting data of its divisions and branches allocated to a separate balance sheet, but not being independent legal entities.
If parent organizations have subsidiaries and affiliates.
These instructions are contained in the Regulations on the conduct of accounting and accounting reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of July 29, 1998. There is no separate provision on accounting (PBU) on the preparation of consolidated financial statements. Instead, the Methodological Recommendations for the Preparation and Presentation of Consolidated Accounting Statements, approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 30, 1996, are applied. They are applied in the new edition, approved on May 12, 1999.
The International Committee on Financial Reporting Standards has approved three standards related to the consolidation of financial statements: IFRS-22 “Business Combinations”, IFRS-27 “Consolidated Financial Reporting and Accounting for Investments in Subsidiaries”, IFRS-28 “Accounting for Investments in Associates”.
Consolidated statements are prepared not only for the consolidated group of organizations and companies. It also takes place during the unification and reorganization of organizations.
Consolidation is the combination of certain elements according to certain criteria. Consolidated, that is, combined (consolidated), reporting appears when in real economic life there are associations of organizations - primarily associations of joint-stock and other business companies.
Consolidated financial statements are intended to provide information characterizing a group of business entities operating as a single economic entity. It is necessary for everyone who has interests or intends to have them in this group of organizations: investors, lenders, suppliers, customers, personnel and trade unions, banks, other financial investors, government agencies and local authorities.
Consolidated financial statements allow the use of group income from a business association as a basis for calculating dividends on shares of organizations that are part of the association.
The consolidated financial statements reflect the interests of a minority of investors, that is, those shareholders who have less than half of the votes at shareholder meetings.
Consolidated financial statements create the possibility of using the aggregate group income and group profit as the basis for calculating taxable profit in those countries in which this is provided for by tax legislation. Consolidated statements contain verified data for control and management both by the management of organizations and by all other stakeholders.
Consolidated financial statements are prepared for the following activities:
The main activity of industrial organizations;
The main activity of construction, installation, repair and construction, drilling, design and survey organizations;
The main activity of geological organizations and topographic and geodetic organizations (expeditions);
The main activities of scientific organizations;
The main activities of organizations for material and technical supply and sales;
The main activity of trade and catering organizations;
The main activities of organizations for the production of agricultural products;
The main activity of computing centers and other organizations providing information and computing services;
The main activity of transport organizations;
The main activities of organizations for the repair and maintenance of roads;
The main activity of organizations of housing and communal services;
The main activity of foreign economic organizations.
Consolidated financial statements combine the accounting statements of the parent organization and its subsidiaries, and also include data on affiliated companies. The parent organization acts as a parent company (partnership) in relation to subsidiaries, and as a dominant (participating) company in relation to dependent companies. Moreover, both the subsidiary and the dependent are legal entities.
The accounting statements of a subsidiary are combined into consolidated accounting statements if the parent organization:
Determines the decisions made by the subsidiary in accordance with the agreement concluded between the parent organization and the subsidiary;
Has other ways of determining decisions made by the subsidiary.
Information about the dependent company is included in the consolidated financial statements if the parent company has a 20% stake in the voting shares of a joint stock company or more than 20% of the authorized capital of a limited liability company.
Data on a subsidiary or dependent company may not be included in the consolidated financial statements if the parent organization:
Acquired shares in the authorized capital of a subsidiary or dependent company for a short-term period with the aim of subsequent resale;
Cannot determine the decisions made by the subsidiary.
The parent organization adheres to the accepted form of the consolidated balance sheet, consolidated income statement and explanations to them from one reporting period to another. Changes in these reporting forms are disclosed in the notes to the consolidated financial statements, indicating the reasons that caused these changes.
The reliability of the preparation and compliance with the procedure for submitting consolidated financial statements is ensured by the head of the parent organization.
The volume, timing, procedure for submitting the financial statements of subsidiaries and dependent companies of the parent organization (including additional information required for the preparation of consolidated financial statements) is established by the parent organization.
Before drawing up the consolidated financial statements, it is necessary to settle all the settlements between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries.
If the parent organization has subsidiaries and affiliates at the same time, consolidated financial statements are prepared by combining the accounting indicators of the parent organization and subsidiaries and including data on participation in affiliated companies.
Consolidated statements are prepared and submitted in Russian in thousands of rubles or in millions of rubles with one decimal place.
The name of each component of the consolidated financial statements must contain the word “consolidated” and the name of the Group.
It is advisable to draw up consolidated statements no later than June 30 of the next year after the reporting year, unless otherwise established by the legislation of the Russian Federation or the constituent documents of the organization.
By decision of the participants, the consolidated statements may be published as part of the published accounting statements of the parent organization.
As a result of market transformations in the Russian Federation, the previous accounting system could not fully reflect the new financial and business operations of organizations. It required changes in legislation, clarification of the conceptual framework and methodology of accounting and reporting.
The definition of consolidated financial statements as a system of indicators reflecting the financial position at the reporting date and financial results for the reporting period of a group of related organizations, given in the Methodological Recommendations for the Preparation and Presentation of Consolidated Financial Statements, is, in fact, close to the definition of consolidated financial statements in IFRS.
The introduction of this document is an important stage in the development of consolidated reporting in Russia. However, the equalization of the concepts of consolidated and consolidated reporting, which are different in their content, does not help to identify the remaining differences.
In most cases, consolidated statements are prepared within the framework of one owner or for statistical aggregation, and consolidated statements are prepared by several owners for jointly controlled property.
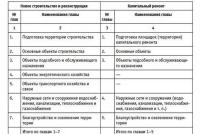
Consolidated financial statements are a special type of financial statements compiled by combining (a set) of accounting data from several companies. Currently, there are two types of consolidated accounting statements in the Russian Federation:
Consolidated accounting statements of federal executive bodies (ministries and departments);
Consolidated accounting statements of a group of related companies.
The first type of consolidated reporting - consolidated financial statements of federal executive bodies (ministries and departments) was compiled in our country before, in the conditions of a socialist economy. The purpose of the summary report was to provide an opportunity for government bodies to assess the activities of their subordinate ministries and departments. Consolidated reports of ministries and departments included:
Current consolidated statistical reporting;
Periodic consolidated financial statements;
Annual consolidated accounting statements.
The characteristic features of consolidated financial statements compiled by federal ministries and other federal executive bodies are:
The owner of all organizations included in the consolidated report, with the exception of joint stock companies, is the state represented by the relevant executive authority;
All organizations included in the report belong to the same industry;
The main consumer of such reporting information is the state represented by the statistical and financial authorities;
The consolidated reporting of federal executive bodies is part of the current system of state financial control and planning.
The second type of consolidated reporting is consolidated (consolidated) financial statements of a group of related organizations. The rules and procedure for compiling this type of consolidated reporting differs significantly from the rules and procedure for compiling consolidated reporting of executive authorities. Currently, the rules and procedure for preparing consolidated financial statements for groups of related organizations are governed by the Methodological Recommendations for the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements.
In domestic practice, there are the terms "consolidated reporting" and "consolidated reporting", which differ in nature.
Consolidated financial statements in the traditional sense are statements that are compiled by government bodies (ministries, departments) for state enterprises under their subordination.
The purpose of the summary report is to provide an opportunity for governing bodies to assess the activities of subordinates and organizations.
Most of the indicators of consolidated reporting, indicators of production, the number of personnel and payroll, production costs, profit and loss, and others were obtained by simply adding the indicators of the consolidated reports. In addition, individual indicators of consolidated reporting are obtained by calculating averages and relative values \u200b\u200bboth for summary data and for data from organizations' reports, that is, statistical indicators can be used to obtain summary data.
Consolidated financial statements have a number of distinctive features:
1.characterizes the property and financial position of the group as a single economic entity, in this connection, the main feature of the method of drawing up a consolidated report, along with the summation of indicators, is mutual exclusion, i.e. elimination of indicators of intra-group settlements, as well as the elimination of intra-group sales and profits from transactions between the enterprises of the group;
2. is compiled for a group of companies consisting of a parent company and subsidiaries, while subsidiaries are under the direct or indirect control of the parent company. Control of the parent company over subsidiaries is carried out in the form of managing their financial and economic activities and with the aim of obtaining economic benefits;
3. the share of the assets and capital of the group that does not belong to the parent company is allocated, that is, the share of the owners of the group enterprises that are in the minority.
Thus, consolidated financial statements are a specific, unconventional form of accounting statements, since they:
Contains information about the property and financial position of a group of interconnected enterprises, that is, several legal entities, and not one legal entity, which goes beyond the principle of property isolation;
It is compiled on the basis of the reporting data of the enterprises of the group, and not on the basis of accounting. Consolidated accounting for the group is not maintained.
The use of consolidated financial statements as a source of information about the financial position of a group of enterprises is conditioned by the concept of a single economic entity. In accordance with this concept, the enterprises of the group, due to their close economic relationship, are considered as a single subject of the economy and are obliged to provide interested users with unified accounting reports characterizing the results of their joint financial and economic activities as the results of the activities of a single enterprise.
Consolidated financial statements occupy an important place in the system of modern economic information, being the main source of economic information about the activities of a group of interconnected enterprises.
2.2 Preparation and requirements of consolidated reporting
Among the main problems arising in the preparation of consolidated statements, one can point out the great laboriousness of collecting and summarizing data in geographically distributed structures, the lack of operational information about the activities of the companies belonging to the group, different accounting and reporting methodology at different enterprises, and an unclear order of interactions between companies.
The first step towards optimizing the consolidated reporting process is the appointment of responsible persons and the development of a clear system of interactions between them. For this, it seems necessary to create a separate subdivision in the head organization, subordinate to the financial director.
In practice, often a special unit is not created; the chief accountant is engaged in the preparation of consolidated statements. This approach is not correct, since in this case an increased load falls on him and he experiences a constant shortage of time. Moreover, according to the existing world practice, the issues of consolidated reporting are in the sphere of competence of the CFO. Sometimes, if the group is small, the described option has the right to exist, but only at first.
If the group has many subsidiaries or its activities are multi-disciplinary, a consolidation unit is necessary. Moreover, it is advisable to single out in it individual employees responsible for interaction with one or more subsidiaries.
The general consolidation department should be autonomous. Including him in the accounting department is incorrect, since in this case it turns out that he develops regulatory documents and control procedures for his own management.
Employees in this department can be attracted both from the accounting department and from other departments: you will also need knowledge of economists, financiers and others. However, it is advisable that the department is managed by someone with good accounting knowledge and skills.
In each of the subsidiaries, it is necessary to appoint a person responsible for preparing the data for consolidation. It would be optimal to entrust this to the employees of subsidiary accounting departments under the control of their chief accountant or financial director, who should be responsible for the information submitted to the parent organization.
In large subsidiaries, it is possible to create separate divisions subordinate to the chief accountant or financial director.
The tasks of the department dealing with consolidated reporting include the development and support of internal regulations for its preparation. This can be, for example, a unified accounting policy, guidelines for the accounting and reflection of intragroup transactions, schedules for the preparation and presentation of statements of subsidiaries, and more.
Employees of subsidiaries responsible for the preparation of data for consolidated financial statements must be fully informed about the rules and procedure for preparing the consolidated financial statements of the group. The main document for them is detailed instructions for filling out the forms on the basis of which this reporting is made. The guidelines should be regularly updated.
First of all, the company's management and all divisions interested in obtaining consolidated information must determine the composition and content of the final forms of such reporting. Usually the company prepares consolidated financial statements in accordance with already established standards (for example, IFRS).
Next, it is necessary to develop data collection forms that will be filled in by subsidiaries and transmitted to the head office on a regular basis. The most practical is the use of the main forms of reporting: balance sheet, profit and loss statement, movement money with adjustments. But this is not enough.
In addition to the data collection forms, it is necessary to develop detailed transcript forms, as well as forms that will contain all additional information that is not available in accounting... These are mainly physical indicators, as well as the necessary data of non-financial divisions of subsidiaries.
The basis for the high-quality preparation of consolidated financial statements is control over the individual statements of subsidiaries submitted to the parent organization. General Consolidation staff should ensure strict control over the correctness of filling out the group reporting forms by subsidiaries. A subsidiary's reporting cannot be considered complete if the company has not reported to its parent organization.
In order to avoid major errors in reports, it seems important to organize automated control of their integrity, putting in the forms filled in by "daughters", algorithms for checks and internal interconnections. An example of such control can be the automatic calculation of the totals of the balance sheet items and their reconciliation with the data of the forms in which the decoding of the balance sheet items is provided.
The implementation of a unified accounting policy is a complex and time consuming process. For large companies that prepare financial statements in accordance with IFRS and have a sufficient number of highly qualified employees both at the head office and in the field, it is possible to use a single detailed Chart of Accounts.
This procedure takes considerable time and in most cases involves the involvement of expensive consultants. However, in large companies, such costs are likely to pay off in the end.
Sometimes subsidiaries do not have the opportunity to apply the methods chosen in the accounting policies for consolidated financial statements. In such cases, it is impractical to unify the accounting policy completely - it is easier to make amendments before consolidation.
Typically, the process of reconciliation of intra-group calculations takes quite a long time and in large groups is one of the most difficult stages of preparing consolidated statements.
An important part of the information used in the process of drawing up consolidated financial statements is information about the composition of the group, about subsidiaries and dependent companies controlled by the parent organization - that is, data about the perimeter of consolidation.
It seems important to develop a system - a register of the group's enterprises, which will provide the ability to store the necessary data for all enterprises without exception. They should include the name, organizational and legal form, share of the parent company, a list of executives and other parameters.
The data in the system should be contained in standard forms defined in advance by all interested users.
One of the tasks of the General Consolidation Department is to interact with the collection and verification of information with other divisions within the company to ensure the basic requirements for consolidated reporting: timing and quality. In addition to the divisions of subsidiaries who directly fill out the group reporting forms, close ties and interaction with the central accounting department, production services, the treasury, the capital construction department, the planning and budget department, the sales department, the internal audit department and other departments should be established.
Preparation of consolidated financial statements is a rather complicated and lengthy process. However, attention to the correct organization of the process, training and education of personnel, as well as to an effective system of internal control can reduce the preparation time and avoid most mistakes.
For the preparation of consolidated consolidated financial statements of a group of related enterprises, the methodological recommendations prescribe the following rules to be applied:
The accounting statements of the parent organization and subsidiaries are combined by line-by-line summing of the relevant data;
Items reflecting the financial investments of the parent organization in the authorized capitals of subsidiaries and, accordingly, in the authorized capitals of subsidiaries in the part belonging to the parent organization are excluded from the consolidated balance sheet;
In the event that the amount of financial investments of the parent company does not coincide with the value of shares, the shares reflected in the balance sheet of the subsidiary company, there is a positive or negative difference, which is reflected in the consolidated balance sheet as a separate item "Business reputation";
Indicators reflecting the consolidated debit and credit debts between the parent company and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries, are excluded from the consolidated statements;
Dividends paid by subsidiaries of the parent organization or other subsidiaries of that parent organization, as well as the parent organization to its subsidiaries, are excluded from the consolidated statements. Consolidated financial statements reflect only dividends payable to organizations and individuals outside the group;
The consolidated reporting excludes proceeds from the sale of products, goods, works, services between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries of one parent organization and the costs attributable to these sales, as well as any other income and expenses, profits and losses arising as a result of transactions between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries of the parent organization;
When combining the accounting statements of the parent organization and the accounting statements of a subsidiary in which the parent organization has more than 50%, but less than 100% of voting shares, shares, indicators reflecting the minority share in the authorized capital are distinguished in the consolidated balance sheet and the consolidated income statement and financial results of the company
In accordance with international standards, consolidated financial statements must meet certain principles and methods, that is, certain requirements.
1) The principle of completeness means that all assets, liabilities, deferred expenses, deferred income of the consolidated group are accepted in full, regardless of the share of the parent company. The minority share is shown in the balance sheet as a separate item under the appropriate heading.
2) The principle of equity capital - since the parent company and subsidiaries are considered as a single economic unit, equity is determined by book value shares of consolidated enterprises, as well as on the financial results of the activities of these enterprises and reserves.
3) The principle of fair and reliable assessment - the consolidated statements must be presented in a clear and easy-to-understand form, and give a true and reliable picture of the assets, liabilities, financial position, profits and losses of the enterprises belonging to the group and considered as a whole.
4) The principle of consistency in the use of consolidation and valuation methods and principles of a going concern suggests that consolidation methods should be applied for a long time, provided that the company is a going concern, i.e. does not intend to terminate its activities in the foreseeable future. Deviations are permissible in exceptional cases, and they must be disclosed in annexes to the statements with appropriate justification. These principles apply to both forms and methods of preparing consolidated financial statements.
5) The principle of materiality provides for the disclosure of such items, the amount of which may affect the adoption or change of the decision on the financial and economic activities of the company.
6) Unified valuation methods - assets, liabilities, deferred expenses, profits and costs of the consolidated company should be taken into account in their entirety. It does not matter how they are presented in the current accounting and reporting of enterprises belonging to the group, since the parent company does not impose bans and does not implement selective accounting approaches. It is important that, when consolidating, the assets and liabilities of the parent company and subsidiaries are valued using the same methodology applied by the parent company. Valuation methods according to the legislation that the parent company complies with should be applied when preparing consolidated financial statements.
7) A single compilation date - consolidated statements should be prepared on the balance sheet date of the parent company. The financial statements of subsidiaries should also be restated at the date of the consolidated financial statements.
Most of the principles discussed above, on which the consolidated financial statements are based in accordance with international standards, are reflected in the Russian regulatory documents governing the preparation of consolidated financial statements. In accordance with the Methodological Recommendations and PBU 4/99, the consolidated financial statements must meet the requirements of reliability, integrity, consistency, comparability, reporting period and registration of financial statements.
3. Practical part
Option 2
STATUS OF ASSETS AND LIABILITIES OF ETALON LLC AS OF DECEMBER 1, 2005 (according to the working chart of accounts)
|
Account number |
Assets and liabilities |
Amount, rub. |
|
|
Fixed assets |
|||
|
Depreciation of fixed assets |
|||
|
Intangible assets |
|||
|
Amortization of intangible assets |
|||
|
Deferred tax assets |
|||
|
Materials |
|||
|
Deviations in the value of material assets |
|||
|
Value added tax (VAT) on purchased inventories |
|||
Main production - totalincluding products A |
33 090 |
||
|
Finished products |
|||
|
Settlement accounts |
|||
|
Financial investments (long-term) |
|||
|
Settlements with suppliers and contractors (credit) |
|||
|
Settlements with buyers and customers (debit) |
|||
|
Calculations on advances received (credit) |
|||
|
Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings |
|||
|
Calculations for taxes and fees - total including: |
|||
|
income tax |
|||
|
personal income tax |
|||
|
Calculations for social insurance and providing - total including: |
|||
|
Social insurance fund |
|||
|
insurance premiums against accidents |
|||
|
Unified social tax, contributions for the insurance and funded parts of labor pension |
|||
|
Federal Mandatory Health Insurance Fund |
|||
|
Territorial Compulsory Health Insurance Fund |
|||
|
Payments to personnel |
|||
|
Settlements with accountable persons (debit) |
|||
|
Settlements with personnel for other operations |
|||
|
Settlements with different debtors |
|||
|
Settlements with different creditors |
|||
|
Deferred tax liabilities |
|||
|
Authorized capital |
|||
|
Reserve capital |
|||
|
Extra capital |
|||
|
Retained earnings (uncovered loss) including: |
|||
|
retained earnings in circulation |
|||
|
retained earnings in use |
|||
|
Cost of sales |
|||
|
General running costs |
|||
|
Business expenses |
|||
|
Profit / loss from sales (profit) |
|||
|
Other income |
|||
|
other expenses |
|||
|
Balance of other income and expenses |
|||
|
Profit and loss |
SALDO AT THE BEGINNING OF THE YEAR AND THE TURNOVER FOR JANUARY-NOVEMBER 2005 BY SYNTHETIC ACCOUNTS (extract from the General Ledger)
|
Account name and code |
Balance at the beginning of the year, rubles |
Turnover for January-November, rubles |
|||
|
Fixed assets (01) |
|||||
|
Depreciation of property, plant and equipment (02) |
|||||
|
Intangible assets (04) |
|||||
|
Amortization of intangible assets (05) ... |
Similar documents
The concept of accounting, the system of regulatory regulation of accounting and reporting in Russia. Varieties and characteristics of Reporting Forms, correctness of filling. Features of drawing up consolidated and consolidated financial statements.
course of lectures added on 06/11/2009
Essence, meaning and types of reporting. Legal regulation of the compilation of consolidated documentation. Description of the activity of LLC "IRIDIUM". Drawing up a consolidated balance sheet. Report about incomes and material losses. Interrelation of forms of financial statements.
term paper, added 03/28/2012
Normative regulation of the formation of reports of an economic entity carrying out trading activities. Purpose, types and composition of financial statements and requirements for it. Basic rules of consolidated financial statements.
test, added 10/04/2009
The essence of financial statements as a unified system of indicators about the property and financial position of the organization, the results of its economic activities. Purpose of consolidated and consolidated statements, modern methods of their formation.
term paper added 01/13/2011
The essence and content of the consolidated (consolidated) reporting. Financial reporting standards for consolidated reporting. Technical and economic characteristics of OJSC "SZ" Lotos ". Formation of accounting indicators at this enterprise.
term paper added 01/14/2008
The concept of "consolidated reporting" and "consolidated reporting". Compilation of consolidated reporting for one owner or for statistical aggregation of data. Preparation of consolidated statements by several owners for joint property.
lecture added on 12/05/2008
Regulatory regulation of financial statements in the Russian Federation. Composition, structure and requirements for financial statements, the procedure for forming indicators. Study of financial statements as a basis for analyzing its indicators.
term paper, added 12/16/2010
The concept and meaning of financial statements. The composition of the financial statements. The procedure for drawing up financial statements. Legal framework for accounting. Requirements for information generated in financial statements. Regulations.
abstract, added 01/13/2009
Requirements, rules and methodological features of drawing up accounting (financial) statements. Drawing up financial statements on the example of Technopark LLC. Analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise. Basic forms of financial statements.
term paper added 02/16/2015
Composition and basic requirements for the preparation of financial statements. Balance sheet: profit and loss statement, capital flow, cash. The procedure for the provision of financial statements and the preparation of consolidated financial statements.
If an organization has subsidiaries and affiliates, in addition to individual financial statements, it must also compile consolidated financial statements, including the indicators of the reports of such companies (clause 91 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 29.07. 1998 No. 34n ((as amended on 12/24/2010 as amended on 09/14/2012))).
Consolidated financial statements is a system of indicators that reflects the financial position at the reporting date and financial results for the reporting period of a group of related organizations (hereinafter referred to as the group), formed in accordance with the Methodological Recommendations.
The consolidated financial statements of the group combine the financial statements of the parent company and its subsidiaries, and also include data on the dependent companies.
In relation to subsidiaries, the parent organization acts as the parent company (partnership), in relation to dependent companies - as the dominant (participating) company.
Financial statements of the subsidiary combined into consolidated financial statements in the cases provided for in clause 1.3 of the Methodological Recommendations. In particular, if:
the parent organization has the ability to determine the decisions made by the subsidiary in accordance with the agreement concluded between the parent organization and the subsidiary;
if the parent organization has other methods of determining the decisions made by the subsidiary.
Data on affiliated companies are included in the consolidated financial statements if the parent organization has more than 20% of the voting shares of a joint stock company or more than 20% of the authorized capital of a limited liability company (clause 1.4 of the Methodological Recommendations).
Financial statements are not combined into consolidated statements in the following cases:
1) Data on a subsidiary or dependent company may not be included in the consolidated financial statements if:
· The parent organization cannot determine the decisions made by the subsidiary.
In this case, the cost estimate of the participation of the parent organization in a subsidiary or dependent company is reflected in the consolidated financial statements in the manner established to reflect financial investments (in the amount of actual costs reflected in the balance sheet of the parent organization). Each such case is subject to disclosure in the notes to the consolidated balance sheet and the consolidated income statement.
2) If the parent organization has the ability to use other methods of determining the decisions made by the subsidiary (dependent) company, data about this company may not be included in the consolidated financial statements, provided the following conditions are met:
· Data on the subsidiary (dependent) company does not have a significant impact on the formation of an understanding of the financial position and financial performance of the group. For example, if the authorized capital of a subsidiary does not exceed 3% of the capital of the group, and in the amount of the capital of other subsidiaries, participation in which is reflected in the consolidated financial statements in the general procedure established to reflect financial investments, - 10% of the capital of the group;
The inclusion of the financial statements of a subsidiary (dependent) company in the consolidated financial statements contradicts the requirement of rationality established by the Regulation on accounting "Accounting policy of the enterprise" (PBU 1/2008). The validity of non-inclusion is confirmed by an independent auditor (audit firm).
In these cases, the cost estimate of the participation of the parent organization in the subsidiary (dependent) company may be reflected in the consolidated financial statements in the manner established to reflect financial investments. Each such case is subject to disclosure in the notes to the consolidated balance sheet and consolidated income statement indicating:
· Full name of the subsidiary (dependent) company;
· Place of state registration and / or place of business;
· The size of the authorized capital, the share of participation in it of the parent organization;
· The share of voting shares (authorized capital) belonging to the parent organization, if it differs from the share of participation;
· Main financial indicators of the subsidiary.
3) A subsidiary, which, in turn, acts as a parent organization in relation to its subsidiaries, may not prepare consolidated financial statements (except for cases when it is registered and / or conducts business outside the Russian Federation) if:
4) The parent organization may not draw up consolidated financial statements if it only has dependent companies (however, this should be disclosed in the notes to the balance sheet and the statement of financial transactions of the parent organization).
5) The Group may not draw up consolidated financial statements in accordance with the rules provided for by regulatory enactments and methodological guidelines for accounting of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
· Consolidated financial statements are compiled on the basis of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), developed by the International Financial Reporting Standards Committee;
· The group has ensured the reliability of the consolidated financial statements prepared on the basis of IFRS;
· An explanatory note to the consolidated financial statements contains a list of applicable accounting requirements, discloses the methods of accounting, including estimates that differ from the rules provided for by regulatory acts and guidelines for accounting of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Basic rules for combining accounting indicators of the parent organization and subsidiaries into consolidated financial statements
1) The consolidated financial statements combine all assets and liabilities, income and expenses of the parent organization and subsidiaries by line-by-line summing up of the relevant data (except for cases not provided for in Methodological Recommendations No. 112).
2) When compiling consolidated financial statements, a single accounting policy in relation to similar items of property and liabilities, income and expenses of the accounting statements of the parent organization and subsidiaries.
3) Consolidated financial statements are prepared for the same reporting period and for the same reporting date.
If the financial statements of any subsidiary (for example, located outside the Russian Federation) are drawn up for the same reporting period, but a different reporting date, then such subsidiary prepares interim financial statements as of the same reporting date as the reporting date of the consolidated financial statements ...
4) For inclusion in the consolidated financial statements, the indicators of the financial statements of the subsidiary, drawn up in foreign currency, are recalculated into the currency of the Russian Federation.
5) When combining the accounting statements of the parent organization and subsidiaries, the consolidated balance sheet does not include:
· Financial investments of the parent organization in the authorized capitals of subsidiaries and, accordingly, authorized capitals of subsidiaries in the part belonging to the parent organization;
Indicators reflecting accounts receivable and accounts payable between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries;
· Profit and loss from transactions between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries;
· Dividends paid by subsidiaries of the parent organization or other subsidiaries of the same parent organization, as well as by the parent organization to its subsidiaries. Consolidated financial statements reflect only dividends payable to organizations and individuals outside the group;
· Part of the assets and liabilities of subsidiaries not related to the activities of the group, when the parent organization has 50% (or less) of the voting shares of the joint stock company or the authorized capital in the limited liability company.
6) When combining the financial statements of the parent organization and subsidiaries, the consolidated income statement does not include:
· Revenue from the sale of products (goods, works, services) between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries of one parent organization, and the costs of this sale;
· Dividends paid by subsidiaries of the parent organization, or other subsidiaries of the same parent organization, as well as by the parent organization to its subsidiaries. The consolidated income statement reflects only dividends payable to organizations and persons outside the group;
· Any other income and expenses arising from transactions between the parent organization and subsidiaries, as well as between subsidiaries of one parent organization;
· The financial result of the activities of subsidiaries in terms of income and expenses not related to the activities of the group, when the parent organization has 50% (or less) of voting shares in a joint-stock company or 50% (or less) of the authorized capital in a limited liability company.
7) When combining the accounting statements of the parent organization and the subsidiary, in which the parent organization has more than 50% but less than 100% of the voting shares of the joint stock company or more than 50% but less than 100% of the authorized capital of the limited liability company, in the consolidated balance sheet and In the profit and loss statement, there are separately calculated indicators reflecting the minority share, respectively, in the authorized capital and financial results of the company.
Thus, the summary (consolidated) financial statements in accordance with Methodological Recommendations No. 112:
1. combines the financial statements of the parent company, subsidiaries, branches, and other dependent companies;
2. reflects the movement of all financial flows (assets, liabilities, income and expenses) of both the parent organization and subsidiaries; this implies a complete settlement of current mutual settlements and financial obligations between the parent organization and subsidiaries (dependent) enterprises;
3. compiled for the same reporting period and for the same reporting date;
4. implies the calculation of all accounting transactions in thousands or millions of rubles (depending on the size of the enterprise) and is drawn up only in Russian;
5. is presented to the founders (participants) of the parent organization and other interested users in cases established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, or by decision of the parent organization;
6. can be published as part of the financial statements of the parent organization (by decision of the group members).
In the event that the consolidated financial statements are compiled on the basis of IFRS, the group may not draw up consolidated financial statements according to the rules provided for in the methodological recommendations, but only if the group ensures the reliability of the consolidated financial statements based on IFRS, and the explanatory note provides a list of requirements accounting statements and disclosed methods of accounting, including estimates that differ from the rules provided for by regulations and guidelines for accounting of the Ministry of Finance of Russia (clause 8 of the Methodological Recommendations).
What is reporting
Reporting types:
- Annual reporting is reporting for a full year. Formed in late December and early January next year. Annual reports include accounting information for a full year.
- Interim reporting is reporting for each quarter throughout the year. For example, interim reporting for the 1st quarter is formed at the beginning of April, after all transactions for the quarter are closed. Reporting for the 2nd quarter is formed at the beginning of July. Reporting for the 3rd quarter is formed at the beginning of October, also after the closing of all transactions for the quarter.
- Internal reporting. Such reports are prepared for the purposes of the organization itself.
- External and pivot and so on.
Let's consider these types of reporting in more detail.
Summary reporting
Features of consolidated financial statements
- Consolidated reporting is compiled for a group of related enterprises, which are necessarily headed by the management of an administrative organization.
- Consolidated reporting has the main goal: to provide holistic results of a group of financial and economic enterprises.
- Consolidated statements should highlight the share of assets and capital of the group that does not belong to the parent organization.
Formation of consolidated reporting
Consolidated reporting is formed in several stages:
Collection of accounting reports.
All child structures must in fixed time submit their reports to the parent organization. The reports must be signed by the head and chief accountant of the subsidiary. There must be a seal of the organization. The reports are provided to the chief accountant of the parent organization. All reports are checked, all amounts and totals are viewed. The chief accountant of the parent organization discusses with the chief accountant of the subsidiary all the points of interest regarding the preparation of reporting.
Registration of the general balance sheet.
At this stage, the general balance sheet is formed. Formation occurs after checking all reports of child structures. Then comes the set of reports and the balance sheet of the parent organization itself. The general balance sheet of the parent organization is compiled by the chief accountant of the parent organization. The report is approved by the head of the parent organization and the chief accountant of the parent organization. Be sure to put the seal of the parent organization on the report.
Deduction of investments in the enterprises of the group and subsidiaries, debts on loans and debits.
Exclusion of profit and loss.
Consolidated financial statements must be correctly drawn up. For incomplete or incorrect information in the financial statements, penalties are provided, as well as criminal liability. The head of the organization and the chief accountant of the organization are responsible for the correctness and completeness of the accounting statements.
Gorepyakina N.V. p. 9 10.3.2017
Topic 5: Consolidated (consolidated) reporting.
The essence and purpose of the consolidated (consolidated) reporting.
Requirements for the preparation of consolidated and consolidated statements and the timing of its preparation.
Composition and procedure for drawing up consolidated reporting.
Features of the consolidation of balance sheets.
The essence and purpose of the consolidated (consolidated) reporting.
Consolidated (consolidated) financial statementsis a system of indicators that reflect the financial position at the reporting date and financial results for the reporting period of a group of related organizations.
Definition consolidated reporting, given in the Methodological Recommendations for the Preparation and Presentation of Consolidated Financial Statements, is close, in fact, to the definition of consolidated financial statements in IFRS. However, it does not specify what specific relationships exist between enterprises. The introduction of this document is an important stage in the development of consolidated reporting in Russia. However, the equalization of the concepts of consolidated and consolidated financial statements, which differ in their content, in our opinion, does not help to identify the remaining differences.
Consolidated financial statements- This is a special type of financial statements, compiled by combining (set) of financial statements of several companies. Currently, there are two types of consolidated financial statements in the Russian Federation:
consolidated financial statements of federal executive bodies (ministries and departments);
consolidated financial statements of a group of related enterprises.
The first type of consolidated reporting- consolidated financial statements of federal executive bodies (ministries and departments). The purpose of the summary report is to provide an opportunity for government bodies to assess the activities of their subordinate ministries and departments.
The second type of consolidated reporting- summary (consolidated) financial statements of a group of related organizations. Consolidated statements are prepared with the aim of presenting independent business entities as a single organization. It is necessary as an information base for managing a complex economic object, which is a controlled association of independent legal entities.
Business companies are united in two main forms:
creation of a legal entity as an association of two or more companies (merger, acquisition, acquisition);
without forming a legal entity, by uniting a group of two or more business entities on the basis of the economic and legal dependence of one on the other (controlled group, concern, holding).
In the first caseconsolidation of financial statements is carried out at the time of consolidation and then prepared as financial statements of one legal entity. In the second- the consolidated reporting of the combined legal entities is reproduced anew and compiled again for each reporting period.
Consolidation methods are determined by investments in shares (shares in capital) of other joint-stock (business) companies, which generates various consequences both for the investor society and for the company that received capital. If an investor invests insignificant funds, not exceeding 20% \u200b\u200bof the capital of the invested company, he can count on future income from his investments. To assess the effectiveness of investments, the investor reflects them in his balance sheet at the actual costs of purchasing securities.
If an investor invests significant funds that allow influencing the decisions made by the subject of investment, the investor society becomes dominant, which changes the approaches to accounting for his investments. The predominant share is recognized to be more than 20%, but less than half of the voting shares. In international practice, the statement of financial results of the dominant company reflects not the amount of dividends received from the dependent company, but the investor's share in the net profit of the dependent company. However, Russian tax legislation does not provide for equity accounting of the net profit of associates. It is necessary to apply the equity method of accounting for net profit as an option for drawing up a consolidated report.
If an investor company invests in the shares of another company funds that allow obtaining more than 50% of voting shares, this company is recognized as a subsidiary, and its financial statements are included in the consolidated statements, which the parent company is obliged to draw up and submit in accordance with Russian and international law.
The consolidated accounting report covers the activities of all organizations (business entities) that are controlled by the main parent company and are included in the scope of its consolidation. Controlled business entities are determined by the fact that the parent company has the right to make decisions on the principles of their financial, industrial and commercial activities, propose and elect the board of directors, other governing bodies of the company, approve the budget, etc. Control of a parent company is deemed to exist when it owns, directly or through its subsidiaries, more than 50% of the voting shares of the joint stock company or more than 50% of the authorized capital of the limited liability company.
Consolidated financial statements reports are not included organizations (societies) included in the scope of consolidation, but not of interest for consolidation. These include:
business entities, control over which is considered temporary;
subsidiaries operating in conditions of long-term insurmountable restrictions that make it impossible for them (or significantly reduce it) to transfer funds to the account of the parent company, for example, due to currency restrictions on foreign accounts;
subsidiaries whose economic activities differ sharply from the nature of the parent company, for example, a bank and an industrial joint-stock company;
subsidiaries with which the main parent company has special agreements restricting the right to determine the structure and composition of the board of directors or other similar management bodies, regardless of the holding of a controlling stake in its shares.
As you know, financial statements can be of different types: annual, interim, internal, external, and so on - depending on the intended purpose, information content and other factors. There is also consolidated accounting reporting, which contains data on subsidiaries.
Basic terms
First of all, let's figure out the basic concepts. The reporting documentation is formed in accordance with the requirements of the legislation to provide regulatory authorities with information on the movement of company funds and the legality of economic actions. But, in addition to this, accounting is an excellent management tool. Since the reports clearly demonstrate which operations bring less income and which are more profitable, they allow us to draw a conclusion about the profitability of maintaining a certain direction and the possible investment of funds in its further development or restructuring.
So, financial statements are a package of documents that gives a complete and reliable picture of the property and economic situation of an enterprise for a certain period (usually the accounting year is taken). Generally, when we say “accounting statements,” we mean the balance sheet (including the explanatory annexes) and the statement of financial results of the company.
Summary documentation
Each organization regularly prepares an annual report for the tax service. If the enterprise is quite large, has subsidiaries, or is a combination of several organizations, the report should also include a report on the activities of each branch. In this case, there should be not a set of reports - separately for each organization - but one consolidated document that will include all the necessary indicators. It is called consolidated accounting.
Such a report covers not only the activities of organizations located on the territory of the Russian Federation, but also information about branches that are located and operate abroad.
Under what circumstances should
As a rule, summary statements are formed in two cases:
- if the parent organization owns more than fifty percent of the shares of a joint stock company or more than fifty percent of the authorized capital of a limited liability company;
- if the parent company has the power to determine the decisions made by the subsidiary.
Two types of statements
Since the consolidated financial statements contain combined data for several branches, it can be of two types:
- data of a group of interconnected enterprises (subsidiaries or dependent organizations);
- statement of federal executive authorities.
In the second case, the financial statements present consolidated documentation separately for unitary companies and separately for joint-stock companies, some of the shares or shares of which are in federal ownership.
Reports are drawn up in four copies (one remains with the organization) and sent immediately to the Ministry of Finance, the Ministry of Economy and the State Statistics Committee. At the same time, the annual reporting for unitary enterprises is submitted no later than the twenty-fifth of April current year, and for joint stock companies - no later than August 1 of the current year.
Creating a financial statement

 It should be noted that the principles of formation of any financial statements, the procedure for their maintenance and execution are described in the federal law "On accounting". It is also worth paying attention to the articles of the Labor, Tax and Civil Codes of the Russian Federation, various instructions and regulations adopted by the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
It should be noted that the principles of formation of any financial statements, the procedure for their maintenance and execution are described in the federal law "On accounting". It is also worth paying attention to the articles of the Labor, Tax and Civil Codes of the Russian Federation, various instructions and regulations adopted by the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
To conduct financial reporting directly for each enterprise, an accounting policy must be formed that takes into account both the norms of legislation and the peculiarities of the company itself: the number of employees, the specifics of production, and so on.
Once adopted, an accounting policy must be recorded in the internal acts of the enterprise and applied rigorously and constantly - this is one of the requirements that the legislation imposes on business representatives in relation to the maintenance of financial documents. Exactly the same requirements apply to consolidated documentation: in the constituent documents of an enterprise or association of organizations on a voluntary basis, an established accounting policy is prescribed, which regulates the procedure for drawing up and submitting financial statements, as well as the timing of its submission, taking into account the norms of the law.
Features of building summary reports
In addition to the requirements for ordinary financial statements, when forming a consolidated report, you must also comply with the norms of the appendix to the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1996 No. 112 "On Methodological Recommendations for the preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements", as well as the requirements of the order of the Ministry of Finance 14.09.2012 No. 126n.
The following requirements are imposed on consolidated reporting:
- the content of information on all assets and liabilities, income and expenses of each subsidiary, as well as the parent organization;
- consistency of assessment methods for each line item for all subsidiaries;
- coincidence of the periods of formation of the reporting of each subsidiary company and the accounting report of the parent company;
- unity of currency (however, according to the requirements of the legislation in terms of accounting, in any case, the national currency of Russia should be used).
In addition, consolidated documentation, in accordance with the principles of accounting, must be complete, reliable, measurable, complete, consistent, neutral, substantial, consistent and rational.
Requirements for documents
Consolidated financial statements of a group of companies are characterized by the following parameters:
- always compiled according to a group of interconnected enterprises, the head of which is necessarily the parent organization;
- pursues the main goal: the provision of the results of financial and economic activities of several enterprises. As a rule, the main users of such information, in addition to regulatory bodies, can be investors;
- since the financial statements characterize the financial and economic position of the group as a whole, the final report not only summarizes the indicators, but also excludes some of them (for example, intra-group calculations and income from transactions between the enterprises of the group);
- the consolidated documentation should highlight the share of the group's assets and capital that does not belong to the parent organization.
Stages of formation of consolidated documents
Since consolidated reporting is a collection of several reports, its formation occurs in several stages.

- investments in the authorized capital of subsidiaries or group companies;
- mutual creditor and receivablesthat will be repaid less than and more than one year after the reporting date;
- intragroup loans, loans and borrowings that will be repaid or received less than or more than one year after the reporting date.
- Exclusion of profit and loss. At this stage, the consolidated financial statements are almost ready, it remains to prepare a consolidated statement of financial results. To do this, the indicators are added up, after which those incomes and losses are deducted from the amounts received, which were formed as a result of business transactions between subsidiaries or enterprises of a group of business operations or between subsidiaries (or enterprises of a group) and the parent organization.
Thus, the final consolidated financial statements will contain only the amounts of profits, losses and dividends of the parent organization, taking into account the activities of the entire group of enterprises.