Firms for the purchase of land. Sale of land: tax costs under the general tax regime and simplified taxation system. Sale of title to land
- Sale of real estate below the cadastral value - tax implications
- Sale of land below cadastral value - consequences
- Real estate sales tax and cadastral value
- Land sales tax: what has changed since 2016
- Clarifications
Sale of real estate below the cadastral value - tax implications For example, such an opportunity is provided by Rosreestr, which enters each site into the register and a public map. There are also more convenient ways: the online service "CTOTAM.PRO" provides any information about real estate and land plots at any time convenient for you.
Sale of land below cadastral value - consequences
Attention
As a result, the sale of an apartment below the cadastral value (CC) will significantly reduce tax burden for the seller This issue should be considered carefully, since apartments that are bought in 2016 will be able to be exempt from tax only in 2021, which is a long time for the real estate market. Selling real estate at cadastral value significantly affects the tax base that the seller must cover.
Info
On one transaction in Moscow, the difference in taxes can exceed 100 thousand rubles. The Cadastre and Registration Center "Star-Service" offers several legal and legal ways to minimize taxes when selling real estate. The cadastral value tax is calculated when selling apartments, rooms and houses.
But this rule does not always apply.
Is it possible to sell a land plot below the cadastral value
Important
It should be remembered that the overpaid amount of tax for previous years is not refundable, so it is important not to delay challenging the cadastral valuation. If you are sure that the cadastral value of your site was overstated, you have documents confirming this and you want to save your money on paying taxes, you should contact special organizations that represent interests in disputes over cadastral value.
Specialists of such firms will deal with paperwork and help you win the case. Results In conclusion, we can say that any games with the state are fraught with trouble.
Tax evasion will sooner or later be revealed, and the negligent taxpayer will have to pay all the arrears, along with fines and penalties. It is possible to reduce the personal income tax tax by legal means, for this it is worth consulting with specialized law firms.
Is it possible to sell land below the cadastral value
For example, this opportunity is provided by Rosreestr, which enters each site into the register and a public map. A certificate of value for the inventory is issued within 5 days.
There are also more convenient ways: the online service "CTOTAM.PRO" provides any information about real estate and land plots at any time convenient for you. It is enough to follow the link https://kadastr.ktotam.pro/ and enter the address of the object and its cadastral number. You will receive an answer in a few minutes. How is property sales tax calculated? If the owner sells a plot or real estate, he is obliged to pay income tax (personal income tax). Earlier, unscrupulous sellers tried to avoid the tax burden and indicated insignificant amounts in contracts.
Taxes from the sale of a land plot below the cadastral value
Important It is enough to follow the link https://kadastr.ktotam.pro/ and enter the address of the object and its cadastral number. You will receive an answer in a few minutes. How is property sales tax calculated? If the owner sells a plot or real estate, he is obliged to pay income tax (personal income tax). Previously, unscrupulous sellers tried to avoid the tax burden and indicated insignificant amounts in contracts. Sale of land below the cadastral value - consequences Standard deduction of RUB 1 million) If the property was purchased after January 1, 2016 If you purchased property after January 1, 2016 and sell it, then your taxable income depends on whether the specified in the contract is the value is higher than 70% of the cadastral value.
Sale of land plots by an entrepreneur below their cadastral value
If you try to sell an apartment below the cadastral value, then such a deal may attract the attention of the tax police. If tax fraud is revealed, they will have to be paid in full, together with penalties.
Risk tax audit increases if the purchase of real estate is made using borrowed funds from the bank. In this case, after studying the loan agreement, tax inspectors will be able to determine the cadastral and market price of the object for calculating income tax. Thus, we can say that the sale of real estate below the cadastral value is actually impossible and unprofitable, since the tax office will still calculate personal income tax at a rate of 70% of the cadastral value. However, there are legal ways to reduce your tax burden after you sell your property.
Sell \u200b\u200ba plot for a price below the cadastral value
Go back to Cadastral value 2018In tax legislation Russian Federation significant changes were made regarding the taxation of transactions for the sale of real estate and land plots. Now the amount of the tax levy depends on the cadastral value of the land.
In connection with the changes, real estate owners have a lot of questions, the most popular of which is whether it is possible to sell land and real estate below the cadastral value. Let's consider this moment in detail. The cadastral value is the amount of land valuation carried out by certified organizations.
The cost of the cadastre depends on several factors at once: the type and purpose of the land, the availability of social infrastructure, the area of \u200b\u200bthe site, its location, the number of sites in a certain area.
Real estate sales below cadastral value - tax implications
Since 2016, significant changes have been made to the tax legislation of the Russian Federation concerning the taxation of transactions for the sale of real estate and land plots. Now the amount of the tax levy depends on the cadastral value of the land.
In connection with the changes, real estate owners have a lot of questions, the most popular of which is whether it is possible to sell land and real estate below the cadastral value. Let's consider this moment in detail. Content:
- Cadastral value: calculation method
- How is property sales tax calculated?
- Sale of real estate and land below the cadastral value
- Legal ways to reduce personal income tax
- Outcome
Cadastral value: method of calculation The cadastral value is the amount of land valuation carried out by certified organizations.
If tax fraud is revealed, they will have to be paid in full, together with penalties. The risk of a tax audit increases if the purchase of real estate is made using borrowed funds from the bank.
In this case, after studying the loan agreement, tax inspectors will be able to determine the cadastral and market price of the object for calculating income tax. Thus, we can say that the sale of real estate below the cadastral value is actually impossible and unprofitable, since the tax office will still calculate personal income tax at a rate of 70% of the cadastral value. However, there are legal ways to reduce your tax burden after you sell your property.
The organization sells a land plot below the cadastral value
Regions have the right to set their own deadline for owning property to exempt it from taxes, as well as use their coefficient from the cadastral value to calculate personal income tax. These values \u200b\u200bcan be reduced down to zero. Selling land below the cadastral value is theoretically possible. The state does not restrict owners in setting the price when selling their own property, and the amount in the purchase and sale agreement can be set any. But the state requires strict observance of certain rules, including the payment of income tax. individuals in full. Changes in Tax Code establish minimum amounttaxed at 70% of the cadastral value of the property. If you try to sell an apartment below the cadastral value, then such a deal may attract the attention of the tax police.
The company "Invest-Real Estate" has an extensive database of land plots offers. Among them are lands that can be used for the placement of businesses - warehouses, factories, service workshops, etc. When choosing a site for a business, you first need to establish the main search criteria. Determine the search area: in the city or in the countryside. The price of land depends on this. For some types of plots for commercial development, the choice of location will be decisive, in other cases, the availability of communications or the price. If land for business is required, it is necessary to take into account its purpose and the type of permitted use.
Under certain conditions, the category of permitted use of the site can be changed in accordance with current legislation. When choosing the location of the site, take into account the nature of the business for which it is intended. A supermarket will require land in a city, an area with a high population density, with good transport accessibility.
For a car service workshop or car wash, sites close to highways are convenient. If it is planned to build a gas station, the best would be a site with a convenient access to it, located near a large road junction, near a car service company or a parking lot. This takes into account the hazard category of the enterprise and the possibility of meeting the requirements for distance from the nearest buildings, etc. When choosing land for a warehouse, take into account its purpose. If it is a finished goods warehouse or a wholesale warehouse for a commercial enterprise, you will need to place it near the serviced facility. An important selection criterion is also the presence or possibility of supplying communications, their characteristics. It is necessary to find out the need for the enterprise of electric power, water, etc. A land plot for business can be purchased as property or a long-term lease agreement can be drawn up for it. Thus, the choice of land for business and registration of property rights and other documents on it is a difficult task, it will be necessary to take into account many nuances.
Invest-Nedvizhimost specialists have extensive experience in real estate in the region, and are able to assist in choosing the most suitable site for a particular enterprise. With our help, the choice of land for business will be done correctly from the point of view of optimal costs and development prospects of the enterprise.
If an organization sells a land plot, it should be guided by the rules established in paragraph 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It should be borne in mind that these rules apply only to those land plots acquired from state or municipal property, on which, at the time of their purchase, buildings, structures, structures of the taxpayer were already located or that were purchased for capital construction of fixed assets on them. In addition, contracts for the acquisition of the specified land plots by the taxpayer must be concluded in the period from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2011. The basis is clause 5 of article 5 of the Federal Law of December 30, 2006 No. 268-FZ.
If an organization sells a land plot, it should be guided by the rules established in paragraph 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It should be borne in mind that these rules apply only to those land plots acquired from state or municipal property, on which, at the time of their purchase, buildings, structures, structures of the taxpayer were already located or that were purchased for capital construction of fixed assets on them. In addition, contracts for the acquisition of the specified land plots by the taxpayer must be concluded between January 1, 2007 and December 31, 2011. The basis is clause 5 of Article 5 of the Federal Law dated 30.12.2006 No. 268-FZ.
Let's say a company sells land plotwhich she acquired before 2007 or which was purchased from a Russian or foreign commercial organization either from an individual. In such circumstances, the seller company is not entitled to be guided by the provisions of clause 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The profit or loss from a land sale transaction should be determined in accordance with article 268 of the Tax Code.
Please note: transactions for the sale of land plots (shares in them) are not subject to VAT. This is indicated in subparagraph 6 of paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Sale of a land plot acquired from the state (municipality) in 2007 or later
If an organization sells a land plot, the contract for the purchase of which from state or municipal property it entered into in 2007 or later, the result from its implementation for tax purposes should be calculated in the manner prescribed in paragraph 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the profit (loss) from the sale of the right to the land plot and the profit (loss) from the sale of buildings (structures, structures) located on it are calculated separately.
Sale of title to land
Profit (loss) from the sale of the right to a land plot is determined as the difference between the price of its sale and the costs of acquiring the right to this plot, not reimbursed to the taxpayer. Unreimbursed costs are understood as the difference between the costs incurred by the taxpayer in connection with the acquisition of the right to a land plot and the amount of expenses accounted for by him for tax purposes until the moment the right to the land plot is exercised (subparagraph 2, clause 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It turns out that the seller of the land plot has the right to reduce the income from the sale by the amount of expenses for its acquisition, which he did not manage to write off in reducing the tax base for income tax during the period of using this land plot.
So, profit or loss from a transaction for the sale of the right to a land plot is calculated using the formula:
Pr (Ub) \u003d C realiz - (P total - P recognized),
where Pr is the profit from the transaction for the realization of the right to the land plot;
Ub - loss from a transaction on the implementation of the right to a land plot;
C realiz - the price of realizing the right to a land plot;
R total - the total amount of expenses associated with the acquisition of the right to a land plot;
Р recognized - the amount of expenses for the acquisition of the right to a land plot recognized for tax purposes until the moment the right to a land plot is exercised.
Does the organization have the right in the month in which it sold the land plot to include in other expenses the next part of the cost of acquiring this land plot, which is written off monthly in tax accounting?
The Tax Code does not contain an answer to this question. However, after analyzing the norms of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation concerning the recognition in tax accounting of expenses in the form of depreciation amounts, we come to the conclusion that in the month of sale of a land plot, the monthly amount of expenses for its acquisition should not be included in expenses and taken into account for tax purposes. The fact is that depreciation on objects of depreciable property is charged starting from the 1st day of the month, following the month in which this facility was put into operation (Clause 4 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the event of the sale of depreciable property, depreciation ceases from the 1st day of the month, next month him sales (Clause 5 of Article 259.1 and Clause 8 of Article 259.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The above rules apply when using both linear and non-linear depreciation methods.
In other words, in the month in which an object of depreciable property is accepted for accounting and put into operation, the amount of depreciation for such an object cannot yet be recognized for tax purposes. However, in the month of sale of the depreciable property, the organization still has the right to record the amount of depreciation accrued on this property for that month. It turns out that expenses in the form of depreciation amounts are recognized with a shift (deferral) by one month.
At the same time, the cost of acquiring land rights reduces taxable profit immediately from the moment of submitting documents for state registration rights to a land plot regardless of its commissioning (sub-clause 2, clause 3, article 264.1 of the RF Tax Code). This means that, by analogy, taking into account the depreciation amounts in the month of sale of the land plot, the amount of expenses for its acquisition, written off monthly, should no longer be included in expenses.
Example 1
LLC "Interchem" on 23 July 2010 sold for 4,000,000 rubles. the land plot, which it acquired in 2008 from the municipal executive authorities for the construction of a new production workshop. The total cost of acquiring the right to a land plot amounted to 1,680,000 rubles. The organization has written off these expenses in tax accounting since October 2008 (since the documents for state registration of ownership of the land plot were submitted to the territorial body of Rosreestr on October 14, 2008). The term for writing off the costs of acquiring the right to a land plot established in the organization's accounting policy for tax purposes is 5 years (60 months).
Since October 2008, LLC Interchem has included in expenses that reduce taxable profit each month 28,000 rubles. (RUB 1,680,000 ÷ 60 months). 21 months have passed since the beginning of the write-off of these expenses until the month preceding the date of sale of the land plot (from October 2008 to June 2010). For the specified period, the organization recognized 588,000 rubles in other expenses. (28,000 rubles × 21 months).
Thus, by the time of the sale of the land plot (by July 2010), the amount of unreimbursed expenses related to the acquisition of the right to land amounted to 1,092,000 rubles. (RUB 1,680,000 - RUB 588,000). Profit from the sale of the land plot is 2,908,000 rubles. (4,000,000 rubles - 1,092,000 rubles). The organization takes this amount into account when forming the tax base for income tax for the nine months of 2010.
Sale of objects located on the land
Profit (loss) from the sale of buildings (structures, structures) located on the land plot and sold together with it is determined in the general procedure provided for the sale of property (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Buildings, structures and structures are depreciable property (clause 1 of article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, in the event of the sale of a land plot together with them, the selling organization reduces the income received by the residual value of this property, as well as by the amount of expenses directly related to the sale of these objects (subparagraph 1 of clause 1 of article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the residual value of the sold building (structure, structure), taking into account the costs of its sale, exceeds the amount of proceeds from the sale, the difference between these values \u200b\u200bis recognized as a loss of the taxpayer. The resulting loss is accounted for for tax purposes in a special procedure established in paragraph 3 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The loss is included in other expenses in equal installments over the period determined as the difference between the period useful use buildings (structures, structures) and the actual life of its operation until the moment of sale.
Expert opinion
O. A. Kurbangaleeva, expert of the Russian Tax Courier magazine:
"In tax accounting, the monthly share of expenses for the acquisition of a land plot is included in the composition of other expenses of the organization starting from the month in which the documents on the transfer of ownership of this plot to it were submitted for state registration (subparagraph 2, clause 3 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation The write-off of these expenses is terminated in the month preceding the month of the sale of the land plot.In the month in which the documents for state registration of the new owner's ownership of the land plot are submitted, the seller organization is not entitled to include in other expenses the next part of the costs associated with its acquisition.
However, in the event of a sale of a land plot with a loss in the month of its sale, the seller may recognize the corresponding part of the loss for tax purposes. The basis is subparagraph 3 of paragraph 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Let me explain this with an example. Let's say in July 2009 the organization acquired for 12 million rubles. land plot previously in municipal ownership. In the same month, the documents necessary to register the transfer of ownership of the land plot were submitted, which is confirmed by a receipt for receipt of documents issued by the registration authority. But already in July 2010, the organization had to sell this site twice cheaper - for 6 million rubles. According to the accounting policy, the organization recognizes the costs of acquiring the right to land plots in tax accounting evenly over 10 years. Therefore, starting from July 2009 (the month of filing documents for state registration) to June 2010 (the month preceding the month of the sale of the site), the company monthly included in other expenses 100,000 rubles. (12 million rubles ÷ 10 years ÷ 12 months). In the month of the sale of the land plot - in July 2010, the organization was no longer entitled to reflect the same amount in expenses.
In total, during the ownership of the land plot, the organization recognized 1.2 million rubles in other expenses. (100,000 rubles × 12 months). This means that the amount of unreimbursed costs (the difference between the total cost of acquiring a land plot and the amount of expenses accounted for for tax purposes prior to the sale) amounted to 10.8 million rubles. (12 million - 1.2 million rubles). That is, as a result of the sale of the land plot in the tax records of the seller, a loss of 4.8 million rubles was formed. (10.8 million rubles - 6 million rubles). The amount of the resulting loss will be recognized by the organization for tax purposes in equal shares over 10 years (the period for writing off the costs of acquiring the land plot established by it in the accounting policy). Monthly it will be able to include 40,000 rubles in other expenses. (4.8 million rubles ÷ 10 years ÷ 12 months). Thus, in July 2010 the company has the right to recognize in expenses only part of the loss in the amount of 40,000 rubles. "
If, as a result of the sale of the land plot, a loss is received
Let's say the amount of unreimbursed costs of the taxpayer related to the acquisition of the right to a land plot exceeded the selling price. In this case, it is considered that the seller of the land plot received a loss. However, he cannot recognize the amount of the loss at a time for tax purposes. In subparagraph 3 of paragraph 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is indicated that the loss from the exercise of the right to a land plot is included in the composition of other expenses of the taxpayer in equal shares within a certain period.
Unfortunately, from a literal reading of subparagraph 3 of paragraph 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is difficult to understand how to calculate this period. The Ministry of Finance of Russia in letters dated 08.05.07 No. 03-03-05 / 111 and dated 31.10.07 No. 03-03-06 / 1/752 explained that the calculation rules this period depend on the procedure chosen by the taxpayer for recognizing the costs associated with the acquisition of land. Recall that the selected procedure for writing off these expenses must be fixed in the accounting policy applied for tax purposes (paragraph 2, sub. 1, clause 3, article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Option one - in tax accounting, the organization recognizes the costs of acquiring land plots evenly within a period set by her independently. Such a period cannot be less than five years (paragraph 1 of sub. 1 of item 3 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If an organization has received a loss from the sale of a land plot, then the period during which it will have to write off the amount of this loss on a straight-line basis in reducing the tax base is taken equal to the period established by it for recognizing the costs of acquiring a land plot.
Please note: the seller includes the specified loss in equal shares in other expenses starting from the reporting (tax) period in which he received this loss. This is the position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, cited in the letter dated 31.10.07 No. 03-03-06 / 1/752.
Example 2
Let's use the condition of example 1. Suppose LLC "Interchem" was forced to sell a land plot for 1,000,000 rubles.
Since the amount of unreimbursed expenses related to the acquisition of the right to land (1,092,000 rubles) exceeded the selling price of the land plot, as a result of this transaction the organization received a loss. The amount of the loss was RUR 92,000. (1,092,000 rubles - 1,000,000 rubles).
According to the accounting policy, LLC Interkhim planned to recognize the costs associated with the acquisition of the land plot within 5 years (60 months). Therefore, during the same period, it will include in equal shares in other expenses the loss received from the sale of land. The organization will be able to write off 1,533.33 rubles per month. (92,000 rubles ÷ 60 months). That is, by the end of 2010, the company will take into account other expenses 9199.98 rubles. (1,533.33 rubles × 6 months). The organization will complete the write-off of the entire amount of the loss received in July 2010 from the sale of the land plot only in June 2015.
note
If all expenses have already been written off
A situation is possible when, by the time of the sale of a land plot, all expenses associated with its acquisition have already been completely written off in tax accounting. This is typical primarily for organizations that have chosen the method of writing off these expenses based on the tax base of the previous tax period. Indeed, if in the year preceding the year of acquisition of the land plot, the company had a high profit, it may well recognize for tax purposes the entire amount of expenses for acquiring the land plot immediately in the year of its purchase (of course, if the profit is so high that even the cost of the land plot is less than 30% of it).
Another example is an organization that has written off the costs of acquiring a land plot evenly over five years, sells it after a five-year tenure period (for example, 6 or 10 years after the acquisition of the land plot and submission of documents for state registration of ownership of it).
Under these circumstances, the seller has no unrecovered costs associated with the purchase of land. After all, all costs associated with the acquisition of a land plot have already been taken into account for tax purposes. Therefore, in tax accounting, the selling organization is not entitled to reduce the selling price for any expenses. This means that from the entire amount received from the sale of the land plot, the organization is obliged to pay income tax
Option two - for tax purposes, the organization recognizes the costs associated with the acquisition of land plots in the amount of a certain percentage of the tax base for income tax of the previous tax period. The specific percentage of write-off (no more than 30%) is set by the taxpayer independently in the accounting policy for tax purposes (paragraphs 1 and 2 of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Ministry of Finance of Russia clarified that when choosing this option for recognizing the costs of acquiring land, the loss received from the sale of a land plot is written off evenly over the period of actual ownership of this land plot. To write off a loss in tax accounting starts from the reporting (tax) period in which it was received.
How to determine the period of actual ownership of a land plot? Land plots are immovable property, and therefore the transfer of ownership of them is subject to state registration with the territorial authority of Rosreestr (clause 1 of article 130, clause 1 of article 551 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and clause 1 of article 25 of the Land Code). Thus, the period of actual ownership of a land plot should be determined on the basis of certificates of state registration of rights issued by the territorial body of Rosreestr. This period is calculated from the date of state registration of ownership of land and ends at the time of transfer of ownership to the new owner (buyer of the land plot).
State registration of rights to real estate is carried out no later than one month from the date of receipt of the documents required for registration. This is established in paragraph 3 of Article 13 of the Federal Law of 21.07.97 No. 122-FZ "On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it." As a rule, the date of submission of documents to the registering authorities and the date of state registration of ownership of a land plot fall on different months. In the event of such a discrepancy, the month in which the documents were submitted for state registration when purchasing a land plot is not included in the period of actual ownership of the plot used to write off the amount of loss. And, conversely, the month of submission of documents for state registration during the subsequent sale of this land plot is taken into account by the seller organization in the time of actual ownership of the plot.
Example 3
In April 2009, Business Center LLC acquired for 5,300,000 rubles. a land plot that was in municipal ownership for the construction of a shopping and office center on it. In the same month, documents were submitted for state registration of ownership of the land plot. The ownership right of LLC Business Center to the site was registered on May 15, 2009, which is confirmed by the corresponding certificate. In the accounting policy, the organization has established that for tax purposes, it recognizes the costs of acquiring the right to land plots at 25% of the tax base of the previous tax period. However, in June 2010 the company was forced to sell this land plot for 3,000,000 rubles. The ownership right of the new owner to the land plot was registered on July 16, 2010, and in the same month the land plot was transferred to the new owner under the acceptance certificate. In 2009, the organization included in expenses that reduce taxable profit the cost of purchasing a land plot in the amount of RUB 125,000, and in 2010 - RUB 75,000.
The amount of unreimbursed costs associated with the acquisition of a land plot is 5,100,000 rubles. (5,300,000 rubles - 125,000 rubles - 75,000 rubles). This means that the loss from the sale of the land plot amounted to 2,100,000 rubles. (5,100,000 rubles - 3,000,000 rubles).
By the time the ownership of the land plot was transferred to the new owner, Business Center LLC owned the land plot for 15 months (from May 2009 to July 2010). Consequently, over the same period, the organization will write off the loss it received as a result of the sale of the land plot in equal shares. Every month, starting from July 2010 (the month of the actual transfer of the site to the new owner), the company includes 140,000 rubles in other expenses. (RUB 2,100,000 ÷ 15 months). Thus, until the end of 2010, she recognizes in expenses 840,000 rubles. (140,000 rubles × 6 months). The amount of the loss that remained not written off at the end of 2010 - 1,260,000 rubles. (2,100,000 rubles - 840,000 rubles), the organization will be able to fully take into account the expenses already for the first nine months of 2011.
Expert opinion
E.S. Romanchuk, expert of the magazine "Russian Tax Courier":
"Let's say in February 2010 an organization sold a land plot that it acquired in December last year. That is, the site was in its ownership for only three months - one month in 2009 and two months in 2010. The organization's accounting policy established that expenses for the acquisition of land plots are recognized for tax purposes in the amount of 30% of the tax base of the previous tax period. in tax accounting to determine the result of a transaction for the sale of a land plot?
First of all, it is necessary to calculate the amount of expenses for the acquisition of a plot that were not reimbursed by the time of its sale. Obviously, in the situation described, this is what raises the most questions. The problem is that Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not stipulate at what point it is possible to recognize the costs of acquiring land when choosing the specified method of writing them off (as a percentage of the tax base for income tax previous year). At the same time, in article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation there is no requirement for equal recognition of expenses when using this method. Therefore, we can conclude that costs should be reflected regardless of the number of months during which the organization actually owned the land in the calendar year.
The correctness of this conclusion is also confirmed by the fact that the norms of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provide taxpayers with the right to independently determine the procedure for recognizing the costs of acquiring land and fix it in the accounting policy for tax purposes. So, the organization has the right to indicate the following in the accounting policy. In the year in which the land plot was purchased, the corresponding part of the expenses is taken into account for tax purposes in the month of submission of documents for state registration of the right to the land plot. In subsequent years, part of the cost of acquiring a land plot relating to the current tax period is included in expenses at a lump sum on the last day of the first month of that year (that is, January 31).
Let's return to the calculation of the result from the transaction for the sale of a land plot that was owned by the owner for only three months. In the presence of the above formulations in the accounting policy, the organization was entitled in December 2009 to take into account for tax purposes the entire amount of expenses allowed for recognition for that year (that is, 30% of the tax base for 2008). In January 2010, the company could include in expenses an amount equal to 30% of the 2009 taxable profit. To calculate this amount, the tax base calculated for 2009 should have been increased by the amount of expenses for the acquisition of a land plot recognized in December this year (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of article 264.1 of the RF Tax Code).
The difference between the cost of acquiring a land plot and the amount of expenses recorded by the organization in December 2009 and January 2010 is its unrecovered costs. By reducing the selling price of the plot by the amount of unreimbursed costs, the company will determine the result of this transaction - profit or loss. Income tax must be paid on the entire amount of the profit received. If a loss is incurred, it cannot be recognized at a time for tax purposes. The amount of loss from the sale of a land plot must be included in other expenses in equal shares during the actual period of ownership of this land plot (in our case, within three months). That is, the organization had the right to recognize the entire amount of the loss (if, of course, the site was sold at a loss) directly in 2010 - in the period from February to April inclusive.
Let me give you another interesting example. Suppose an organization purchased a land plot in July 2010 for 20 million rubles. and already in August sold it for only 4 million rubles. Based on taxable income for 2009, in July current year she included 6 million rubles in expenses. Thus, by the time of the sale of the land plot, the unreimbursed costs amounted to RUB 14 million. (20 million rubles - 6 million rubles). That is, the amount of the loss from the transaction is 10 million rubles. (14 million rubles - 4 million rubles). Since the site was owned by the seller for only one month, he has the right to take into account the entire amount of the loss in the amount of 10 million rubles. already in August 2010 "
Reflection in the income tax return
In the income tax return, the results from the sale of land plots are reflected in Appendix No. 3 to sheet 02. Recall that this appendix is \u200b\u200bintended for calculating the amount of expenses on operations, the financial results of which are taken into account when taxing profits in a special manner.
So, if an organization recognizes the costs associated with the sale of a land plot, in accordance with the rules established in paragraph 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in Appendix No. 3 to sheet 02 of the declaration, it fills in lines 240-260. They indicate:
- in line 240 - the selling price of the land plot;
- line 250 - the amount of unreimbursed costs associated with the acquisition of this land plot;
- line 260 - loss from the sale of a land plot (the amount of loss is determined separately for each sold land plot).
In case of receiving profit from the sale of a land plot, line 260 is not filled in, and the amount of profit in Appendix No. 3 to sheet 02 is not separately reflected.
The amount of loss from the sale of a land plot, which the organization in the current reporting (tax) period includes in other expenses on the basis of subparagraph 3 of paragraph 5 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is indicated in line 110 of Appendix No. 2 to sheet 02 of the declaration.
Sale of a land plot acquired before 2007 or purchased from outside the state (municipality)
Once again, we note that the effect of clause 5 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which sets out the procedure for calculating profit (loss) from the sale of a land plot and the rules for writing off such a loss, does not apply to all cases of sale of land plots by legal entities. So, an organization is not obliged to apply the norms of the named paragraph if it sells a land plot that was acquired:
- from the state or municipality before 2007;
- another Russian or foreign commercial organization or from an individual (regardless of the year of purchase);
- state or municipality in 2007 or later, provided that at the time of acquisition, there were no buildings (buildings, structures, structures) owned by the taxpayer on the land plot, and capital construction of fixed assets was not originally planned or actually carried out on it (for example , land plots with targeted use for agricultural purposes).
For profit tax purposes, the sale of land plots in the above situations is regarded as the sale of other property. Consequently, the profit (loss) from the sale of such plots is determined on the basis of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It states that the seller has the right to reduce the income received from the sale of other property by the purchase price. Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04.03.10 No. 03-03-06 / 1/111. This letter examines the situation with the sale of an agricultural land plot, the intended use of which did not imply capital construction. The possibility of reducing income from the sale of a land plot purchased earlier from a commercial organization or an individual by the purchase price of this plot is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 22, 2010 No. 03-03-06 / 1/282.
Unlike the sale of land acquired from the state (municipality) in 2007 or later, when determining the profit (loss) from the sale of other property, the income received can be reduced by the whole amount of expensesassociated with the acquisition of the site, and not just the amount of unreimbursed costs. Indeed, from the moment of the purchase of the site until its sale, the organization did not take into account the costs associated with its acquisition for tax purposes (clause 1 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The opportunity to recognize these expenses appears only in the event of the subsequent sale of such a land plot.
In addition, the seller of a land plot that does not meet the requirements of clause 1 of Article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has the right to reduce the income from the sale of this plot by the amount of expenses directly related to its sale (for example, expenses for assessing a land plot). This is indicated in paragraph 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the purchase price of the land plot, taking into account the costs associated with its sale, exceeds the proceeds from its sale, the excess is recognized as a loss. Such a loss is accounted for for profit tax purposes at a time in the reporting (tax) period in which it was received. The basis is clause 2 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example 4
In 2006, LLC Aspect acquired a land plot from an individual entrepreneur A.N. Karapetyan for 5,200,000 rubles. In July 2010, the organization sold this site to ZAO Stroykompleks for 6,600,000 rubles. Before putting the plot up for sale, Aspect LLC invited an independent appraiser. The cost of his services for assessing the market value of the land was 259,600 rubles. (including VAT RUB 39,600).
Since the land plot was purchased from an individual, LLC Aspect did not take into account the costs associated with its acquisition when calculating income tax in 2006-2010. In July 2010, when the organization sold the land plot, it included 6,600,000 rubles in income. In the expenses, the selling company took into account the acquisition cost of the land plot and the cost of its assessment, that is, 5,420,000 rubles. (5,200,000 rubles + 259,600 rubles - 39,600 rubles). Thus, the profit from the sale of the land plot, recognized in tax accounting, amounted to 1,180,000 rubles. (6,600,000 rubles - 5,420,000 rubles)
Sale of land plots by organizations under the general taxation regime
In accordance with paragraphs. 6 p. 2 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, proceeds from the sale of land plots (shares in them) are not recognized as an object of taxation as value added tax.
Income tax
Determination procedure financial result on the sale of land plots depends on who owned the land at the time of its acquisition: in state or municipal ownership, or in the ownership of individuals (organizations and citizens), and on when the land was acquired.
If the land plot was purchased from the state (municipality) in the period from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2011, the profit (loss) from the sale is determined in accordance with the procedure established by paragraph 5 of Art. 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the land was purchased before or after the specified period or purchased from a private owner, profit or loss is determined in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
1. If the land plot was purchased in the period from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2011 from the executive authorities or local self-government bodies that are authorized to dispose of it.
In Art. 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation established a special rule for accounting for the costs of acquiring land plots for taxpayers who acquired land plots in the period from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2011 from lands that are in state or municipal ownership, on which buildings, structures, structures or that are acquired for the purposes of capital construction of fixed assets on these sites.
So, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 p. 3 art. 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, at the choice of the taxpayer, the amount of expenses for acquiring the right to land plots:
1) is recognized as expenses of the reporting (tax) period evenly over a period that is determined by the taxpayer independently and must not be less than five years;
2) is recognized as expenses of the reporting (tax) period in an amount not exceeding 30% calculated in accordance with Art. 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation of the tax base of the previous tax period, until the full recognition of the entire amount of these expenses.
In the event that the contract for the sale and purchase of a land plot stipulates a condition for payment in installments and at the same time the payment term under the contract exceeds the period during which the organization recognizes the costs of acquiring a land plot in accordance with accounting policies - costs should be distributed evenly during the period stipulated by the contract (paragraph 4 of clause 1 of paragraph 3 of article 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In paragraph 5 of Art. 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the procedure for determining profit (loss) when selling these land plots. Thus, the profit (loss) from the sale of the right to a land plot is determined as the difference between the selling price and the costs not reimbursed to the taxpayer associated with the acquisition of the right to this plot. Unreimbursed costs mean the difference between the costs of the taxpayer to acquire the right to a land plot and the amount of expenses accounted for for tax purposes until the moment the said right is exercised in the manner prescribed by Art. 264.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If a loss is incurred during the exercise of the right to a land plot, it is included in the taxpayer's other expenses in equal shares during the period established in accordance with paragraphs. 1 p. 3 art. 264 .1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and the actual period of ownership of this site.
2. If the land plot was purchased before January 1, 2007, or after December 31, 2011, either from organizations or individuals.
Until the moment of its subsequent sale, this land plot in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not subject to depreciation.
Considering that, according to paragraph 2 of Art. 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, property in the Tax Code means the types of objects of civil rights (with the exception of property rights) related to property in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, and taking into account that Art. 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, land plots are classified as immovable things (real estate, real estate), land plots for tax purposes are classified as property.
According to paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when selling other property (except for securities, products of its own production, purchased goods), has the right to reduce income from such an operation by the purchase (creation) price of this property, as well as by the amount of expenses specified in para. 2 p. 2 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When selling property and (or) property rights specified in Art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer also has the right to reduce income from such operations by the amount of expenses directly related to such sales, in particular, expenses for the assessment and maintenance of the property being sold.
Thus, the taxpayer has the right to take into account the cost of a land plot acquired from organizations or individuals in expenses for the purposes of taxation of profits during its sale (this position is confirmed by the joint Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation of 07.06.2012 N ED-4-3 / 9380 @ and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of May 28, 2012 N 03-03-10 / 57 and the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 08.30.2012 N 03-03-06 / 1/443).
Despite the fact that paragraph 2 of Art. 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is established that if the purchase price of the property specified in particular in subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of this article, taking into account the costs associated with its sale, exceeds the proceeds from its sale, the difference between these values \u200b\u200bis recognized as a taxpayer's loss, taken into account for the purposes of taxation, tax authorities in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 09.07.2010. ShS-37-3 / 6383 @ explain that the loss received from the sale of land plots of this category is accounted for in accordance with Art. 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, it is transferred to the future for ten years following that tax periodin which this loss was received.
Sale of land plots by organizations using the simplified tax system
The costs of acquiring a land plot cannot be taken into account by organizations using the simplified tax system as the cost of acquiring fixed assets, since land plots for the purposes of Ch. 26.2 "Simplified taxation system" of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not apply to fixed assets.
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, only those that are recognized as depreciable property in accordance with Ch. 25 "Tax on the profit of organizations" of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and according to clause 2 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, land is not subject to depreciation.
It should be noted that chapter 26.2. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a direct answer to the question of whether the initial cost of the land plots sold is taken into account as expenses.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in its Letter dated February 28, 2013 N 03-11-06 / 2/5946 explains that taxpayers have the right to reduce income received from the sale of land plots by the amount of expenses actually incurred by them for the acquisition of these plots, only if the land plots were acquired for the purpose of their further resale.
In this case, land plots should be classified as goods for tax purposes.
In this case, one should be guided by paragraphs. 23 p. 1 of art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which taxpayers who apply the simplified taxation system and who have chosen income reduced by the amount of expenses as an object of taxation, when determining the object of taxation, reduce the income received by the cost of paying for the cost of goods purchased for further sale (reduced by the amount of expenses specified in clauses 8 of clause 1 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), as well as for expenses associated with the purchase and sale of these goods, including expenses for storage, maintenance and transportation of goods.
According to paragraphs. 2 p. 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses related to payment of the cost of goods purchased for further sale are accounted for as expenses as the specified goods are sold.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, goods for tax purposes are any property sold or intended for sale.
Thus, taxpayers have the right to reduce the income received by the amount actually incurred by them for the acquisition of land plots that are acquired for the purpose of further resale at the time of their sale. In other cases, expenses for the acquisition of land plots for tax purposes are not taken into account within the framework of the simplified taxation system.
A similar position is set out in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 08.04.2011 N 03-11-06 / 2/46.
It should be noted that, according to the explanations set out in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 06/08/2011 N 03-11-06 / 2/91, additional work performed on the sold land plots, which were a condition for their sale, such as, for example, strengthening ditches , the formation of paths (sites), the construction of fences, etc. not taken into account for tax purposes due to the fact that Ch. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for an increase in the cost of acquiring goods for the costs of bringing them to a state in which they are suitable for sale.
Technology for the sale of land plots for privatized enterprises
Restrictions on the purchase of land plots for privatized enterprises
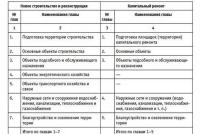
In procedural and legal terms, when buying out land plots, one should distinguish between the built-up and vacant parts (Figure 15.3).
Built up land plots in cities and towns are plots on which or under which enterprises, buildings, structures, structures are located. The built-up land plot of a privatized enterprise is the entire territory of the enterprise, with the exception of empty undeveloped (including those reserved in accordance with the design documentation) land plots.
Empty undeveloped land plots (plot), the land user of which is the privatized enterprise, may be, by the decision of the enterprise:
- a) retained in municipal (state) ownership with or without lease to this enterprise;
- b) purchased by the enterprise together with the built-up plot and along the same chain, provided that the enterprise carries out their development in accordance with the established procedure within three years from the date of entry into ownership.
If the enterprise does not fulfill the last condition, it is obliged to sell it in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation for the sale of undeveloped plots that are in state (municipal) ownership. In this case, as well as in the case of the sale of an undeveloped plot before the expiration of three years from the date of entry into ownership, the seller is charged a one-time fee to the local budget in the amount of 30% of the amount by which the sale price of the plot exceeded the cost of its acquisition.
When privatizing land plots, the procedure for using subsoil is determined in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation on Subsoil.
When selling a built-up land plot within the boundaries of cities and other settlements in accordance with the Basic Provisions, the owner's right to a land plot includes the right to any permitted use of it, which, until the entry into force of the legislation on territorial zoning, means the right to use the plot together with those located on it. buildings, structures, structures
Scheme 15.3.
in all ways that do not contradict the restrictions established by the relevant authorities (local authorities) on the basis of current legislation and approved construction, sanitary, environmental and fire safety standards.
It is not allowed to establish the target (unique) method of using the property, including the land plot, as well as the establishment of restrictions on the use of a separate plot. Such restrictions can be established only for all areas within this functional area in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. The owner has the right to use the built-up land plot together with the buildings, structures, structures, premises located on it in those ways and for those purposes that are not prohibited within the given functional zone of this city (settlement) or within a radius of 100 m from the boundaries of this plot.
The owners of land plots have the right to register, free of charge, that part of the engineering infrastructure that is used exclusively to provide the property (s) of this owner's real estate (up to the border of the site or, for cables and pipelines, before connecting to the relevant highways) under an agreement with the relevant authority ... Construction of new infrastructure facilities on the site, including the laying of electrical and telephone cables, water and gas pipelines, sewers, the placement of which may damage the owner, is carried out on a compensation basis in accordance with an agreement between the site owner and the relevant state (municipal) body Restrictions on the use of a built-up land plot existing at the time of privatization (sale) of an enterprise or other real estate object are valid.
The relevant territorial bodies of Rosreestr and Gosstroy are obliged, within 2 months, to provide the applicant with information on the restriction of the rights to use the land plot, including the public servitudes existing on the date of sale of the building, structure, structure, enterprise, as well as such easements, the establishment of which was provided for by decisions of the competent state authorities (local authorities), adopted on the specified date.
Registration of ownership of a land plot
The final stage of the purchase of a land plot includes the established procedures for registering ownership of it (Schemes 15.4-15.9). The buyer submits a complete package of documents together with application No. 2 (see Figure 15.2) to the territorial executive authority for property management, which concludes a contract for the sale of a land plot.
Within a week from the moment the documents submitted by the buyer are received from the Federal Property Management Agency, the seller signs with the buyer an agreement on the sale and purchase of a land plot and issues a payment order to the buyer to pay the cost of the land plot in the established amount.
If the documents presented to the seller do not meet the established requirements, the seller returns them to the Federal Property Management Agency.
If the buyer refuses to conclude a contract or does not appear within three months, the seller returns the documents to the Federal Property Management Agency with a corresponding notification.
Within a week from the date of issuance of a payment order to the buyer, he presents it to the seller in a properly executed, paid, confirming transfer money to the account specified by the seller.
Within two weeks after the full payment of the cost of the site in accordance with the sale and purchase agreement, the Federal Property Management Agency sends the following documents to the registration service of the Federal State Registration Service:
- o a copy of the land purchase and sale agreement;
- o a letter confirming the full payment under the contract and with a proposal to issue, in accordance with the established procedure, documents certifying the ownership of the land plot.
A paid payment order and a land plot sale and purchase agreement are indisputable grounds for issuing to the buyer documents certifying the ownership of the land plot. The documents must be issued by the district (city) administration within two weeks from the date of receipt of the letter territorial body executive power but property management. For violation of the terms and procedure for re-registering the right of permanent (unlimited) use of land plots for ownership or lease, a fine of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs from 01.01.2013 is set in the amount of 20 thousand to 100 thousand rubles. (Article 7.34 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Scheme 15.4.

Scheme 15.5.

Scheme 15.6.

Scheme 15.7. Rights to a land plot when a building (structure) is sold, located on it

Scheme 15.8. Rights of the owner of the building (structure) to a part of the sold them land

Scheme 15.9.

Sale of the right to lease land plots in Moscow by tender
In Moscow, land can now be transferred to private ownership and the rights for long-term leases are being sold through a competition. Ownership of any building does not automatically entail ownership of the land plot it owns. In this case, the redemption of the right to lease the plot located under the dimensions of the privatized building (structure) is not made. In the case of its exclusion from general use, the lease right to the adjacent plot can be redeemed at the request of the land user.
The procedure for holding tenders for the provision of long-term lease of land plots in Moscow is presented in the schemes 15.10-15.13.
Scheme 15.10.

Scheme 15.11.

Scheme 15.12.

Scheme 15.13. The procedure for concluding contracts and settlements based on the results of a tender for the right to lease land plots in Moscow

To calculate the buyout of long-term and short-term lease rights for land plots, base rates have been approved based on market prices for lease rights based on the results of tenders held. It was established that the amount of payment for the purchase of the right to long-term lease of land for the construction of commercial, residential and other capital objects does not depend on the lease term.
If a physical or legal entity there is a right of ownership (economic management or operational management) only to a part of the structure, then the area of \u200b\u200bits land share is calculated in proportion to the area of \u200b\u200bthe building belonging to it without allocating this share in kind. In a residential microdistrict with complex development, when the establishment of the boundaries of home ownership in kind is impractical, the area of \u200b\u200bthe land plot is determined by calculation (Figure 15.14).
Scheme 15.14.