What is a special account in accounting. Characteristics and purpose of special bank accounts
Count. 55 "Special accounts in banks" is used by legal entities to collect information on transactions in Russian rubles and foreign currency, carried out through settlements with counterparties by letters of credit, checkbooks and other methods money circulation (except for settlements by promissory notes).
Account 55 in accounting - collection of information on transactions on current and special accounts of the organization, made using letters of credit, checkbooks and special payment documents. Data on payments in rubles are displayed here Russian Federation and foreign currencies... In addition, on account 55, the receipt and expenditure of targeted funding can be taken into account, which are displayed separately in the accounting.
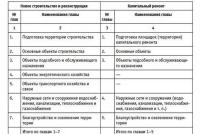
Count. 55 is active, the following sub-accounts are opened for it:
- 55.01 - settlements through letters of credit.
Keep in mind! A letter of credit is a bank's obligation to transfer funds to their recipient (beneficiary) upon meeting the conditions and providing pre-agreed documentation.
The receipt of money for the bank guarantee is displayed according to Dt55 in correspondence with the corresponding accounts 51, 52, 67, etc. The withdrawal of funds is accounted for in accordance with the bank statements, as they are transferred, the amounts are displayed at CT55. The credit institution returns unused amounts to the accounts from which they were accepted for the letter of credit. Analytical analysis is carried out separately for each opened obligation.
- 55.02 - settlements by checkbooks. On debit 55, the deposit of funds is taken into account when opening a checkbook in correspondence with account 51.52, etc., on credit - the repayment by the bank of the amounts presented for payment of checks. The deposited money, not issued for redemption, remains registered in Dt55.02. Unused amounts are returned to the company (Kt55.02).
Attention! The balance on 55.02 must fully correspond to the bank statements.
Analytical analysis is carried out separately for each issued checkbook.
- 55.03 - accounting of investments legal entity in bank and other deposits. The opening of a deposit is displayed by Dt55.03 (Kt51.52). The closure of deposits and the return of money to the enterprise is fixed by a reverse business transaction. Analytical monitoring - separately each deposit.
- The amount of targeted financing received by the enterprise in the banks is displayed separately: budget transfers, financing of capital investments, the accounting of which is carried out separately, etc.
- Additionally, sub-accounts are opened to account for receipts and spending of money aimed at meeting the current needs of branches and representative offices of the enterprise.
Keep in mind! All settlements denominated in foreign currency should be accounted for separately.
Regulatory regulation
Using the count. 55 for the concentration of information on settlements carried out by letters of credit, checkbooks or other methods of monetary circulation is carried out in accordance with the current Chart of Accounts approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated 31.10.2000 No. 94. In addition, settlement operations with special payment documents are governed by Bank of Russia Regulation No. 383-P (transfer rules money).
Account 55 and common postings in accounting
- Capitalization of funds on special accounts
Dt55 Kt50 - credited from the cash desk of the organization
Dt55 Kt51.52 - from the current settlement, foreign currency accounts
Dt55 Kt60.62 - from suppliers, buyers for the purpose of repayment accounts receivable
- Opening bank guarantees, checkbooks by means of borrowed funds
Dt55 Kt66.67
- Posting target financing
- Debit
Dt51.52 Kt55 - crediting of unused amounts to the organization's accounts
Dt60.62 Kt55 - repayment accounts payable
Dt86 Kt55 - covering the costs of targeted financing
Entrepreneurs who are engaged in e-commerce, due to the specifics of this business, in addition to a regular account, in some situations it is also necessary to open a special account No. 40821. This procedure became the norm after it was adopted in 2009. Federal Law No. 103, which regulates the work of paying agents. For laymen, it is worth clarifying that 40821 is actually just the first five digits of a score of twenty, which clearly indicate its purpose.
When to open account # 40821: specific examples
First of all, you need to understand what is meant by a special account. A special bank account is an account that has a specific purpose. Its use is regulated by law and is mandatory. Speaking specifically about special account number 40821, it is necessary for interaction with legal entities that have entered into an agreement with a supplier (online store) on the implementation of activities for accepting cash.
In what cases it is necessary to open an account, and in what not, it is better to analyze it with specific examples. If an online store has couriers in its state, then it acts as an ordinary business entity without intermediaries. This means that there is no need for invoice No. 40821.
Another option is also possible. Products purchased from an online store are delivered by a third-party shipping service. This service collects some amount from the buyer, and then transfers it to the store. This means that this service can be considered an intermediary. And just in order to settle accounts with such an intermediary (payment agent), an online store needs a special account number 40821. alternative ways you cannot interact with such a courier service.
Electronic wallet systems (for example, PayPal and Webmoney) can also play the role of payment agents. For mutual settlements with them, you also need a special account.
And finally, the online stores themselves sometimes act as intermediaries that accept funds from customers. This happens when the goods do not belong this online store, and someone else. Here, the online store also needs a special account for mutual settlements with different parties (moreover, the store must be formalized exactly as a paying agent).
Important information about account number 40821
Those who are going to open a special bank account No. 40821 should know the following information: in accordance with Article 86 Tax Code The Russian bank must notify the tax office of the opening, change of details and closing of special accounts of taxpayers.
Art. 86 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Of course, these requirements apply to accounts starting with 40821 - this is clear from paragraph 2 of Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. By the way, the tax inspectorate has the right to receive all the necessary information on them directly from the bank, without sending requests and notifications to the online store itself.
By the way, accounting of funds in special accounts in banks is also conducted in a special way - for this, in the accounting plan, there is a special account 55.
And one more interesting and significant fact. In relation to the special account of the paying agent, the bank can only carry out the following debit transactions:
- transfer of money received from end users to the address of a supplier selling goods (carrying out work, providing services);
- payment for "communal" and rent of premises;
- transfer of the amount of remuneration to the ordinary current account of the paying agent in accordance with the agreement between the agent and the supplier (online store).
That is, the list of possible operations is strictly regulated. However, there is good news: no enforcement is applied to special accounts.
Features of the procedure for opening such an account
In general terms, the opening of a special account No. 40821 is about the same as opening an ordinary account. It is necessary to write the application established in the form and attach a certain list of documents to it. Among them:
- a photocopy of an agreement for accepting payments from individuals or another document that confirms the status of a paying agent;
- a photocopy of the certificate of state registration of a legal entity;
- a photocopy of a document certifying registration with a department of the Federal Tax Service (tax service);
- a photocopy of an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities;
- a special bank account agreement (it must be prepared by the bank);
- a photocopy of the decision to create a legal entity (it must be certified by the director's signature and official seal);
- the questionnaire of a bank client and other individuals who have the right to dispose of the special account being opened (in particular, using online banking);
- it is necessary to attach correctly certified photocopies of passports to the questionnaires;
- an order to maintain accounting directly by the head and to submit payment documentation to the bank with one signature (this is necessary when the position of the chief accountant is not on the staff of the organization), etc.

Specific content required package documents should be checked with a bank employee or other specialized specialists. Here a lot depends on the format in which the company exists (LLC or IE), whether it is a resident or non-resident. And, finally, you need to understand that a special account can be opened by a paying agent, a subagent, or a supplier - and in each case you will need your own set of documents.
Is it possible to do without opening an account No. 40821
At the moment, there are schemes for settlements with paying agents, where the use of account No. 40821 is not required. One of the schemes is the conclusion of special agreements between the supplier organization, the banking structure and the paying agent. In such contracts it is simply prescribed that settlements between the bank and the agent are carried out without any involvement of the supplier.
The current legislation specifies that the supplier of goods must have a separate account for working with legal entities that accept cash as intermediaries. And, accordingly, if this agreement is signed between a banking structure and a company that receives money from buyers of goods of an online store, you do not need to open anything additionally.
To account for funds in letters of credit, checks and other payment documents that are placed on special and special bank accounts, organizations use account 55. Everything you need to know about the rules for using account 55, our article will tell you, and illustrative examples will help you understand the accounting typical operations with special accounts.
Account 55: features of use
Account 55 is used to reflect generalized information about the funds that the organization stores in special accounts with the bank. To organize analytical accounting enterprises open sub-accounts to account 55 in the context of the operations performed:
- settlements on letters of credit;
- operations with checkbooks;
- funds in foreign currency;
- bank loans (deposits);
- other settlements carried out on special accounts.
To reflect operations on crediting funds to a special account, Dt 55 is used, when writing off, they make transactions at Kt 55.
Funds credited to a special account can come from various sources. Let's consider operations for some of them:
| Debit | Credit | Description | Document |
| 55 | 52 | Foreign currency purchased as a deposit is credited to a special account | Bank statement |
| 55 | 62 | The amount of receivables for the goods shipped has been repaid | Bank statement |
| 55 | 60 | Funds were credited that were overly (erroneously) paid to suppliers (contractors) | Bank statement |
| 55 | 68, 69… | Admission budget funds in the amount of overpayment of taxes and fees | Bank statement |
Funds are debited from account 55, as a rule, for the purpose of making settlements with accountable persons (credit, debit cards), as well as for settlements on loans and borrowings. Consider typical wiring:
| Debit | Credit | Description | Document |
| 67 | 55 | Repayment of the amount of debt on a long-term loan | Bank statement |
| 79 | 55 | Transfer of funds in favor of separate structural divisions | Bank statement |
| 71 | 55 | Issuance of funds for settlements with accountable persons | Bank statement |
| 76 | 55 | Transfer of funds for settlements by other counterparties | Bank statement |
Account 55 in accounting: checkbook settlements
For settlements with suppliers and contractors, Magistral JSC issued a limited checkbook (120 checks) in the Banker Plus bank, in connection with which 347,250 rubles were transferred to the bank. The bank was paid 320 rubles for the services of drawing up the book.
At the end of August 2015, the book was used for the following calculations:
- payment for construction worksexecuted by OOO Stroymontazh - 5 checks for a total amount of 185,500 rubles;
- settlements with LLC Kantseriya for the supply of paper - 3 checks for a total amount of 24,200 rubles;
- payment for production materials received from JSC “Magnit” - 4 checks for a total amount of 74.350 rubles.
The balance of funds was credited by Banker Plus bank to the current account of Magistrala. Unused checks were returned to the bank.
To record checks on the off-balance sheet account, their notional value was used - 3 rubles / piece.
Reflecting these transactions, the accountant of JSC “Magistral” made the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Description | Amount | Document |
| 91.2 | 76 | The amount of the bank's commission for book registration services is included in the expenses | 320 RUB | Bank agreement |
| 76 | 51 | Funds were debited from the settlement account of JSC "Magistral" as payment for checkbook registration services | 320 RUB | Bank statement |
| 55.2 | 51 | Reflected the amount of funds deposited for settlements by checks | RUB 347.250 | Bank statement |
| 006 | Limited checkbook recorded on off-balance sheet account (3 rubles * 120 pcs.) | 360 RUB | Acceptance certificate | |
| 60 | 55.2 | The amount of funds debited for settlements with suppliers and contractors is reflected (185.500 rubles + 24.200 rubles + 74.350 rubles) | RUB 284.050 | Bank statement |
| 006 | The writing off of checks used for settlements with suppliers and contractors is reflected ((5 pcs. + 3 pcs. + 4 pcs.) * 3 rubles) | RUB 36 | Write-off act | |
| 51 | 55.2 | The funds previously deposited, but not used, were credited to the current account (347.250 rubles - 284.050 rubles) | RUB 63.200 | Bank statement |
| 006 | The write-off of unused checks is reflected (360 rubles - 36 rubles) | 324 r | Write-off act |
Account 55: transactions with a covered letter of credit
AO Flagman and LLC Promyshlennik signed a contract for the supply of equipment for merchant ships in the amount of 1,314,500 rubles. The agreement stipulates that the payment in favor of Promyshlennik LLC is carried out by means of a covered letter of credit, in connection with which Flagman JSC opened a letter of credit in Omega Bank in the amount of 1,314,500 rubles.
The supply of equipment under the contract was carried out in an incomplete volume for the amount of 1,220,300 rubles, about which the relevant documents were provided. The rest of the funds was credited to the current account of "Flagman".
For servicing the letter of credit, Omega Bank withheld a commission of 0.05% of the amount of the letter of credit.
Settlements under the supply agreement were made upon the provision of transport documents and an invoice to Promyshlennik LLC.
The following entries were made in the accounting of Flagman JSC:
| Debit | Credit | Description | Amount | Document |
| 55.1 | 51 | Reflected the amount of funds deposited on a covered letter of credit | RUB 1.314.500 | Bank statement |
| 08.4 | 60 | Equipment purchased from Promyshlennik LLC is accepted for accounting | RUB 1.220.300 | Packing list |
| 60 | 55.1 | Funds were transferred in favor of Promyshlennik LLC as payment for the purchased equipment | RUB 1.220.300 | Payment order |
| 08.4 | 51 | The amount of the commission of Omega Bank for servicing the letter of credit is taken into account (1,314,500 rubles * 0.05%) | 657 r | Bank statement |
| 51 | 55.1 | The balance of unused funds was credited to the current account of "Flagman" (1,314,500 rubles - 1,220,300 rubles) | RUB 94.200 | Bank statement |
Score 55: Credit Card Payments
In April 2015, Segment JSC and Vostochny Bank signed an agreement for the issue and servicing of a credit card. According to the terms of the contract:
- the loan was issued in the amount of 218,000 rubles;
- maturity - 18 months;
- interest rate - 15% per annum;
- the amount of interest is charged monthly (for the amount of funds that were actually spent in the current period).
In June 2015, the employee of JSC “Segment” Savelyev K.P. was sent on a business trip to Krasnodar, in connection with which he was given an advance in the amount of 4.850 rubles. Travel and accommodation expenses on a business trip (4.850 rubles) Saveliev paid by credit card.
The accountant of Segment JSC reflected these operations as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Description | Amount | Document |
| 55 | 66 | The received loan amount was taken into account upon withdrawal of funds from a credit card | RUB 4.850 | Bank statement |
| 71 | 55 | Savelyev K.P. an advance payment was issued for a business trip to Krasnodar | RUB 4.850 | Application for advance payment |
| 26 | 71 | Saveliev's business trip expenses included | RUB 4.850 | Advance report |
| 91.2 | 66 | The amount of interest for using a credit card was written off as expenses (4.850 rubles * 15% / 12 months) | RUB 61 | Bank agreement |
| 66 | 51 | Reflected payment of interest for using a credit card | RUB 61 | Bank statement |
Account 55: debit card payments
For the director of JSC "Condor" Timofeev V.S. a bank card was issued for making payments during business trips, in connection with which 43,500 rubles were transferred to a special bank account of Kondor JSC.
In August 2015, during a business trip to Tula, Timofeev made a calculation by credit card for hotel accommodation (12.300 rubles).
Upon receipt advance report Timofeeva, the accountant of Kondor JSC made the following entries in the accounting:
Read more about the accounts used in the articles: (current account), (accounting of settlements with accountable persons), (general business expenses).
Account 55: accounting of operations on deposit accounts
In March 2015, Sfera JSC placed a deposit in the Central Bank.
Of the Russian Federation and the features established by this Code. Funds deposited into a special account are used for the purposes specified in Article 174 of this Code.
2. The owner of a special account may be:
1) an association of homeowners that manages an apartment building and is created by the owners of premises in one apartment building or several apartment buildings, in accordance with paragraph 1 of part 2 of Article 136 of this Code;
2) the housing cooperative that manages the apartment building;
(see text in previous edition)
3) a management organization that manages an apartment building on the basis of a management agreement.
(see text in previous edition)
3. The owners of premises in an apartment building have the right to decide on the choice of a regional operator as the owner of a special account.
3.1. The decision of the general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building on the formation of a capital repair fund on a special account must also contain a decision on choosing a person authorized to provide services for the submission of payment documents, including using the system, to pay contributions for capital repairs to a special account, on determining the procedure for submitting payment documents and on the amount of expenses associated with the submission of payment documents, on determining the terms of payment for these services. In this case, the choice of the authorized person specified in this paragraph is carried out in agreement with him.
3.2. The authorized person specified in part 3.1 of this article is obliged to provide the holder of the special account in the manner and within the time limits established by the law of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, information on the amount of funds accrued as contributions for capital repairs.
4. The owners of premises in an apartment building shall have the right to carry out the formation of a capital repair fund only on one special account. A special account can accumulate funds from the fund for capital repairs of owners of premises in only one apartment building.
5. The special account agreement is open-ended.
6. The funds in the special account cannot be foreclosed on the obligations of the owner of this account, with the exception of obligations arising from contracts concluded on the basis of decisions of the general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building specified in clause 1.2 of part 2 of Article 44 of this Code, as well as contracts for the provision of services and (or) performance of work on capital repairs common property in this apartment building, concluded on the basis of a decision of the general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building to carry out major repairs or on another legal basis.
8. In the event that a decision is made to liquidate and (or) reorganize the owner of the special account, the owner of the special account is declared bankrupt, as well as if the management organization, a homeowners' association or a housing cooperative that is the owners of the special account terminates the management of an apartment building on the basis of decisions of the general meeting of owners of premises in this house or such termination of management of an apartment building is provided for by legislation or a court decision, the owners of premises in an apartment building are obliged at the general meeting to decide on the choice of the owner of a special account or on changing the method of forming a capital repair fund. This decision must be made and implemented no later than two months from the date of termination of the management of an apartment building, termination of management of an apartment building by persons who are holders of a special account and specified in this part. The date of termination of the management of an apartment building is determined in accordance with the requirements of Articles 162 and this Code.
9. Not later than one month before the end of the period established by part 8 of this article, the body local government convene a general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building to resolve the issue of choosing the owner of a special account or changing the method of forming a capital repair fund. If the decision to choose the owner of a special account or to change the method of forming the capital repair fund is not made or implemented, or this meeting has not been held, the local government, no later than the expiration date specified in part 8 of this article, makes a decision on determining the regional operator by the owner of a special account. At the same time, the local self-government body sends a copy of the decision to the address of the regional operator, the state housing supervision body, the Russian credit institution in which a special account is opened, and also posts this decision in the system.
(see text in previous edition)
10. To the owner of a special account, determined on the basis of a decision of the general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building in accordance with part 8 of this article or a local government body in accordance with part 9 of this article, from the moment such a decision is made, all the rights and obligations of the previous owner of the special accounts, including rights and obligations arising under agreements concluded with a Russian credit institution in which a special account is opened, as well as under other loan agreements and (or) credit agreements under which the repayment of the corresponding loans and (or) loans is carried out at the expense of funds credited to a special account (if any).
Subaccount 55-1 "Letters of credit" records the movement of funds in letters of credit.
Crediting of funds in letters of credit is reflected in the debit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" and credit of accounts 51 "Current accounts", 52 "Currency accounts", 66 "Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings" and other similar accounts.
Funds in letters of credit accepted on account 55 "Special accounts in banks" are written off as they are used (according to the statements of the credit institution), as a rule, in the debit of account 60 "Settlements with suppliers and contractors". Unused funds in letters of credit after being restored by the credit institution to the account from which they were transferred are reflected in the credit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" in correspondence with account 51 "Current accounts" or 52 "Currency accounts".
Analytical accounting for subaccount 55-1 "Letters of credit" is kept for each letter of credit issued by the organization.
On subaccount 55-2 "Checkbooks" the movement of funds in the checkbooks is taken into account.
Depositing funds when issuing checkbooks is reflected in the debit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" and the credit of accounts 51 "Current accounts", 52 "Currency accounts", 66 "Settlements on short-term credits and loans" and other similar accounts. The amounts on the checkbooks received from the credit institution are written off as the checks issued by the organization are paid, i.e. in the amounts of the repayment of the checks presented to it by the credit institution (according to the statements of the credit institution), from the credit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" to the debit of accounting accounts (76 "Settlements with various debtors and creditors", etc.). The amounts of checks issued but not paid by a credit institution (not presented for payment) remain on account 55 "Special accounts in banks"; the balance on subaccount 55-2 "Checkbooks" must correspond to the balance on the statement of the credit institution. The amounts on the checks returned to the credit organization (remaining unused) are reflected in the credit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" in correspondence with account 51 "Current accounts" or 52 "Currency accounts".
Analytical accounting for subaccount 55-2 "Checkbooks" is kept for each received checkbook.
Subaccount 55-3 "Deposit accounts" records the movement of funds invested by the organization in bank and other deposits.
The transfer of funds to deposits is reflected by the organization on the debit of account 55 "Special accounts in banks" in correspondence with account 51 "Current accounts" or 52 "Currency accounts". When a credit institution returns the amount of deposits in the accounting of the organization, reverse entries are made.
Analytical accounting for subaccount 55-3 "Deposit accounts" is maintained for each deposit.
On separate sub-accounts opened to account 55 "Special accounts in banks", the movement of funds of targeted financing separately stored in a credit institution is taken into account. In particular, received budget funds, funds for financing capital investmentsaccumulated and spent by the organization from a separate account, etc.
Branches, representative offices and other structural divisions of the organization, allocated to a separate balance sheet, which open current accounts in credit institutions for the implementation of current expenses (wages, individual business expenses, travel expenses, etc.), reflect the movement of these funds in a separate subaccount to account 55 "Special accounts in banks".
The presence and movement of funds in foreign currencies are accounted for on account 55 "Special accounts in banks" separately. The construction of analytical accounting for this account should provide the ability to obtain data on the availability and movement of funds in letters of credit, checkbooks, deposits, etc. on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad.