Pregnancy management according to OMS what is included. The OMC program for various stages of pregnancy. Hospitalization and inpatient treatment during pregnancy under compulsory medical insurance
Pregnancy and childbirth under compulsory health insurance
Pregnancy is a wonderful period in the life of every woman. Expectant mothers approach this issue with all responsibility and want to know in advance when to go to the doctor, when to do an ultrasound, how long to go on maternity leave, and, finally, what to take to the hospital for themselves and their baby. Information on the management of pregnancy can be found in various sources and, at times, it is even too much. To help expectant mothers, SOGAZ-Med specialists have collected the most up-to-date information about examinations during pregnancy, the necessary procedures and documents for mothers and children.
It is important
SOGAZ-Med employees remind that the policy is mandatory health insurance (OMS) operates throughout the Russian Federation. Medical care within the framework of the basic compulsory medical insurance program, which includes monitoring of pregnancy, delivery, and examinations in the postpartum period, as well as (if necessary) hospitalization in a gynecological hospital (up to 22 weeks of pregnancy) or in the pregnancy pathology department of a maternity hospital (after 22 weeks ), is provided free of charge throughout Russia. If a woman goes to a maternity hospital outside the registration area, and she has medical indications for hospitalization (for example, the threat of termination of pregnancy, childbirth, etc.), then the refusal to provide her with medical care is unlawful, as well as the requirement to pay for any medical services.
In addition to funding from the compulsory medical insurance system, the management of pregnancy and childbirth is additionally supported by the state through the "Birth Certificate" program. A birth certificate is a document on the basis of which settlements are made with the medical institution that provided the woman and her child with the appropriate healthcare services. The certificate is issued in the antenatal clinic where the pregnant woman is observed. If a pregnant woman is observed in a private clinic, but wants to receive a birth certificate for compulsory medical insurance, she needs to go to the antenatal clinic to which she is attached for up to 32 weeks and ask for a document based on an exchange card issued in a private clinic. Remember pay private clinic or you cannot cash out the generic certificate!
Examination during pregnancy
The gestational age is determined by 3 trimesters.
In the 1st trimester up to 12 weeks, at the first appearance of the pregnant woman, the obstetrician-gynecologist collects anamnesis, conducts a general examination of organs and systems; anthropometry (measurement of height, body weight, determination of body mass index); measuring the size of the pelvis; gynecological examination. In addition, a woman undergoes examinations and consultations of narrow specialists: a therapist, dentist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist and other doctors - according to indications. And he passes a clinical and biochemical blood test, a coagulogram, a blood test for HIV, syphilis and hepatitis, TORCH infections, a vaginal smear and a general urine test. In addition, the doctor fills out the necessary documents, gives recommendations on nutrition and taking vitamins.
At 10-12 weeks, prenatal screening is carried out - this is a mass examination of pregnant women, which is carried out in order to identify the "risk group". This group includes expectant mothers who have a high probability of giving birth to a child with a hereditary disease or congenital malformations. Prenatal screening allows the fetus to be suspected of Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome and neural tube defects in the early stages of pregnancy. The examination also includes biochemical (blood test) screenings. These studies are safe, that is, they do not affect the health of the expectant mother, the course of pregnancy and the development of the baby, and they can be carried out for all pregnant women.
In the 2nd trimester, parents, if they wish, can already find out the gender of the child. Also at this time, the risk of the threat of termination of pregnancy decreases, in most cases toxicosis passes (if it was in the 1st trimester) and the expectant mother can enjoy her position and the appearing tummy. For a period of 13-24 weeks, a urine test is performed before each visit to the doctor (once every 3 weeks).
The second screening during pregnancy is carried out at 18–21 weeks in a medical organization that carries out prenatal diagnostics to exclude congenital malformations of the fetus. Like the first screening, it consists of two stages - ultrasound and blood tests.
In the 3rd trimester, at 24-28 weeks, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) or glucose tolerance test is performed, which allows you to identify violations of carbohydrate metabolism during pregnancy, that is, to check how well the body regulates sugar levels. This test determines the presence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) - Pregnancy-related high blood glucose (sugar) levels.
With a gestational age of 30-34 weeks, an ultrasound scan is performed at the place of observation of the pregnant woman. At this time, a study of blood circulation in the placenta and in the baby is carried out. At the 30th week of pregnancy, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued for maternity leave.
After 32 weeks, regular fetal cardiotocography (CTG) recordings begin. This is a modern technique for assessing the condition of the fetus by the nature of its heartbeat.
From week 36, a doctor's examination is carried out every 7 days. Routine hospitalization for delivery is carried out at 40-41 weeks. If medically indicated, pregnant women are offered earlier antenatal hospitalization. By this time, the mother should have a “bag to the hospital” ready with certain documents and things for herself and the child.
What documents and things to take to the hospital
Passport, compulsory medical insurance policy, birth certificate, exchange card from the antenatal clinic, SNILS. The mom will need personal hygiene items (soap, toothpaste and a brush, etc.), rubber slippers, clothes (bathrobe, socks, etc.). For a newborn, you need to prepare: hats (1-2 pcs., Flannel and cotton), undershirts / bodysuits (1-2 pcs., Flannel and cotton), sliders (2-3 pcs.), Diapers for newborns, booties and "scratches", normal and disposable diapers (3 or more), diaper cream, wet wipes.
Before discharge at the hospital, the mother will undergo an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and advise on the benefits and the recommended duration of breastfeeding.
What documents to take from the hospital
When discharged from the hospital, the mother or next of kin must receive the following documents: a page from the birth certificate of the mother's health, an exchange card for the child, a vaccination card (if the hospital was vaccinated against viral hepatitis B and tuberculosis), a certificate for the registry office about the birth of a child.
One of the first concerns of parents will be the paperwork for a newborn child. SOGAZ-Med recalls that a compulsory medical insurance policy is a document that entitles a child to receive free of charge all basic types of medical care in medical organizations operating in the compulsory medical insurance system. A newborn child from the date of birth until the expiration of 30 days from the date of state registration of birth receives all the necessary medical assistance for compulsory medical insurance policy mom or other legal representative.
To apply for a compulsory medical insurance policy, you must contact insurance company... The SOGAZ-Med insurance policy can be issued by visiting one of the company's offices, or by leaving a request on the website.
To issue a compulsory medical insurance policy for a child, you will need the following documents:
Birth certificate of the child;
SNILS of the child (if any);
Identity document of the child's legal representative.
Regarding the procedure for obtaining medical assistance within the framework of the CHI system, SOGAZ-Med insured persons can contact their insurance representative by calling the 24-hour contact center at 8-800-100-07-02 (free calls within Russia) or check the information on the website.
Company information
The SOGAZ-Med insurance company has been operating since 1998. The number of insured people is over 19 million. Regional network - more than 660 divisions in 40 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. SOGAZ-Med carries out compulsory medical insurance activities: it controls the quality of services provided to the insured when receiving medical assistance in the compulsory medical insurance system, protects the rights of insured citizens, and restores violated rights of citizens in the pre-trial and judicial order. In 2018 rating agency Expert RA has confirmed the rating of reliability and quality of services of SOGAZ-Med insurance company at the A ++ level (the highest level of reliability and quality of services in the framework of the MHI program according to the applicable scale). For several years now, SOGAZ-Med has been awarded this high level of assessment.
Pregnancy is a time of special female vulnerability, when the expectant mother is immediately worried about her health and the health of her baby. Therefore, it is not surprising that many of us decide to follow the well-established stereotype: it is better to pay and even overpay for medical care, but save both pregnancy and nerves. This position, unfortunately, is supported by the frequent suppression of the full list of services provided by the pregnancy management program under the compulsory medical insurance policy. And yet, before choosing a private clinic, it would be good to have a complete understanding of what exactly and in what amount can be obtained free of charge, in accordance with the procedure and standards for the provision of medical care approved by the Ministry of Health.
The right of pregnant women to free medical care is provided by the compulsory health insurance policy (MHI). Within the framework of this document, the patient has the full right to choose any clinic operating under the compulsory health insurance system for medical care and pregnancy monitoring. This means that every expectant mother can be monitored completely free of charge, not only in the regional antenatal clinic at the place of registration, but also in any other state clinic in her city.
The compulsory medical insurance program includes both doctor's consultations and the necessary list of examinations and diagnostic procedures. The medical insurance policy and its copy will be needed both when contacting the antenatal clinic and when admitted to the hospital. Unfortunately, without a compulsory medical insurance policy for free expectant mother can only provide emergency medical assistance.
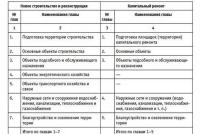
The compulsory health insurance program for pregnancy includes:
- therapeutic and prophylactic procedures;
- active home visiting (patronage);
- instrumental and laboratory examinations with the necessary clinical, laboratory and instrumental studies;
- hospitalization (if necessary), including day hospitals;
- early diagnosis of fetal malformations;
- psychological and physical preparation for childbirth, the formation of motivation for the birth and upbringing of a healthy child;
- breastfeeding training;
- examinations and consultations of other specialists;
- referral, if necessary, to receive free medical care to other medical institutions.
Also in accordance with Art. 19 Federal Law "On the basics of health protection Russian Federation»When seeking medical care and receiving it, the patient has the right, inter alia, to:
- choice of a doctor, subject to the consent of the doctor, and the choice of a medical organization
- prevention, diagnosis, treatment, medical rehabilitation in medical organizations in conditions that meet sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- obtaining advice from specialist doctors;
- relief of pain associated with a disease or medical intervention with available means and drugs;
- protection of information constituting a medical secret;
- refusal of medical intervention;
- admission of a lawyer, clergyman or legal representative to defend their rights; for pregnant women, this, in particular, means that you can come to any maternity hospital with your husband or girlfriend, if you stock up on this knowledge of your rights and a power of attorney.
Physiological course of pregnancy
Doctor visit
In the normal, that is, physiological, course of pregnancy without complications, according to the CHI program, the gynecologist invites you for an examination during the first half (up to the 20th week) once a month, during the second half of pregnancy - twice a month, and in the last month of pregnancy - weekly.
Also, during pregnancy, an examination by a general practitioner should be carried out twice: the first time - after the first examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist; the second - at a gestational age of 30 weeks.
When a pregnant woman first contacts an antenatal clinic, an obstetrician-gynecologist is obliged to issue directions for a free examination by the following doctors: an ophthalmologist, an otolaryngologist, a dentist.
Analyzes, laboratory tests, ultrasound
All examinations of a pregnant woman, including ultrasound, laboratory tests, tests for intrauterine infections, genetics and hemostasis, should be carried out free of charge, under a compulsory health insurance policy.
If in the antenatal clinic it is not possible to conduct the necessary research, then the doctor should give a referral to another antenatal clinic or hospital.
Also, under the compulsory medical insurance program during pregnancy, two screening ultrasounds are expected (as part of a screening test): for a period of 11-13 weeks and 16-20 weeks. This test is also free: it is funded by the state program for the health of the nation, as it allows you to identify abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
Vitamins and medicines
During pregnancy, the compulsory health insurance program relies on free vitamins and, if necessary, drugs. In 2015, the list of such vitamin preparations included:
- folic acid;
- multivitamins;
- multivitamins + minerals;
- iron (III) hydroxide polymaltose;
- iron fumarate + folic acid;
- iron (III) hydroxide polymaltozad + folic acid;
- potassium iodide;
- vitamin E;
- calcium carbonate.
The list of free medicines for pregnant women is similar to the list of vital and essential medicines (VED), which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. It can be found on the websites of the Russian and regional Ministry of Health.
Treatment of pathologies during pregnancy
No one is immune from surprises, and it happens that physiological, that is, normally proceeding, pregnancy suddenly turns into pathological. During pregnancy, problems arise quite often, and there are many reasons for this: poor ecology, various infectious diseases of a woman or man, latent inflammatory processes and chronic diseases, unhealthy diet and, of course, stress. Problems can be both serious, posing a danger to the child and requiring deep examination and treatment, and caused by an elementary deficiency of vitamins and minerals, immunodeficiency or disorders of the body's microflora.
In any case, the compulsory medical insurance program provides for free treatment and assistance to maintain pregnancy, and hence a number of additional studies and manipulations.
Examination and laboratory research
Thus, in the case of a complicated pregnancy, the number of examinations, including by various specialist doctors, is determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist, taking into account the state of health. According to his purpose, such examinations are carried out free of charge, as well as additional ultrasound and screening studies, Doppler ultrasound, etc.
In the pathological course of pregnancy, many examinations, which are usually offered to be paid for, are obliged to provide the woman free of charge, if it is necessary to identify any deviations in the health of the mother and child. If the LCD does not have the necessary equipment, then, according to the law, the LCD must find an institution that will carry out this examination on their behalf at the expense of the CHI funds. That is, any examination prescribed by a doctor as necessary for the normal course of pregnancy, as well as for suspicions of any deviations, should be provided free of charge.
Rh factor negative
In Rh-negative women, the father of the child is additionally examined for group and Rh-affiliation, and if the father is Rh-positive, the blood of a pregnant woman is tested for Rh antibodies on a monthly basis.
Emergency hospitalization and hospital treatment
According to the testimony of the supervising doctor, the expectant mother can be prescribed hospital treatment. Planned treatmentas well as emergency hospitalization, should be carried out free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance program. In the clinic, the expectant mother should undergo a full examination and offer tactics for managing and maintaining pregnancy, as well as a method of delivery. At the same time, a hospital providing the required treatment must operate under the compulsory medical insurance system.
Usually in the maternity hospital, examinations and treatment of pregnant women are carried out for the following pathologies:
- habitual miscarriage;
- toxicosis of the first and second half of pregnancy;
- placental insufficiency;
- pregnancy with pathological features of the genital organs;
- the presence of a scar on the uterus;
- uterine fibroids.
Assistance is provided with the use of ultrasound examinations, CTG - computer monitoring of the condition of the fetus, examinations for genital tract infections and laboratory tests.
Inpatient treatment of other diseases, including chronic and infectious diseases that threaten pregnancy and the child, is carried out in specialized hospitals, according to a doctor's referral.
Just like a polyclinic, the expectant mother has the right to choose a hospital at her own discretion, if she is not satisfied with the institution to which the referral to the LCD was issued.
Sanatorium for pregnant women
In addition to hospital treatment, every expectant mother has the right to free spa treatment, subject to the availability of indications and a referral from the attending physician.
You can count on a voucher in the following cases:
- miscarriage;
- infertility;
- fibroids;
- malformations of the uterus;
- caesarean section or other stitches in the uterus
- primiparous under the age of 18 or over 28;
- anemia;
- hormonal disruptions;
- a history of diseases related to risk groups during pregnancy.
The total duration of such a spa treatment can be 21 days.
IVF procedure
It is enough to have a compulsory medical insurance policy to get on the waiting list for the IVF procedure, since infertility is considered an insured event.
Free IVF conditions:
- availability of a compulsory medical insurance policy;
- medical indications for IVF;
- the age of the expectant mother (from 22 to 39 years old);
- no contraindications to IVF procedures;
- normospermia in the father of the unborn child;
- passing the course of infertility treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Under the new conditions, an unlimited number of IVF attempts can be made until a positive result is achieved.
The federal quota provides for expenses of up to 106,000 rubles, that is, unforeseen expenses that exceed the preferential limit will have to be covered on their own.
The cost of the benefit includes:
- hormonal stimulation of follicular growth;
- collection of the required number of cells;
- fertilization procedure in vitro.
Under the compulsory medical insurance program (or under the quota) there is also an IVF protocol, where after the transfer of the procedure to mandatory appoint support that is individual for each patient. Usually these are vitamins and progesterone - the dosage is prescribed by the doctor. If necessary, according to the results of analyzes (blood, hormones), additional medicinal, hormonal and vitamin preparations are prescribed. After confirmation of pregnancy, the content of the hormone progesterone (and the patient's individual indicators) is monitored and the doses adjusted. After confirming the pregnancy and adjusting the support, the expectant mother registers with the LCD, where she is observed as in a normal pregnancy, but taking into account the peculiarities. At the slightest occurrence of problems, it is put on the preservation of pregnancy.
Under the influence of hormones, many women become very suspicious during pregnancy and constantly worry about their baby. To eliminate any danger to him, they voluntarily agree to paid medical care, believing that this is the only safe option to bear and give birth to a baby. Meanwhile, the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation has approved a pregnancy management program under the compulsory medical insurance policy. A full list of medical services that she provides, the expectant mother receives free of charge. Within the framework of state support for pregnancy, all the necessary procedures are taken into account so that a woman in a position feels protected. We will find out further what services and in what volume she can receive for free.
Compulsory health insurance policy (MHI), which is regulated by Federal law dated 29. 10. 2010 No. 326-FZ "On compulsory medical insurance of citizens in the Russian Federation", gives expectant mothers the right to free medical care. Pregnancy support can be entrusted not only to the specialists of the regional antenatal clinic at the place of registration, but also to contact any other medical institution in your city that participates in the compulsory health insurance program.
What is included in the management of pregnancy under compulsory medical insurance
Availability of insurance medical policy provides a free regular examination by a specialist, as well as basic diagnostic procedures and all necessary examinations. The original and a copy of the insurance document must be provided both when visiting the LCD and when applying to the hospital. If a pregnant woman does not have a compulsory medical insurance policy, then she can only count on free emergency medical assistance.
The compulsory health insurance program for pregnancy support consists of a number of services:
- treatment and prevention of various diseases;
- home patronage;
- instrumental and laboratory examinations;
- day hospital;
- hospitalization (if necessary);
- diagnostic tests for the presence of fetal defects;
- psychological support for a pregnant woman;
- educational program on breastfeeding;
- consultations and examinations with specialists of narrow specialties;
- referral to other medical institutions with the provision free service, if necessary (for example, in the absence of the necessary equipment in the institution where the woman first applied).

Taking into account Art. 19 of the Federal Law "On the Basics of Health Protection of Citizens in the Russian Federation" dated 01. 01. 2012, we remind you that a person, when seeking medical help, can also count on the provision of the following services:
- free choice of the state organization where the treatment will take place;
- choice of the attending physician (with his consent);
- diagnostics and treatment-and-prophylactic procedures;
- medical rehabilitation after illness;
- competent consulting;
- anesthesia;
- the right to confidentiality of information regarding treatment;
- refusal of a surgical operation;
- visiting a medical facility accompanied by a lawyer, priest or legal representative who will represent the patient's rights. This means that the expectant mother can safely go to the hospital with her husband, mother or friend.

Physiological pregnancy under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Let's take a look at what the compulsory health insurance program looks like in general terms.
Visiting a doctor during pregnancy under the compulsory medical insurance policy
If the pregnancy is going well and the expectant mother has nothing to complain about, she visits the gynecologist once a month up to 20 weeks of gestation. From the second half of pregnancy, the doctor invites the patient twice a month. A month before the expected date of birth, you will have to go to the LCD every week.
According to the compulsory medical insurance program, a woman is examined by a therapist 2 times during pregnancy: first after the first visit to the obstetrician-gynecologist, then at the 30th week of pregnancy.
As soon as a woman applies to the ZhK for registration, she is given directions for free consultation and examination by an ENT specialist, ophthalmologist and dentist.

Analyzes and ultrasound during pregnancy under the compulsory medical insurance policy
The health insurance policy provides the expectant mother with the opportunity to undergo all examinations free of charge, in particular:
- laboratory research;
- tests to detect intrauterine infections;
- genetic analyzes;
- analysis for hemostasis.
Within the framework of the CHI program during pregnancy, 2 screening tests are carried out: the first - in the period from 11 to 13 weeks, the second - in the period from 16 to 20 weeks. The procedure is also completely free. It is available to expectant mothers thanks to the state program for the health of the nation, which acts with the aim of timely detection of intrauterine developmental defects of the child.

Medical provision during pregnancy under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Under the compulsory health insurance program, pregnant women receive free vitamins and medicines. In 2018, the list of basic vitamin preparations for expectant mothers looks like this:
- Elevit Prenatal;
- Vitrum Prenatal;
- Vita Spectrum;
- Hexavite;
- Complivit;
- Maltofer;
- Revit;
- Terawit;
- Undevit;
- Fenuls;
- Ferrovit, etc.

In addition, the regional government annually approves a list of medicines that pregnant women need first of all, especially in cases where the intrauterine development of a child is associated with any acute or chronic pathologies:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- blood diseases;
- diabetes;
- endocrine system pathology;
- osteochondrosis, etc.
The attending physician always has information about the exact list of medicines and vitamins.
Pathological pregnancy management under compulsory medical insurance policy
No matter how well the pregnancy proceeds, there is always a risk that it will become pathological. There are many reasons for this. Some disorders can be caused by an elementary lack of vitamins or a failure of the body's immune system, while others are so serious that they endanger the lives of the mother and child.
In order to preserve problem pregnancy, the compulsory medical insurance policy provides a woman with appropriate free treatment and a number of additional studies.
During pregnancy with complications, the woman will have to visit the gynecologist more often and the examinations will be free of charge. The same goes for additional ultrasounds, Doppler ultrasound and screenings.

Negative Rh factor and pregnancy management under compulsory health insurance
If there is a high risk of developing Rh-conflict, the Rh of the child's father is additionally determined, and if the father is Rh-positive, the blood of the expectant mother is checked for Rh antibodies every month.
Hospitalization and inpatient treatment during pregnancy under compulsory medical insurance
If there are absolute indications for immediate hospitalization, the pregnant woman is admitted to the hospital and the necessary treatment is prescribed. Hospitalization and planned therapy for a patient under the compulsory medical insurance policy does not cost anything, as well as a full examination, all measures to preserve the baby and the method of childbirth. The hospital should work in accordance with the CHI program.
In the maternity hospital, the expectant mother will be examined and will certainly be treated if there are such complications:
- gestosis at the beginning and at the end of pregnancy;
- habitual miscarriage;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- fetal development against the background of pathological disorders in the activity or structure of the female genital organs;
- scar on the uterus;
- benign neoplasm in the uterus.
The treatment of chronic, infectious and other diseases of a pregnant woman, which endanger the very existence of the fetus, is carried out by specialized hospitals, where the woman is referred by her doctor.

Rest for pregnant women
Each woman, while waiting for a baby, is provided with the right to a free stay in a medical sanatorium for up to 21 days. To exercise this right, there must be weighty evidence and, of course, a referral from a doctor.
You can really get a ticket in such cases:
- habitual miscarriage;
- prolonged difficulty conceiving;
- tumors in the uterus;
- anomalies in the development of the uterus;
- scars after cesarean section and others surgical operations on the uterus;
- pregnancy under the age of 18 and over 28;
- iron-deficiency anemia;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system.

In vitro fertilization and compulsory medical insurance policy
Since infertility belongs to the category of insured events, the presence of a compulsory medical insurance policy allows every woman to apply for a free IVF procedure.
In order not to pay a dime for fertilization in a test tube, it is important to comply with all the prerequisites:
- have an OMS policy on hand;
- have a medical indication for this method of getting pregnant;
- be at the appropriate age for the procedure (22 - 39 years old);
- have no contraindications to artificial insemination;
- the future father should be diagnosed with normospermia;
- undergo infertility treatment under the supervision of your doctor.

In connection with the latest amendments to the law, attempts to get pregnant through IVF within the framework of compulsory insurance medicine are not limited, that is, a woman can undergo the procedure until she gets the desired result. However, it should be taken into account that the federal quota indicates a preferential limit in the amount of 106,000 rubles, all cash expenses in excess of it will be borne by the future parents.
The benefit covers the cost of such procedures:
- stimulation of ovulation with hormonal drugs;
- collection of the optimal number of cells;
- artificial insemination procedure.

After the embryos are implanted to the mother, the newly-made pregnant woman can count on expert advice, as well as free medical support in the form of vitamin preparations and progesterone. When the pregnancy is officially confirmed, the patient is sent to the LCD for registration. There she will be observed as in a normal physiological pregnancy, but taking into account the characteristics of fertilization.
And what to do if they don't give it
Theoretically, all roads are open for a pregnant woman - even a private maternity hospital cannot but accept her if she appears on the doorstep already with contractions. However, in practice, the rights of pregnant women are sometimes violated. Therefore, every expectant mother does not bother to know that she is entitled to free under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Alexey Bereznikov, an expert of the Interregional Union of Medical Insurers, head of the working group on the organization of compulsory medical insurance of the All-Russian Union of Insurers, told MK about this.
- What services and examinations under the compulsory medical insurance policy can a pregnant woman in medical institution?
- Within the framework of the basic and territorial programs, all insured persons, including pregnant women, are entitled to free medical care for diseases and conditions of all organs and systems (including dental ones) under the compulsory medical insurance policy. In addition, expectant mothers are provided with free medical services for the management of pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period and abortion. Not covered by the policy OMS cases treatment of sexually transmitted diseases caused by human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, tuberculosis, mental disorders and behavioral disorders. But the state guarantees citizens free treatment of these diseases at the expense of budget funds.
You can get more detailed information by contacting your medical insurance organization (HMO) by calling the hotline or at the office. There you can also get acquainted with the list of medical organizations working in the system CHI subject RF, with their addresses and operating hours. In addition, this information is available on the official website of the health insurance organization, in which the citizen is insured, and on the official website of the TFOMI of this constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
- Where to complain if a medical organization charges money inappropriately, or if maximum term the doctor's expectations have expired, or is the woman not at all satisfied with the services provided?
- In such situations, you can contact both the management of the medical institution and the insurance representative of your health insurance company by calling the "hot line", as well as by calling the "hot line" of the TFOMS of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. Information about phone numbers is posted on the official websites of the CMO and TFOMS. If a citizen is outside the insurance region, then for the protection of his rights and interests, you must contact Territorial fund Compulsory health insurance of the region where he wants to receive medical assistance.
- For what services, examinations, analyzes most often medical organizations may be trying to improperly take money?
- Monitoring of pregnant women in antenatal clinics is carried out in accordance with the standards and procedures for the provision of medical care. In our country, this area is quite well controlled at all levels, therefore, cases of poor-quality monitoring of pregnant women, including illegal collection money are quite rare. In addition, adequate response measures are immediately taken on them. For example, there were situations when a pregnant woman was offered to pay for laboratory tests or diagnostic tests. In this case, you need to call your CMO, insurance representatives will clarify with the medical organization the reasons for this situation and, as a rule, the pregnant woman will receive an analysis or examination, if it is, of course, included in the list of paid compulsory medical insurance funds... As a rule, the reason for such situations is the "human factor", when the doctor is not sufficiently informed about the list of services territorial program Compulsory medical insurance provided to the patient free of charge.
- What are the most frequent violations of the rights of pregnant women in the CHI system?
- It is rather difficult to single them out, since such specific reporting is not provided in the CHI system and, accordingly, there are no statistics. But according to the experience of the service for the protection of the rights of the insured, we can say that if cases of complaints or complaints about violations of the rights of pregnant women are recorded, then they are about the same as in other patients. Sometimes the facts stated in the complaint are not confirmed or confirmed, but it turns out that the patient (pregnant woman) misinterpreted them, since, of course, not all patients are professionally versed in matters of health and management of pregnant women.
The best in "MK" - in a short evening newsletter: subscribe to our channel in
Many people justify contracting for childbirth with their own confidence and calmness. Some consider it to be a kind of guarantee that everything will go well, the baby will be healthy, etc. In fact, much of what the contract for childbirth gives can be obtained under the usual compulsory medical insurance policy, that is, free of charge. What exactly and what myths should be debunked about paid childbirth, AiF.ru told pediatrician, organizer of the national prize for children's products "Parents' Choice" Tatiana Butskaya.
Better quality, more reliable
Many women, especially those who go to the hospital for the first time, naturally worry: how the process will go, how easy the birth will be, what you can ask the doctors, what is better to refuse. Therefore, it is not uncommon for young mothers to enter into a contract, believing that this is how they receive better medical services.
I would like to illustrate this myth with the answer of a doctor I know to a question about the difference between a “paid” and “free” patient. He said: “Imagine that I am a pilot of a large plane. And so we take off. I have business class on board and economy class. One board. Can you imagine a situation where I will think more about business class safety than economy class? "
So, firstly, the concepts of "paid" and "free" childbirth, in principle, do not exist. Any childbirth is paid for by the hospital and the doctor, just from different budgets. If you give birth under compulsory medical insurance, this does not mean that the doctor will not receive money for your birth. This means that the funds will come to him not from you personally, but from the state.
In addition, as a doctor, I cannot even imagine such a situation that I would prescribe the necessary tests or procedures for a “paid” patient, but not for a “free” one. This is my responsibility. Which, with this approach, can easily become criminal.
I also often hear stories about childbirth, where women complain that they were treated “for free” just awful: “pierced the bubble, pressed on the stomach” and so on. Believe me, not a single procedure during childbirth can be performed for any other reason than the doctor's desire to safely "get" a healthy baby out of you. A woman in childbirth is in a somewhat altered state of consciousness, bodily sensations are also distorted, so she can not always adequately perceive the necessary medical manipulations. “They pressed me on my stomach,” the doctor checked how the uterus was contracting. “I got a bladder pierced, but I didn’t want to,” the doctor will write a justification for this in the delivery protocol. Believe me, in childbirth, which you call "paid", the doctor will pierce the bladder in the same way and check the contractions of the uterus when it is vital for you and the baby inside.
We buy childbirth and a healthy baby
Often women, concluding a contract, go into the mode: "Give birth for me." That is, in this way they psychologically relieve themselves of responsibility for childbirth. Believe me, no one is able to give birth for a mother, either for free or for free: in any case, you will have to work on your own.
The same goes for a cesarean section. It's not worth paying for a contract birth if you just don't want to give birth yourself. No doctor will perform an operation without indications for it. Even if you pay for it. For money, you can only choose the method of delivery: vertical childbirth, childbirth in the bathroom, lotus, home. And then only if the conditions of the maternity hospital allow it and there are no contraindications. But you can't buy yourself an operation. Therefore, it is not even worth overpaying to save yourself from the "torment".
Also, do not sign a contract in the hope that this will guarantee you a healthy child. No doctor, no matter how experienced, can predict at the very beginning of labor how it will go. Unforeseen situations can happen even in a textbook process. The only plus in this situation that a contract can give is that the expectant mother can choose a doctor with whom she would be comfortable or who specializes in certain cases of pathologies, if any were diagnosed during pregnancy.
Paired childbirth
Often, ladies enter into a contract with a maternity hospital in order to go to a joint birth with her husband. Our legislation is such that a husband today can also attend free childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy. True, there is a small condition: the husband is allowed only if there is a free box. If there is none, the birth together may break.
When is it worth paying
The cost of the contract is determined by the number of options and services included in it. Everything here is very individual. For example, it is important for someone to stay in the VIP room, while for someone it is enough just to have an individual room. Some contracts include supervision of mom and baby after discharge from the hospital. Again, think about whether you need such an option, carefully review the range of services offered and assess their need for the proposed volume. Maybe you do not want to vaccinate the child or carry out any other procedures included in the contract with him. Situations can be very different, and it is worth starting from your preferences and characteristics of the course of pregnancy. The same is with the choice of a doctor. The definition of "dear and experienced doctor" is very vague. Choose a doctor for your pregnancy. If you are 25, this is your first birth and pregnancy is easy, this is one story any good doctor should deal with. If you are 45 and this is your first pregnancy after 15 IVF attempts, it is better to choose a more experienced doctor from a multidisciplinary clinic. A contract with such a doctor may be more expensive, but in a particular case, worth it.
Also, the contract can guarantee constant communication with the doctor up to around the clock. But, as practice shows, not such a large percentage of pregnant women and women in labor need such a connection. In addition, a contract will be required if after giving birth you want your relatives to come to you: without a contract and payment, such a function will not be provided in maternity hospitals.
However, there are situations when a woman, by coincidence and after a free delivery, is alone in the ward: both the child will be with her, and even the husband can be allowed in by agreement. But this is a matter of chance and is not guaranteed. If all these options are important for a young mother, then it is worth concluding a contract. If not, you can do without it. May every birth take place in conditions necessary and sufficient for the mother to be calm and comfortable!