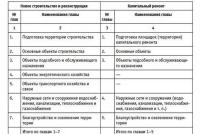
The organization bought a passenger car wiring. How an organization can write off expenses on auto parts. Income tax
The organization purchased a gazelle from a related company for 50,000 rubles, including 18% VAT. The organization applies the general taxation regime, PBU 18/02 does not apply. How to write off expenses in accounting and tax accounting for this vehicle? Do I have to pay property tax and transport tax?
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion:
In accounting, a used car worth over 40,000 rubles. accounted for as part of fixed assets in accordance with the generally established procedure. Depreciation is charged starting from the month following the month when the car was accepted for accounting.
For profit tax purposes, a car is not a depreciable property, its value is accounted for as part of material costs in one of the ways specified in paragraphs. 3 p. 1 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The car is subject to property tax in accordance with the generally established procedure. At the same time, the fact of its acquisition from an interdependent person excludes the possibility of using the privilege provided for in paragraph 25 of Art. 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Transport tax is paid in accordance with the generally established procedure. The constituent entity of the Russian Federation, on the territory of which the car is registered, may establish differentiated tax rates taking into account the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture vehicle, and / or their environmental class.
Rationale for the conclusion:
Accounting
In accounting, the purchased vehicle, which was in operation, is accounted for as part of fixed assets, if the conditions established in clause 4 of PBU 6/01 "Accounting for fixed assets" (hereinafter - PBU 6/01) are simultaneously met, namely:
intended for use in the manufacture of products, in the performance of work or the provision of services, for the managerial needs of the organization, or for provision by the organization for a fee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use;
is intended for use over a period of more than 12 months or a normal operating cycle if it exceeds 12 months;
its subsequent resale is not expected;
is able to bring economic benefits (income) to the organization in the future.
Assets in respect of which the conditions stipulated in clause 4 of PBU 6/01 are met, and the value within the limit established in accounting policy organizations, but not more than 40,000 rubles. per unit, can be reflected in accounting and accounting statements as part of inventories (hereinafter referred to as MPZ) (paragraph 4, clause 5 of PBU 6/01).
In the situation under consideration, the car purchased by the organization meets the above conditions and its cost without VAT exceeds 40,000 rubles. (50,000 rubles - VAT 18% \u003d 42,372 rubles), therefore, is subject to reflection in the composition of fixed assets, and the costs of its acquisition are accounted for in the manner prescribed by PBU 6/01.
A car purchased for a fee is accepted for accounting at its initial cost, which is formed from the actual costs of the organization for its purchase (excluding VAT). The actual costs of the acquisition, construction and manufacture of fixed assets are, in particular, the amounts paid (payable) in accordance with the agreement to the seller (clauses 7, 8 PBU 6/01, clause 24 of the Methodological Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 13.10.2003 N 91n).
This rule also applies to previously purchased fixed assets.
The cost of buying a car is reflected
Debit, subaccount "Purchase of fixed assets" Credit
- reflects the initial cost of the purchased car;
Debit Credit, subaccount "Purchase of fixed assets"
- the car was put into operation.
At the same time, the accounting rules do not make the moment of acceptance of the car for accounting as a fixed asset dependent on the fact of registration of vehicles with the traffic police, since such registration does not confirm the readiness of the car for operation. Based on the provisions of Art. 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a motor vehicle is a movable thing. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 164 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, state registration of transactions with movable property is not required, except in cases provided by law. The need to register transactions with vehicles, as well as the ownership of vehicles, is not established by law. And the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 12.08.1994 N 938 "On state registration of motor vehicles and other types of self-propelled equipment on the territory of the Russian Federation" only regulates the procedure for registering the motor vehicle itself with government agencies.
The cost of fixed assets is repaid through depreciation (clause 17 of PBU 6/01).
Accrual of depreciation on previously used fixed assets is carried out in accordance with the generally established procedure starting from the first day of the month following the month of their acceptance for accounting (clause 21 PBU 6/01).
The annual amount of depreciation deductions is determined in accordance with clause 19 of PBU 6/01, taking into account the useful life of the asset.
The useful life of a car (both new and used) is determined by the organization independently based on (clause 20 PBU 6/01, clause 59 of the Methodological Instructions):
the expected life of this item in accordance with the expected performance or capacity;
expected physical wear and tear, depending on the operating mode (number of shifts), natural conditions and the influence of an aggressive environment, the repair system;
regulatory and other restrictions on the use of this property (for example, the lease period).
The procedure for determining the useful life when accepting fixed assets for accounting should be reflected in the accounting policy of the organization for accounting purposes.
Note that since 01.01.2017, changes have been made to the Classification of fixed assets included in the classification approved by the Government of the Russian Federation of 01.01.2002 N 1. In particular, the provision on the possibility of its use for accounting purposes has been excluded (clause 1 of the Amendments approved by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 07.07.2016 N 640)).
Thus, the organization has the right for accounting purposes to independently determine for the used fixed asset, guided by clause 20 PBU 6/01 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 27, 2006 N 03-06-01-04 / 77).
Accordingly, starting from the month following the month of accepting the car for accounting, and until the full repayment of its value or writing it off the accounting, depreciation is charged:
Debit, (44) Credit
- depreciation is charged for the corresponding month.
The amounts of VAT charged to the taxpayer when purchasing goods (works, services, property rights) are deductible if the following conditions are met simultaneously:
the purchased goods (works, services, property rights) are intended for the performance of transactions subject to VAT or for resale (clause 2 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
goods (works, services, property rights) are taken into account on the basis of the relevant primary documents (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
there are duly executed invoices of the seller (clause 1 of article 172, clause 2 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for any peculiarities for the acceptance of VAT amounts for deduction when purchasing second-hand property.
Accordingly, the right to deduct VAT on a car purchased for production activities arises from the organization in the tax period in which the car was accepted for accounting on the basis of the relevant primary documents, if there is an invoice from the seller (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 01.10.2009 N 03-07-11 / 244).
Income tax
In tax accounting, a car is recognized as a depreciable property if it simultaneously meets the following conditions (clause 1 of article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
is owned by the taxpayer;
used by the taxpayer to generate income;
useful life is more than 12 months;
with an initial value of more than 100,000 rubles (the cost criterion of 100,000 rubles is valid from 01/01/2016 and applies to depreciable property items put into operation starting from 01/01/2016 on the basis of clauses 7, 8, article 2, part 4 , 7 Article 5 of the Federal Law of 08.06.2015 N 150-FZ).
The initial cost of a fixed asset, regardless of whether it is new or used, is defined as the sum of the costs of its acquisition, construction, manufacturing, delivery and bringing it to a condition in which it is suitable for use, minus VAT and excise taxes (cl. 1 article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The presence of interdependence with the seller does not affect the procedure for determining its initial value.
The useful life of a used fixed asset for tax purposes is determined taking into account the provisions of cl. 1, 7 and 12 Art. 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, establishing the possibility of determining the useful life for a used object, taking into account its period of use by the previous owner.
Since the value of property is one of the mandatory features of depreciable property for the purpose of calculating income tax, we believe that in the situation under consideration, a car with an initial value of less than 100,000 rubles is not depreciable property, the value of which is repaid through depreciation.
The cost of acquiring property that is not depreciable property, based on paragraphs. 3 p. 1 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation refer to material costs. The cost of such property is included in the composition of material costs in full as it is put into operation. In this case, the taxpayer has the right to choose the procedure for writing off the value of property that is not recognized as depreciable for tax purposes, namely:
take into account in expenses at a time on the date of putting the asset into operation;
to take into account during several reporting periods in an order independently determined by the organization, and such a procedure should be developed taking into account economically justified indicators, in particular, taking into account the period of use of the property.
The applied procedure must be fixed in the accounting policy for tax purposes (letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/20/2016 N 03-03-06 / 1/29124).
Accordingly, in the situation under consideration, the cost of the car is taken into account as part of material costs in one of the ways specified in paragraphs. 3 p. 1 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note that there are no official explanations in relation to the situation under consideration * (1). We believe that the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia presented in the letter dated 09.02.11 N 03-03-06 / 2/29 testify indirectly to the possibility of accounting for the property acquired by the organization as part of material costs.
In addition, in the resolution of the CA of the East Siberian District of January 19, 2017 N F02-7680 / 16, the judges also concluded that one of the mandatory signs of depreciable property for the purpose of calculating income tax is that the value of this property at the time of its adoption by the taxpayer to be recorded is more than the established limit. In such circumstances, the references to the provisions of paragraphs 1, 5, 7 of Art. 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which determine the procedure for calculating the useful life of depreciable property, do not confirm that the disputed property is depreciable.
Corporate property tax
Organizations with property recognized as an object of taxation in accordance with Art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are recognized as taxpayers of tax (clause 1 of article 373 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The car purchased by the organization, recorded on the balance sheet of the organization as an object of fixed assets in accordance with the established accounting procedure, on the basis of clause 1 of Art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is recognized as an object of taxation as tax on the property of organizations.
The specifics of taxation for used property are not defined. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base for tax is determined as the average annual value of property recognized as an object of taxation, unless otherwise provided by Art. 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, the organization will not be able to take advantage of the stipulated in paragraph 25 of Art. 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation with a benefit, on the basis of which movable property (including a car) registered by an organization since 2013 and accounted for as fixed assets is not subject to corporate property tax, since this benefit does not apply to cases of acquiring such objects from related parties (see, for example, the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia from 30.08.2017 N 03-05-05-01 / 55522).
Accordingly, the purchased car is subject to corporate property tax in accordance with the generally established procedure.
Transport tax
Transport tax in accordance with Ch. 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is established and enacted by the laws of the subjects of the Russian Federation on tax and is obligatory for payment on the territory of the corresponding subject of the Russian Federation (Article 356 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Based on Art. 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a car purchased by an organization, registered in accordance with the established procedure in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, is subject to taxation for transport tax, regardless of whether it is new or used (see also the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 09/08/2011 N 03- 05-04-04 / 10).
The presence of interdependence with the seller of the vehicle or the period of use of the car by the previous owner does not affect the determination of the presence of the object of taxation.
The transport tax rates are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in the amounts specified in paragraph 1 of Art. 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depending on engine power, jet engine thrust or gross tonnage of a vehicle (TC) per one horsepower of vehicle engine power, one kilogram of jet engine thrust, one registered ton of a vehicle or one vehicle unit.
By the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, tax rates can be increased (decreased), but not more than tenfold (clause 2 of article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, it is allowed to establish differentiated tax rates in relation to each category of vehicles, as well as taking into account the number of years that have passed since the year of production of vehicles and (or) their environmental class (clause 3 of article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, when determining the rate of transport tax on a purchased used car, it is necessary to be guided by the relevant law of the subject in whose territory it is registered (see also the letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 12.01.2017 N 03-05-06-04 / 484, dated 04.10.2013 N 03 -05-06-04 / 41282). Note, in particular, that the tax rates established on the territory of the city of Moscow are currently not differentiated depending on the year of manufacture of the car (Law of Moscow dated 09.07.2008 N 33 "On transport tax").
It should also be borne in mind that established in clause 1 of Art. 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, transport tax rates, in addition to engine power, are differentiated depending on the type of vehicle (for example, cars, buses, trucks, etc.) (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02.06.2016 N BS-3-11 / 2508 @ ).
According to the explanations of the financial department, the category of a vehicle for tax purposes should be determined based on its type and purpose (category) indicated in the vehicle's passport (hereinafter referred to as PTS) on the basis of its type approval. At the same time, the main indicator for the purposes of taxing transport tax is the type of vehicle specified in the TCP, since vehicles of the same category may have a different type depending on the purpose (car, truck or bus) (see, for example , letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 10.12.2013 N 03-05-06-04 / 54111, dated 13.08.2012 N 03-05-06-04 / 137, dated 21.10.2010 N 03-05-06-04 / 251, dated 19.03.2010 N 03-05-05-04 / 05, dated 01.07.2009 N 03-05-06-04 / 105, dated 07.02.2008 N 03-05-04-04 / 01, dated 17.01.2008 N 03 -05-04-01 / 1).
In the absence of information about its type in the vehicle's passport or in case of disagreement with taxpayers tax authorities has the right on this issue to apply to the competent authorities and organizations authorized to issue passports of vehicles in accordance with paragraph 2 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 18.05.1993 N 477 "On the introduction of passports of vehicles" (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of 01.07.2009 N 03-05 -06-04 / 105).
Prepared by:
Expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT
auditor, PCA member, professional accountant Makarenko Elena
Answer passed quality control
The material was prepared on the basis of an individual written consultation provided as part of the Legal Consulting service.
* (1) In the event of receipt of property as a result of reorganization, a fixed asset that was in use, in the opinion of the authorized bodies, is not excluded from the composition of the depreciable property by the new owner, regardless of the remaining useful life and value (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 12.05.2005 N 07-05-06 / 138, dated 01.04.2008 N 03-03-06 / 1/241, the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Moscow dated 26.04.2010 N 16-15 / 043777 @).
In preparing this chapter, information was used from the book by MN Agafonova "A car at your enterprise" published by Berator-Press, 2003. I highly recommend it to anyone interested in additional nuances of accounting entries. There you can also find samples of various statements, acts, contracts and other necessary documents.
Special thanks to Alexander Vladimirovich Borodavkin for the advice on the organization of the car fleet.
The chapter is boring enough. The main content is devoted to the design and maintenance of the car on the balance sheet of the organization or rental. When I figured out all this, I became disheartened, as it seems that this should not be done. But, having calmed down a bit, he made the following conclusions: Because of one car, it is not profitable and ineffective to open your own car fleet. The main problems arise at the stage of creation and formation of the organization's vehicle use system. The accountant must either have sufficient qualifications to work with the vehicle fleet, or be ready for the appearance of vehicles on the balance sheet of the organization and not particularly resist innovation. If a small number of cars (1-3) are planned, then at the initial stage it is better to attract a strong specialist for the organization of a motor vehicle fleet for a short period (about two months), pay him decently and then involve him for consultations, doing on his own. The use of cars, especially cars, by an enterprise for its own needs is much easier than for maintenance
third party organizations and individuals.
If there are already at least two cars, and not one, it makes more sense to open a car fleet and write off its maintenance costs, saving on taxes and shifting responsibility from you, as an individual, to a legal entity. In addition, the organization has the opportunity to buy a car not only for cash and on credit, but on lease. Leasing needs to be carefully calculated, but the scheme is attractive.
In general, the content of the chapter shows the labor intensity of organizing a motor vehicle fleet, the need for documentary registration, control and write-off of fuels and lubricants (fuels and lubricants), spare parts and consumables, as well as an additional burden on accountants. You, as a leader, must be prepared for these difficulties, some inconveniences and costs.
Let's move on to the regulatory framework and comments to it.
There are various ways an organization can obtain vehicles, namely: buying, renting, using free of charge, reimbursing its employees for the costs of using their own vehicles for business purposes. All these operations are reflected by the accounting department in its work. Accounting for these transactions is carried out according to the same rules, both at large and small enterprises.
According to PBU (Regulation on accounting) 6/01, vehicles are classified as fixed assets. In order to accept a vehicle purchased by your company for accounting as a fixed asset, the following conditions must be met, as defined in PBU 6/01: the vehicle is used in the production process or for administrative needs; its useful life is over 12 months; the car was not purchased for the purpose of resale; the use of a car is necessary for the implementation of the normal production or management process, as a result of which the company receives economic benefits (income).
Compliance with these requirements will allow you to correctly attribute to costs everything that relates to the maintenance and operation of the car in your organization.
In accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 12, 1994 No. 938 "On state registration of motor vehicles and other types of self-propelled equipment on the territory of the Russian Federation" (as amended on February 21, 2002), the owners must register their vehicles within the validity period of the "Transit" registration plate or within five days from the date of purchase, customs clearance, deregistration of vehicles, replacement of number units or the occurrence of other circumstances that required a change in registration data. The vehicles of the subdivision of the State Inspectorate for Traffic Safety of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation are registered. Registration of vehicles and changes in their registration data are made on the basis of the passports of the corresponding vehicles, certificates, accounts,
issued by manufacturing enterprises, trade enterprises, citizens-entrepreneurs who have licenses for the right to trade in vehicles, or other documents certifying the ownership of the owner of vehicles and confirming the possibility of admitting them to operation on the territory of the Russian Federation. If your organization purchases a car from another organization on the balance sheet of which it was included in fixed assets, then in order to register the car, you must submit a purchase and sale agreement with an acceptance certificate. The organization pays a registration fee for registering a vehicle. In the traffic police department, a certificate of registration of the vehicle, state number plates are issued and a mark is made in the technical passport of the vehicle about registration.
After the state registration of the car, the organization puts it into operation. Commissioning and acceptance of the car for accounting as a fixed asset are carried out on the basis of the order of the head of the enterprise.
If the organization has transport, it pays transport tax. Tax period - calendar year, reporting periods - first quarter, second quarter, third quarter. The procedure and terms for the payment of this tax are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Vst. 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides a table of tax rates for all objects of taxation with transport tax. It is basic. The tax rates indicated in it can be increased or decreased by local laws for each specific region, but not more than five times. The amount of tax rates depends on the engine power.
In accordance with Federal Law No. 7-FZ of January 10, 2002 "On Environmental Protection", all organizations operating motor vehicles (both their own and rented) are charged for the emission of pollutants into the atmosphere from mobile sources ... According to Art. 6 of this Law, standards in the field of protection environment must be established by the state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. At present, the procedure for determining the payment and its maximum size is regulated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 28, 1992 No. 632. This resolution was adopted in accordance with the Law of the RSFSR of December 19, 1991 No. 2060-1. According to this resolution, the basic standards of payment are established for each ingredient of a pollutant, type of harmful effect, taking into account the degree of their danger to the environment and public health. For individual regions, coefficients are established to the basic rates of payment, taking into account environmental factors. The size of the annual payment for environmental pollution by motor vehicles is determined in one of the following ways: by the amount of fuel consumed, taking into account the established unit payment for all its types; by the number and type of vehicles in operation, taking into account the established annual payment for one vehicle.
As a rule, the organization registers the purchased vehicle with the traffic police at the place of its location. it
means that the company is already registered with the tax office as a taxpayer. Does he need to be re-registered as the owner of the vehicle? The tax authorities give an unequivocal answer to this question - it is required. Therefore,
in order to avoid conflict situations, you need to draw up all the necessary documents within the time frame provided by law.
In order to attribute to expenses everything related to the car, it is taken into account in balance sheet at the original cost. The formation of the initial cost depends on the method of purchasing this product. These methods include: purchase; capital contribution; free receipt; exchange.
The purchase is most relevant to us. Bought - put on balance sheet, you operate, pay taxes. In this case, the cost of a vehicle is subject to write-off from accounting in the following cases: sale; gratuitous transfer; moral and physical wear and tear; liquidation in case of accidents, natural disasters and other emergencies; transfers in the form of a contribution to the authorized (pooled) capital of other organizations.
This means that when you buy a car, you start to amortize it and pay transport tax and environmental tax. After some time, you will get rid of it. When selling, you can set any price. You will pay income tax from the difference between the residual (book) value and the sale price (the calculation is not the easiest, but the meaning is exactly that). Residual value is the difference between the initial cost and the depreciation amount.
To operate the car, you will need fuels and lubricants and special fluids. These include fuels (gasoline, diesel fuel, LPG, compressed natural gas), lubricants (motor, gear and special oils, greases), special fluids (brake and cooling). The accounting department of the enterprise maintains quantitative and total accounting of fuels and lubricants and special fluids. Refueling of vehicles is carried out at gas stations for cash or by bank transfer using coupons.
When purchasing fuel and lubricants for cash, the following rules must be observed. The head of the enterprise issues an order in which he determines the circle of persons entitled to receive cash money at the cash desk of the enterprise against the report on the purchase of fuels and lubricants. This order should set the deadline for submitting advance reports to the accounting department. Cash register receipts issued by a gas station (gas station) are attached to the advance report. The cash register receipt must contain the following data:
About the name of the selling organization (gas station);
About the TIN (taxpayer identification number) of the seller organization;
О cash register number;
Number and date of issue of the check;
About the cost of fuels and lubricants including VAT;
About the brand of fuels and lubricants, the amount of fuel and the price per unit. These details are not required for a cash register check. However, most gas stations now issue just such checks. If the check does not contain the specified details, then the gas station issues a sales receipt.
Fuel costs are usually high and VAT cannot always be offset. This is due to the fact that VAT is not allocated from the cost of fuels and lubricants by calculation. For gas stations, the sale of fuels and lubricants with the issuance of a cash register check is retail trade, and Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the acceptance for tax deduction of the amount of VAT allocated by calculation from cash register checks. To offset VAT, it is necessary to work with fuel companies by bank transfer using fuel coupons or fuel cards.
Accounting and tax regulations do not establish maximum norms for attributing to the prime cost the costs associated with the use of fuels and lubricants in the transportation process. The only condition for writing off fuels and lubricants at the prime cost is the availability of documents confirming the fact of their use in the production process. Therefore, each organization has the right to independently determine the consumption rates of fuel, lubricants and special fluids, taking into account the technological features of its production. The organization develops such standards to control the consumption of fuels and lubricants for the operation, maintenance and repair of automotive equipment. They are approved by order of the head of the organization. All drivers of vehicles are introduced to the order. The norms must be real. Otherwise, there will be abuse by drivers and "burned out" of the fuel and, therefore, unnecessary additional costs. These standards are developed by the person in charge of the motor vehicle fleet. For a personal car, you have the right to set fuel consumption rates that are suitable for you.
Please note that in accordance with the provisions of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (income tax), for tax purposes only documented and economically justified expenses are accepted. The consumption of fuels and lubricants can be considered economically justified if it is made according to the norms approved by the head.
When developing standards, organizations are guided by the Standards for the consumption of fuels and lubricants in road transport (Guidance document Р3112194-0366-03), approved by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation on April 29, 2003. These standards are valid until January 1, 2008, then new ones will be introduced. The document contains the values \u200b\u200bof the basic fuel consumption rates for vehicle rolling stock, fuel consumption rates for the operation of special equipment installed on vehicles, and the methodology for their application, as well as the standards for the consumption of lubricating oils. Regulatory materials are intended for all organizations operating automotive equipment in the Russian Federation. Fuel consumption rates are set for each brand and modification of vehicles in use and correspond to certain operating conditions for road transport. Fuel consumption for garage and other household needs is not included in the standards and is set separately.
Write-off of fuels and lubricants to the cost of transportation is carried out on the basis of waybills. In the waybill, readings of the speedometer and fuel consumption indicators are put down. These data are recorded in the waybill by a mechanic or other authorized person. The waybill must also indicate the exact route of travel, confirming the production nature of transport costs. “Exact” means route guidance. For example, St. Petersburg - Tver - Moscow, St. Petersburg and Leningradskaya
region. It is undesirable to indicate the Russian Federation or the Republic of Karelia.
During operation, spare parts are required. They can be made in-house, come from suppliers or accountable persons purchasing materials for cash. All purchased spare parts are received at the warehouse. The financially responsible person, on the day the valuables arrive at the warehouse, draws up a receipt in one copy in the form No. M-4. A receipt warrant is issued for the actually accepted amount of values. Parts arriving at the warehouse are assigned a stock number. For each nomenclature number, a material accounting card in the form No. M-17 is opened. Entries in the card are kept by the materially responsible person on the basis of primary receipts and expenditures on the day of the transaction.
The representative of the repair shop (or the driver, garage mechanic or other appointed person, if the company does not have a repair service) receives spare parts from the warehouse on demand-invoice form No. M-11. The waybill in duplicate is drawn up by the materially responsible person of the warehouse that hand over material assets. It is signed by the deliverer and recipient of the spare parts. New spare parts are handed out from the storeroom only in exchange for worn ones. Worn out spare parts to be repaired are transferred to the repair shop (section), and after repair they are returned to the warehouse. Spare parts that are not suitable for further use are activated and arrive in the storeroom by the mass of scrap, like other materials.
Within the time frame established by the organization, the materially responsible person of the warehouse submits to the accounting department a material report in the form of a register of incoming and outgoing documents with attached primary documents.
The rules for documenting the movement of materials are the same for all enterprises, both large and very small, with up to 10 employees. Even in a small organization, there should be a supply manager (or an employee performing the functions of a supply manager) who keeps a documentary record of material assets acquired by the organization and spent in the process of economic activity. Such material assets include not only spare parts, fuel, but also office supplies, industrial and household equipment with a service life of less than 12 months, etc. In a small enterprise, you can not draw up a bill of lading in the form of M-11, but issue the release of materials directly in the material accounting card of form No. M-17, in which the recipient of the materials signs. (The relief is minimal. As the saying goes: "horseradish is not sweeter than a radish.")
Automobile tires (tires, tubes and rim tapes) that are in the warehouse and in the working capital (in the turnover of the technical maintenance service, the tire shop, in stock on technical assistance vehicles) are standardized and accounted for as working capital. Tires supplied to an enterprise with a car (on wheels and in stock with a vehicle) are included in its initial cost and accounted for as property, plant and equipment.
A record card is kept for each tire, which reflects all movements, defects received, repairs, the number of kilometers traveled. Tire accounting cards are kept by a tire accounting technician or another person appointed by order of the head of the enterprise. The card is the basis for writing off tires for unsuitability, for filing complaints with manufacturers and tire repair plants in case of failure to fulfill the warranty mileage due to their fault. Replacement of worn-out tires with new ones is carried out after the normative operational mileage has been completed. If the tires are not running, the reasons are found out (fault
driver, manufacturer, etc.), which are reflected in the write-off certificate. Car tires from the warehouse are issued only in exchange for returned tires that are subject to restoration or scrapping. Upon delivery, an act of complete unsuitability of tires is drawn up, which indicates: the size of each tire or tube, its serial number, model, nature of damage and mileage. Tires in need of repair are handed over on demand-invoice (form No. M-11) to the vulcanization workshop of the enterprise or a third-party organization under the act of transfer.
Any car needs repair. Depending on the complexity and duration of work, major, medium and current repairs are distinguished. During the overhaul of vehicles, a complete disassembly of the unit, repair of base and body parts and assemblies, restoration or replacement of all worn parts and assemblies with new ones, assembly, regulation, testing is carried out. As a result of modernization, there is an improvement in the standard indicators of the functioning of the vehicle (useful life, power and other technical characteristics). For example, the cost of replacing a car engine with a more powerful one is capital in nature and increases the initial cost of the car. After overhaul, the car receives a new mileage standard until the next overhaul - this is at least 80% of the resource of the new car. With average and current repairs, partial disassembly and replacement of parts and assemblies of the car is carried out.
Carrying out all types of repairs requires compliance with certain documentary rules. Before the beginning of the reporting year, the company draws up a plan for the maintenance and repair of rolling stock. A special commission established at the enterprise draws up a technical inspection report and a defective statement for each car being repaired. These documents indicate: the work to be performed, the timing of the beginning and end of the repair, the parts planned for replacement, the time norms for the work and the manufacture of the replaced parts. The enterprise develops the forms of acts and defective statements independently. On the basis of the defective statement, an estimate is made for the repair. The estimate can be made by the relevant technical service of the enterprise or a third-party specialized organization. The defective statement and estimate are approved by the head of the enterprise. If the repair is carried out in an economic way, then the engineering and technical service of the enterprise (for example, the department of the chief mechanic, the department of major repairs, etc.) writes out work orders according to the data of the defective statement. The first copy of the order is transferred to the repair shop, the second to the accounting department, the third remains in the engineering and technical service to control the timing of the repair work. The accounting department maintains analytical records for the order. On the basis of the defective statement and along with the order, documents are written out to receive from the warehouse the spare parts and materials necessary for the repair, as well as work orders for the manufacture and restoration of individual units and parts. The transfer of the car for repair, both to the repair shop of the enterprise, and to a third-party organization, is carried out on the basis of an act. The act is signed by the delivering and receiving parties. If the repair is carried out by a third-party organization, then the act is drawn up in 2 copies (one for each party). Upon completion of the overhaul, an acceptance certificate is drawn up for the repaired, reconstructed and modernized
objects in the form No. OS-3. When carrying out repair work by a third-party organization, an act in the form of OS-3 is also drawn up in 2 copies. Having received the act of form No. OS-3, the accountant makes an entry in the vehicle inventory card (form No. OS-6) about the work performed.
The car on the balance sheet of the organization is insured. OSAGO is inevitable, and CASCO is optional. Everything is like a private person. For the organization, a compulsory car insurance policy is issued impersonally, that is, without restrictions on drivers.
Every day, before the release of cars on the line, a mechanic inspects them and makes a note in the waybill about the technical serviceability of the car. In enterprises with a large fleet of cars, the mechanic is a full-time employee of the enterprise. He undergoes special training and receives a certificate for the right to admit technically sound vehicles to work. Organizations that do not have a full-time specialist must conclude an agreement with a car repair organization or a car service company, in whose states there are trained mechanics. The costs associated with the daily production of vehicles on the line are charged to cost accounting.
Employees engaged in work related to traffic undergo preliminary (upon admission to work) and periodic (persons under the age of 21 - annual) medical examinations to determine their suitability for the assigned work and prevent occupational diseases (Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ). In accordance with Art. 185 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during the time spent on a medical examination, employees who are obliged to undergo such an examination retain the average earnings at the place of work. Medical examination is carried out during working hours. Currently, medical examinations have become paid. The cost of compulsory medical examinations is charged to the cost of products (works, services) under the item “Expenses for ensuring normal working conditions and safety measures”.
In addition to periodic medical examinations, drivers are required to undergo daily medical control before going on a flight. This control is carried out by a medical institution with which the organization enters into an agreement, or a medical worker who is on the staff of the organization. The contract for daily medical control is concluded with a medical institution that has an appropriate license. A medical worker working at an enterprise under an employment contract (on a permanent basis or on a part-time basis) must have a document on medical education and an appropriate license.
In the waybill in the section on the driver's health, an entry is made daily or a stamp “Medical control (examination) passed” is put down. This record is certified by the signature of a medical worker.
If you are going to use the car to provide services to other organizations and individuals, you will need a license. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 402 of June 10, 2002 approved the Regulation on the licensing of passenger and cargo transportation by road. This Regulation determines the procedure for licensing transportation of: passengers on a commercial basis by light automobile transport; passengers by road, equipped for the carriage of more than eight people (unless the specified activity is carried out to meet the own needs of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur); cargo by road with a carrying capacity of over 3.5 tons (unless the specified activity is carried out to meet the own needs of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur).
For each of the listed types of activities, you must issue a separate license. The licensing authority is the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation. The license is granted for five years. Simultaneously with the license, a license card is issued for each vehicle. When carrying out licensed activities, this card must be with the driver of the vehicle.
To obtain a license, an organization must submit the following documents to the licensing authority: an application for a license; copies of constituent documents; a copy of the certificate of state registration and tax registration; copies of documents that confirm the compliance of the qualifications of the organization's employees with the established requirements for transportation by the relevant road transport; copies of documents confirming the passage of the relevant certification by the officials of the organization responsible for ensuring road safety;
information about vehicles; a document confirming the payment of the license fee.
The decision to issue a license is made within 30 days from the date the licensing authority receives the application and all the necessary documents.
If, during the period of validity of the license, the organization changes in the composition and number of vehicles, then it must inform the licensing authority about each change in writing within 15 days.
A situation may arise when you decide to use your own car or an employee's car for business purposes. It is possible. According to Art. 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees are paid compensation for the wear and tear of personal vehicles and reimbursed for expenses if personal vehicles are used with the consent of the employer for business purposes. The amount of reimbursement of expenses is determined by the agreement of the parties to the employment contract, expressed in writing. Compensation for the use of personal transport for business purposes may be paid to employees if the production (official) activities of employees are associated with constant traveling and employees use personal cars for business trips. In this case, the employee must submit to the accounting department of the organization a copy of the technical passport of the personal car, certified in accordance with the established procedure. If an employee drives a car by power of attorney, then he must submit to the accounting department copies of the technical passport and power of attorney of the car owner. The amount of compensation depends on the intensity of the use of a personal car for business trips. The compensation should provide reimbursement of the employee's expenses related to the operation of the vehicle for official purposes. Compensation is considered according to a special formula - we will not consider it, it will take a third of the chapter.
Compensation is calculated based on the order of the head of the organization. Compensation is calculated monthly in a fixed amount, regardless of the number of calendar days in the month. Compensation is not charged only for the days the employee is on vacation, business trip, as well as for the days of absence from work due to temporary disability or for other reasons.
By Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated November 28, 1997 No. 78, the following forms of primary documentation for accounting work were approved
motor transport: logbook of waybills (form No. 8); waybill of a car (form No. 3); waybill of a special vehicle (form No. 3 (special)); passenger taxi waybill (form No. 4); waybill of a truck (form No. 4-c, form No. 4-p); bus waybill (form No. 6); waybill of a non-public bus (form No. 6 (special)); consignment note (form No. 1-T).
The waybill is the primary document for accounting for the operation of vehicles and the basis for accruing wages drivers. This document is issued in one copy by the dispatcher or an authorized person (the authorized person is appointed by order of the head of the organization). The waybill must contain a serial number, date of issue, stamp and seal of the organization that owns the car.
The waybill is valid for one day or shift only. For a longer period, it is issued only in the event of a business trip, when the driver performs the task for more than one day (shift). Every day before the start of the working day, the driver receives a waybill against receipt, and at the end of the shift returns it to the dispatch office. The waybill for the next day (shift) is issued to the driver, provided that he has passed the waybill of the previous day of work.
When using their own light motor vehicles, organizations have the right to independently develop, approve and apply their own waybill form. It is allowed to use a joint waybill and a waybill valid for a calendar month. This is explained by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility for the correct execution of the waybill is borne by the heads of the organization and persons responsible for the operation of vehicles and participating in filling out the document.
The register of waybills movement (form No. 8) is used by the organization to register waybills issued to the driver and handed over after processing to the accounting department.
Everything seems to be. Which of the above follows? The organization must have someone responsible for the car fleet. You will have to sign a large number of documents when setting up the process and sign continuously in the ongoing work. If it works out - try to delve into what you are signing, it will not work - sign, trusting the person in charge.
The opening of the car fleet directly is carried out simultaneously with the registration of the first car. When opening a car fleet, documents are submitted to the MREO. Specify the list of documents there, mostly copies of constituent documents. The transport can stand on a site equipped with fire extinguishing equipment, suitable for the requirements of the SES, there must be an opportunity for qualified maintenance and repair of the car. If your organization does not have the appropriate capabilities, you will have to conclude fake contracts with organizations that have such capabilities and provide these services.
After the opening of a car fleet and registration, the organization's vehicles must be registered with the military registration and enlistment office. The procedure is quite routine.
This is basically everything about the car on the balance sheet of the organization. In reality, everything is not so scary and quite feasible, but it is necessary to organize in full. Get ready.
You will need
- Passport, certificate of registration of the charter of the enterprise, its copy, application for registration, information letter from Goskomstat, certificate of the presence of premises (own or rented), as well as an extract from the order "On setting a car on the balance of the organization."
Instructions
Remember that to register a car legal entity you need to have full information about the organization, including the name of the head, the person in charge, the accountant, the working phones of all the specified persons. Naturally, you must have a passport, a charter registration certificate, a copy of it, an application for registration, an information letter from Goskomstat, a certificate of the presence of premises (own or rented), as well as an extract from the order "On putting a car on the balance of the organization."
After that, you can put the car on the balance sheet, that is, put it into operation. Include all expenses for the state registration of the vehicle in the initial cost, that is, take it to account 08 in the company's balance sheet. After registration, transfer the car to account 01, which contains the fixed assets in operation. Remember that it is prohibited by law to operate a car without state registration.
The car must be on the balance sheet of the organization as long as it is used in the course of its activities. Remember that it is subject to the same taxes and fees as other property assets in the company's accounts, so you should not just enter the car into the balance sheet.
Every major metropolis has a large number of car dealerships that offer a wide range of vehicles to their customers. Many buyers, walking slowly through these stores, secretly dream of owning their own salon.
You will need
- - Investments;
- - Dealer agreement;
- - Premises of 600-700 square meters.
Instructions
The first and key point when opening a car store is choosing a location. An ideal option is a salon along one of the busiest streets in the city. You can even settle down on the outskirts, if the whole city in which you live can be traveled in three quarters of an hour.
In addition, you need to choose the brand whose products you will present in your store. You need to conclude a dealer agreement with the copyright holders of the brand, then you can freely engage in the sale of cars.
Experts recommend not only organizing a car dealership. A much greater effect will be produced by a large center, where customers can also use the services of a service center and purchase the necessary spare parts. It will be much more convenient for potential buyers to carry out all operations with their car in one place than to visit several places.
To create a modern one, about 650-700 square meters are needed, 250 of which will be reserved for a showroom (a place for showing models), 300-350 - for, and the remaining area will be occupied by premises for the administration. For a showroom, it is necessary to allocate a lot of space (on average 35 sq.m.) so that a potential buyer can freely familiarize himself with the offered product.
The minimum construction costs can range from 600 thousand to one and a half million dollars. On average, the payback period for an enterprise is five to six years. The size of the attachments can fluctuate depending on which brand you represent. If you are a dealer of a well-promoted brand (BMW, Volkswagen, Lexus, etc.), then it is likely that the concern may send its own architect to you to design the design of your interior. As a rule, his services are paid from the fund. But you will have to pay for the services of a designer.
In addition, technical conditions will affect the construction budget. If it is necessary to complete some additional premises or to rebuild the entrance, then this can take up to three hundred thousand dollars. If a car dealership needs to be built from scratch, then the bill can go for millions of dollars.
Sources:
- how to organize a car show
If your business does not have its own vehicles, which are expensive to maintain, then you can rent a vehicle from an organization that specializes in this. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines the possibility of renting two types - with and without a crew (Articles 632 - 649 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).

Instructions
When concluding a vehicle lease agreement, be sure to indicate in it the data that allow you to uniquely identify this vehicle in the event of any dispute. In the contract, also reflect the condition of the vehicle at the time of its transfer from the lessor to the lessee.
Thus, the contract must include the brand and year of manufacture of the car, the body and engine numbers, and its state registration number. For an accurate description, please refer to the data sheet. Indicate in the contract the mileage numbers and the technical condition of the car and list the documents that must be handed over with it: registration certificate, registration certificate and technical inspection coupon. In addition, in it, you will also set the amount of rent, conditions and period of its payment.
When deciding which of the two types of lease to prefer, please note that in the case of a lease with a crew, the lessor is responsible for driving, operating, maintaining, repairing and insuring the vehicle. In addition, in this case, the lessor pays for the services of the crew members, bears the costs of their maintenance and responsibility for the damage caused. When the vehicle is rented without a crew, the listed costs are borne by the renter. But these nuances can be taken into account in the contract.
If you are a tenant, then keep the vehicle accounting separately from fixed assets and property belonging to your company, that is, for. This requirement is set out in paragraph 2 of Art. 8 of Federal Law No. 129-FZ of November 21, 1996. For accounting, use account 001 "Leased Fixed Assets". Estimate the vehicle at the amount indicated in the rental agreement.
To accept the costs of the rented vehicle and take them into account when taxing the profits of an enterprise, you need a package of documents, which must include: a vehicle lease agreement; acts of acceptance of services that were provided under this contract; payment documents confirming the costs of operating the vehicle; applications for the operation of a car rented from the company; the director's order on securing the rented car; waybills, which take into account the frequency of use of the vehicle, the time of its operation and travel routes.
Related Videos
Related article
Sources:
- Federal Law No. 129-FZ dated November 21, 1996
After purchasing a car, the organization must register it with the traffic police of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. The whole process is the same as when registering a car for an individual, the only difference is in the list of required documents.

The features of the organization's registration of the purchase of a car, the procedure for reflecting the costs of paying state duties, civil liability insurance, preparing a car for operation and other issues are considered.
Both new and used cars are purchased under a sales contract. If an organization buys a vehicle from a legal entity, then it is necessary to issue an invoice and a waybill for the car.
The purchased vehicle (hereinafter referred to as the vehicle) is reflected in the accounting records at its initial cost, which includes all actual costs associated with the purchase - the amount paid to the supplier; intermediary fees; payment for information and consulting services; other costs associated with the acquisition of the vehicle (clause 8 PBU 6/01). In most cases, the initial cost of the car in accounting and tax accounting is the same. The exception is interest on borrowed funds (clauses 2 clauses 1 of article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and fees for registering a car with the traffic police, which are not included in the initial tax value and are recognized as non-operating expenses.
The question of the date of acceptance of the car for accounting is important for obtaining the right to a tax deduction for VAT. \\ "Input \\" VAT on the purchased car is accepted for deduction only after reflection of the fixed asset (hereinafter - OS) on account 01 \\ "Fixed assets \\" subject to the conditions established by Art. 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely:
VAT is claimed for deduction in the territory of the Russian Federation or paid when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation;
the car was purchased for the implementation of transactions subject to VAT;
The VAT amount is presented based on the invoice.
If an organization accepts VAT deduction before registering a vehicle with the traffic police, then there is a risk that the tax authorities will refuse to deduct. Judicial practice on this issue has developed in favor of taxpayers, but in order to avoid a dispute with the regulatory authorities, it is advisable to take VAT deduction after registering the car with the traffic police.
In addition, without disputes with the tax authorities in the tax accounting, the car is included in the depreciable property only after commissioning, which is possible only after the registration of the vehicle with the traffic police is completed. Therefore, in accounting, you should put the car on record after its timely registration (see the letter of the Office of the Ministry of Taxes and Tax Collection of Russia in Moscow of 12.05.04, N 26-12 / 32341).
Since the situation regarding the moment when a car is accepted for accounting as an object of fixed assets is not legally regulated, an organization should reflect this issue in its accounting policy for accounting purposes.
When accepting a car for registration, you need to draw up an act in form N OS-1 and open an inventory card in form N OS-6 (approved by the decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 N 7).
The value is formed using account 08 \\ "Investments in non-current assets \\".
An organization that buys a car at the expense of funds received from income-generating activities subject to VAT should pay attention to the peculiarities of accounting for the \\ "input \\" VAT on the purchased car. The tax can be taken for deduction after the car is registered (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to the Federal Tax Service of Russia, this means that this operation is possible when the car is accounted for as part of the OS on account 01. And this does not happen before the car is registered and prepared for operation.
Having bought a car, the owner must register it with the traffic police. The terms of registration are determined by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 12.08.94 N 938 \\ "On the state registration of vehicles and other types of self-propelled equipment in the territory of the Russian Federation \\". You need to register within five days from the date of purchase or during the validity period of the registration plate \\ "Transit \\" (clause 3 of Resolution N 938).
For the state registration of the vehicle and other registration actions with vehicles, the payment of the state duty in the following amount is provided (clause 29 of article 333.33 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
RUB 400 - for the issuance of state registration plates for the vehicle;
RUB 200 - for the issuance of state registration plates for motor vehicles and trailers;
RUB 100 - for issuing a vehicle passport;
RUB 100 - for the issuance of a certificate of registration of the vehicle.
After completing the established actions, the organization receives a certificate of registration of the car, state number plates, technical passport of the vehicle with a mark of state registration.
In accounting, the costs of registering with the traffic police are attributed to the increase in the initial cost of fixed assets (clause 6 of PBU 6/01). However, this will only happen if payments were made before the car was accepted for accounting on account 01.
In tax accounting for calculating income tax on income-generating activities, state duty, like any other taxes, does not increase the cost of fixed assets. They should be written off to other expenses (clause 1 of article 257 and clause 1 of clause 1 of article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Note that the book value of the new car will be higher than the tax value.
From January 1, 2006, state duties are paid in accordance with the rules of Chapter 25.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In tax accounting, the costs of compulsory insurance, including civil liability insurance, refer to other costs within the insurance rates approved in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 3 of article 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If, under the terms of the insurance contract, the payment of the premium is provided in a single payment, then under contracts concluded for a period of more than one reporting period, expenses are recognized on a straight-line basis throughout the contract term in proportion to the number of calendar days of the contract in reporting period (Clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In order to avoid differences and the need to apply PBU 18/02, it is advisable to reflect in accounting the procedure for writing off such expenses in the same way as in tax accounting.
Example 1. An organization purchased a car on July 10, 2007. On July 14, 2007, an employee of the company issued an OSAGO policy, its validity period was from July 14, 2007 to July 13, 2008. The cost of insurance was 12,045 rubles. The accounting policy provides for the same procedure for writing off expenses for both accounting and tax accounting (that is, in proportion to the number of calendar days of the agreement in the reporting period).
Let's calculate the amount of insurance expenses in tax accounting.
For one calendar day, insurance costs will be 33 rubles. (RUB 12,045: 365 days). In the III quarter of 2007, part of the policy cost must be recognized as an expense (from July 14 to September 30, i.e. within 79 days). The amount of expenses will be:
for the III quarter of 2007 - 2607 rubles. (33 rubles x 79 days);
for the IV quarter of 2007 (92 days) - 3036 rubles. (33 rubles x 92 days);
for the I quarter of 2008 (90 days) - 2970 rubles. (33 rubles x 90 days);
for the II quarter of 2008 (91 days) - 3003 rubles. (33 rubles x 91 days);
for the III quarter of 2008 (13 days) - 429 rubles. (33 rubles x 13 days).
In accounting in July 2007 the following entries are made:
Debit 71, Credit 50 - 12,045 rubles. - the employee was given money from the cash desk for the purchase of the OSAGO policy,
Debit 76, Credit 71 - 12,045 rubles. - the employee has purchased a CTP policy,
Debit 97, Credit 76 - 12,045 rubles. - the CMTPL policy is included in the deferred expenses,
Debit 20 (25, 26, 44), Credit 97 - 594 rubles. (33 rubles x 18 days) - the cost of the OSAGO policy for July 2007 is taken into account.
Preparing the car for use
As a rule, car dealerships carry out all the procedures necessary for the normal operation of a new car (installation of crankcase protection and alarms, anti-corrosion coating, etc.). Their cost is included in the price of the car. But sometimes the organization that bought the car, independently or with the help of specialists from the car service, mounts additional sides, installs a better alarm or acoustic system, etc. If, for example, the alarm is installed before the vehicle is put into operation, then the money spent in this case should be included in its initial cost. This applies to both accounting and tax accounting.
Let us consider in more detail how to reflect in the accounting the cost of operations to prepare a car for operation.
The original cost of the car can only be changed if it is retrofitted or modernized, which lead to a change in the technological or service purpose of the car (clause 2 of article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since there are no such changes in connection with the installation of an alarm on a car that is already in use, the alarm must be taken into account as part of the cost of purchasing materials for account 10 \\ "Materials \\".
The price of the car radio is not included in the initial cost of the car. The radio tape recorder is accounted for as a separate inventory item as part of the fixed asset on account 01.
In addition, for a new car, they buy a set of winter tires that last more than one year and are often not cheap. However, they also do not need to be included in the initial cost of the car, since winter tires can be installed on several cars in turn. There are no special rules for accounting for winter tires in tax accounting. Their cost is taken into account as part of material costs on the basis of paragraphs. 7 p. 1 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that material costs include the amounts spent on the maintenance and operation of the OS.
In accounting, winter tires are accounted for on account 10.
Note that both new and used tires can be written off from accounting only after they are completely worn out. When writing off, one should be guided by the order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated June 24, 2003 N 153.
Therefore, for tax purposes, winter tires will be written off earlier than in accounting.
Consequences of incorrect determination of the initial value of the car
Detection of errors in the assessment of the cost of the OS by verifiers can lead to the following.
Firstly, for the systematic (twice or more during a calendar year) incorrect reflection of material assets in accounting accounts and in the reporting, the organization can be fined 5,000 rubles. The reason is a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income and expenses and objects of taxation (clause 1 of article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If such violations have been repeated for more than one tax period, the amount of the fine will increase to 15,000 rubles. (Clause 2, Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Secondly, the overestimation or understatement of the initial value of the property entails a distortion of a number of accounting indicators: the prime cost of the reporting period, the residual value of non-current assets, debts to the budget for property taxes and profit for reporting date... Inexpensive fixed assets can fall into the category of inventories if their cost is unreasonably underestimated. This means that the assets of the organization in the balance sheet will be reflected inaccurately. Distortion of any article (line) of the accounting form by 10% or more in accordance with Art. 15.11 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation is recognized as a gross violation of accounting rules. For this, the officials of the organization (the head and the chief accountant) may face a fine in the amount of 20 to 30 times the minimum wage (hereinafter - the minimum wage).
Thirdly, due to incorrect reflection of the original value of the car, property and income taxes will be incorrectly calculated. The tax base for property tax is formed on the basis of its residual value according to the accounting data (clause 1 of article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of property tax refers to expenses that reduce taxable profit (clauses 1 clause 1 of article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, even if the cost of fixed assets is distorted only in accounting, it will still be necessary to recalculate the profit tax (see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2006 N 03-06-01-04 / 84).
The penalty for incomplete payment of taxes is 20% of the unpaid amount (clause 1 of article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the understatement of the tax base was the result of a gross violation of accounting rules, then the organization will be fined in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of the fine will be two times lower, but not less than 15,000 rubles. At the same time, these two norms cannot be applied (clause 2 of article 108 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Penalties are charged for late payment of taxes only, but not advance payments on them. However, penalties must be paid in any case. Federal Law of 27.07.06 N 137-FZ \\ "On Amendments to Part One and Part Two Of the Tax Code Of the Russian Federation and in certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation in connection with the implementation of measures to improve tax administration \\ "the controversial issue of the accrual of penalties in the event of untimely or incomplete transfer of advance payments has been resolved (clause 3 of article 58 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Vehicle depreciation
Accrual of depreciation on the purchased vehicle starts from the first day of the month following the month of its acceptance for accounting. The calculation of the annual amount of depreciation charges is made linear way based on the initial cost of objects and the depreciation rate determined based on their useful life.
The established useful life for cars and vehicles with a carrying capacity of up to 0.5 tons is from three to five years. During this period, according to the Classification of fixed assets included in the depreciation groups, approved by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 1.01.02, N 1, the organization will be able to write off the cost of the car as an expense.
Example 2. According to the Classification of Fixed Assets, the useful life of a car is 5 years. The initial cost of a passenger car is 300,530 rubles. Annual rate depreciation is 20% (100% / 5 years). The annual depreciation amount is 60,106 rubles. (300 530 rubles x 20%), respectively monthly - 5008.83 rubles. (60 106 rubles / 12 months).
Debit 01, Credit 08 - 300 530 rubles. - the car is accepted for operation,
Debit 20, 26, 44, Credit 02 - RUB 5008.83. - the monthly depreciation amount has been charged.
If the organization purchased a used car, then in the tax accounting in accordance with clause 12 of Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the useful life is determined as the difference between the standard operating life of the facility and the period of its actual operation. In accounting, you can also use this method to determine the useful life of a car. In other words, the entity can account for the useful life of the property during which it belonged to the previous owner.
When calculating income tax, the transfer of expenses for the purchase of a car is possible through depreciation using a linear or non-linear method (Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When making a choice, an accountant must determine which is more important: to reduce the tax base for profits or to simplify his work.
Note that for passenger cars over 600,000 rubles. in tax accounting, a depreciation rate of 0.5 is applied (clause 9 of article 259 of the RF Tax Code).
From January 1, 2006, in tax accounting, up to 10% of the cost of the acquired fixed asset, put into operation, can be written off as expenses at a time (clause 1.1 of article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Purchase of fuels and lubricants
The operation of cars is impossible without fuels and lubricants (hereinafter - fuels and lubricants) and special fluids. The purchase of fuels and lubricants can be carried out by the organization both in cash and in non-cash form, as well as under a supply agreement with the condition of payment by bank transfer. Fuel and lubricants delivered in this way are accepted for accounting on the basis of the consignment note and invoice received from the supplier.
Fuel and lubricants are accounted for on account 10, subaccount \\ "Fuels and lubricants \\". Acceptance for accounting is carried out at the actual cost excluding VAT (when paying with funds received from income-generating activities subject to VAT). Analytical accounting is carried out on the cards of the quantitative and total accounting of material assets. Financially responsible persons must keep records of fuels and lubricants in the book (card) for accounting for material values \u200b\u200bby their names, grades and quantities.
During the operation of the vehicle, fuel is consumed and written off to the costs of the organization. The documentary confirmation of its consumption is the waybill, the form of which was approved by the decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated November 28, 1997 N 78. It is mandatory only for motor transport organizations. The organization can develop its own form of waybill, which will contain all the details provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 9 of the Federal Law of 21.11.96, N 129-FZ \\ "On accounting \\" (see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 1.08.05, N 03-03-04 / 1/117).
Fuel and lubricants can be written off (issued) at the actual cost of each unit or at the average actual cost. The choice of the write-off method must be fixed in the accounting policy of the organization. Evaluation of inventories at the average actual cost is made for each group (type) of inventories by dividing the total actual cost by their number, which are summed up respectively from the average actual cost and the amount of the balance at the beginning of the month and the inventory received during the current month on the date of write-off (vacation).
Accounting for operations on the consumption of material stocks, their disposal, movement within the organization is maintained in the journal of operations for the disposal and movement of materials (fuel).
Features of the reflection of expenses for the repair of vehicles
Accounting for the costs of repairing a vehicle depends, firstly, on the method of reflecting the costs of repairs in accounting (creating a reserve for future expenses for repairing fixed assets or including expenses for repairs directly in the cost price as they arise) and, secondly, on repair method (contract or household).
When creating a reserve for the repair of fixed assets in accounting, a monthly entry is made on the debit of the cost accounting accounts and the credit of account 96 \\ "Provisions for future expenses \\" in the amount of monthly deductions to the reserve. The amount of these deductions is determined based on the standards approved by the organization, which are calculated on the basis of estimates for repairs. The excess of the reserved deductions over the actual repair costs at the end of the year is reversed. The balance of the reserve at the end of the year is not canceled only in cases of a long period of repair work in accordance with clause 69 of the Methodological Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 N 91n (as amended on November 27, 2006 No. ). In the case of contracted repairs, the actual repair costs are debited from the credit of accounts 60 \\ "Settlements with suppliers and contractors \\" or 76 \\ "Settlements with different debtors and creditors \\" to the debit of account 96.
In addition to the cost of fuels and lubricants, organizations will have to periodically spend funds on current car repairs, which can be carried out either on their own or with the involvement of specialized organizations - car services.
Example 3. An organization has entered into a service agreement for two passenger cars used in the framework of statutory activities. The cost of repairs based on the certificate of work performed was 11,800 rubles, including VAT - 1,800 rubles.
The following entries are made in accounting:
Debit 20, 26, 44, Credit 60 - 10,000 rubles. - services are reflected according to the act of work performed,
Debit 19, Credit 60 - 1800 rubles. - VAT on the cost of services is reflected,
Debit 60, Credit 51 - 11 800 rubles. - a settlement was made with a contractor (bank statement).
If, during repair work, numbered spare parts are replaced, then, according to Resolution N 938, organizations are obliged to change the registration data in the traffic police or Gostekhnadzor bodies in the prescribed manner within five days after the replacement of numbered units.
When buying spare parts for the vehicle (engines, batteries, tires, etc.), the organization must keep records of them at account 10 (if the car is rented - on off-balance sheet account 002 \\ "Inventories accepted for safekeeping \\"). Subaccount 10-5 \\ "Spare parts \\" takes into account the presence and movement of spare parts purchased or manufactured for the needs of the main activity, intended for the production of repairs, replacement of worn parts of machines, equipment, vehicles, etc., as well as car tires in stock and turnover.
Automobile tires (tire, tube and rim tape) on wheels and in stock with a vehicle included in its initial cost are accounted for as property, plant and equipment.
Analytical accounting for the account is carried out in the card of quantitative-total accounting in quantitative terms, indicating the position and name of the recipient, date of receipt, serial number.
Example 4. Under an agreement concluded with a repair shop, a car was repaired in an organization (bumper painting). The cost of repairs in accordance with the act of work performed was 5,000 rubles, including VAT - 763 rubles.
In accounting, with the method of including repair costs directly into the cost price, the following entries are made as they arise:
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 44), Credit 60 - 4237 rubles. - the cost of the repair work performed is attributed to the cost price in accordance with the act of work performed,
Debit 19, Credit 60 - 763 rubles. - VAT is reflected on the cost of work performed,
Debit 60, Credit 51 - 5000 rubles. - the debt to the contractor for the repair work performed has been repaid,
Debit 68, Credit 19 - 763 rubles. - presented for deduction of VAT on the work performed and paid.
When repairing fixed assets in an economic way, all costs for each object to be repaired are preliminarily accounted for on account 23 \\ "Auxiliary production \\", and upon completion of the repair work, they are written off either to the debit of account 96, or to the debit of cost accounting accounts, taking into account the place of operation of the facility.
Free transfer of the vehicle
The organization can transfer the vehicle only to individuals or non-profit organizations, since Art. 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation prohibits the donation and transfer of property worth more than 5 minimum wages between commercial organizations.
When calculating taxable profit, the organization will not be able to take into account the costs in the form of the cost of the transferred car and the costs associated with such a transfer (clause 16 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A permanent tax liability should be recorded from these non-taxable expenses (Debit 99, Credit 68). In addition, the taxpayer has tax liabilities for VAT, since in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a gratuitous transfer for the purpose of calculating tax is considered as a sale. The tax base is determined in the manner prescribed by Art. 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, based on market prices.
If the vehicle is transferred to an individual free of charge, he has income in kind, which must be included in the tax base for personal income tax at a rate of 13% (clause 1 of article 210, clause 2 of article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An organization - a tax agent of an individual is obliged to calculate and withhold tax at the time of transfer of the vehicle into ownership. If it is impossible to withhold the calculated amount of tax from the taxpayer, then the tax agent must, within one month from the moment the relevant circumstances arise, notify this in writing, indicating the amount owed, to the tax authority at the place of his registration (clause 5 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, tax payment will be made by the taxpayer on the basis of tax notice (see the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 24.01.05, N 04-1-03 / 800).
Accounting for the transfer of the vehicle free of charge is similar to the procedure for writing it off due to moral or physical wear and tear.
Implementation of the vehicle by organizations applying the simplified tax system
For organizations applying the simplified taxation system (hereinafter - the USN), the accounting rules for the vehicle as an object of fixed assets are similar to those set forth, except that they do not charge VAT upon its implementation and do not apply PBU 18/02 (Article 3 of Law No. 129- FZ).
For such organizations, accounting for the sale of the vehicle consists only in writing off its residual value (they do not need to also reflect the proceeds from the sale).
Unlike accounting, when calculating a single tax, an organization may have problems in the event of a vehicle. If the taxpayer sells the vehicle before the expiration of three years from the moment of accounting for the cost of its acquisition, then from that time he will have to recalculate the entire tax base according to the rules of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and pay an additional amount of tax and penalties (clause 3 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to the Classification of Fixed Assets, tax liabilities in this case will have to be recalculated based on the timing of the write-off of capital costs that exceed the write-off period for the acquisition of fixed assets when using the simplified tax system (clause 3 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The possibility of such tax consequences is unlikely to cover labor losses, even if the car is sold at a profit.
In addition, as a result of the application of the rules of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the vehicle at the time of write-off may increase the residual value, which the organization is not entitled to take into account when calculating the single tax. This point of view was expressed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in a letter dated May 27, 2005 N 03-03-02-04 / 1/131 and is justified by the fact that in the closed list of expenses specified in Art. 341.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the costs are not named in the form of the residual value of fixed assets sold before the expiration of those provided for in paragraph 3 of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, if possible, it is better to postpone the implementation of the vehicle until the expiration of three years from the moment of taking into account the costs of its acquisition.
Other expenses for the maintenance of transport arising during operation
The cost of storing cars in the garage, in the parking lot. The organization can rent either a free-standing garage building or boxes in garages that are owned by other organizations.
Lease relations are regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The lease of buildings and structures is considered as a separate type of lease agreement and is regulated by paragraph 4 of Chapter 34 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Under the lease agreement for the building, the lessor undertakes to transfer the building to the lessee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use (clause 1 of article 650 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, the contract must indicate the amount of the rent.
When concluding a lease agreement for a building and structure, it should be remembered that the lease agreement for immovable property is subject to state registration, unless otherwise provided by law (Article 609 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). However, a lease agreement for a building concluded for a period of at least a year is subject to state registration (clause 2 of article 651 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If a lease agreement, in our case a garage, is concluded for a period of less than a year, then it is not subject to state registration and is considered concluded from the moment determined in accordance with clause 1 of Art. 433 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 02.16.01, N 53). If the lease is extended for a period of less than one year, then state registration is not required (paragraph 10 of letter N 53). The requirements of civil legislation on the registration of a lease agreement also apply to a sublease agreement (clause 19 of the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of January 11, 2002, N 66).
Simultaneously with the transfer of ownership and use of real estate, the tenant is transferred the rights to that part of the land plot that is occupied by this real estate and is necessary for its use (Article 652 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In cases where the lessor is the owner of the land plot on which the leased building is located, the tenant is granted the right to lease or the other right to the relevant part of the land plot provided for in the building lease agreement.
If the contract does not specify the right to the relevant land plot transferred to the lessee, then the right to use that part of the land plot that is occupied by the building and is necessary for its use in accordance with its purpose passes to him for the term of the building lease.
The payment for the use of the land plot on which the building is located, or the corresponding part of the plot transferred with it, is included in the rental payment established by the agreement, unless otherwise provided by law or agreement (clause 2 of article 654 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The expenses of the organization associated with the manufacture and sale of products, the purchase and sale of goods, as well as with the performance of work, the provision of services, are recognized as expenses for ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 10/99).
Consequently, in the case of using the building (premises) of the garage for the purpose of carrying out the ordinary activities of the organization, the costs associated with the payment of rent are included in the costs of ordinary activities. Expenses are recognized in the reporting period in which they were incurred, regardless of the time of the actual payment of funds.
The rented building or premises, the lessee, according to the Chart of Accounts, takes into account the off-balance sheet account 001 \\ "Rented fixed assets \\". On this account, the leased property is accounted for in the amount specified in the lease agreement.
Acceptance of the leased building (premises) for accounting by the tenant is reflected by the entry:
Debit 001 - the cost of the leased property specified in the lease is taken into account.
Settlements with the lessor for rent are reflected in the lessee's accounting as follows:
Debit 44, 26, Credit 76 - rent accrued according to the lessor's account,
Debit 19, Credit 76 - VAT on rent is reflected,
Debit 76, Credit 51 - funds are transferred to the lessor,
Debit 68, Credit 19 - VAT deductible accepted.
In tax accounting, lease payments from the lessee are accounted for as other expenses related to production and sale, based on cl. 10 p. 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 11, 2006, N 03-03-04 / 2/1) In this case, expenses must be justified and documented (clause 1 of article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Expenses can only be economically justified costs incurred for the implementation of activities aimed at generating income. Thus, lease payments can be accepted for tax purposes, provided that the leased property is used in the activities of the organization.
Renting a garage from an individual. In this case, the rent paid by the leasing organization is recognized as its taxable income (clauses 4, clause 1 of article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), in respect of which a tax rate of 13% is applied (clause 1 of article 224 of the Tax Code RF).
Calculation and payment of tax withheld from an individual must be made by a tax agent. In our case, it will be an organization that is a garage tenant (clause 1 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax agent is obliged to withhold the accrued tax amount directly from the taxpayer's income when they are actually paid (clause 4 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax agent is obliged to transfer personal income tax to the budget no later than the day the income is transferred from his bank account to the payer's account or, on his behalf, to the bank accounts of third parties.
If an organization concludes a garage lease agreement with an individual, the UST is not charged on the amount of rent (see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 10.02.04 N 04-04-06 / 21).
Accounting for expenses for paid parking lots. If the organization does not have a garage or a parking space, it can park vehicles in a paid guarded parking lot.
Parking fees are usually paid in cash through an accountable person. Cash is issued to the accountable person from the organization's cash desk in accordance with the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation, approved by the decision of the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia dated September 22, 1993 N 40. Cash is issued according to an expense cash order (form N KO-2, approved by the decree of the Goskomstat of Russia of 18.08.98 N 88) or according to another document (for example, on an application for the issuance of money), which is stamped with the details of an expense cash order. Documents for issuing money must be signed by the head, chief accountant of the enterprise or other authorized persons.
No later than three days after the expiration of the period for which the funds were issued, the accountable person is obliged to submit to the accounting department of the organization a report on the amounts spent in form N AO-1 \\ "Advance report \\", approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 1.08.01, N 55 The advance report must be accompanied by supporting documents confirming the expenditure of funds and allowing to take into account the costs of paying for parking.
Cash payments in the case of the sale of goods, the performance of work, the provision of services are carried out by organizations with the obligatory use of cash registers (CCP) in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of 22.05.03, N 54-FZ \\ "On the use of cash registers in the implementation of cash settlements and (or) payments using payment cards \\". In case of cash payments with organizations, KKT must be applied without fail.
If the accountable person when paying for parking services acts as individual, then the document confirming the payment of the expenses incurred is a receipt for parking the car in the form approved by the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 24, 1994 N 16-38.
When the accountable person, paying for parking services, presents a power of attorney, he acts on behalf of the organization. The party providing parking services is obliged to issue him a cash register receipt and an invoice for the amount of the paid services.
For accounting purposes, the costs of paying for the parking of a company car are related to the costs of ordinary activities as costs of maintaining and operating fixed assets (paragraphs 5, 7 of PBU 10/99).
The costs of paying for parking are taken into account on the basis of the advance report of the reporting person. This will record:
Debit 26, 20, 44, Credit 71.
In tax accounting, the costs of parking official vehicles are included in other costs associated with production and sale, on the basis of cl. 11 p. 1 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters N 03-03-04 / 2/1.
Car wash costs. These costs can be taken into account for the purposes of taxation of profits (see letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia N 03-03-04 / 2/1 and dated 20.06.06 N 03-03-04 / 1/530). Such expenses are expenses for the maintenance of official vehicles and in accordance with clauses 11 p. 1 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation relate to other expenses related to production and (or) sale.
The primary documents confirming the expense incurred may be KKT checks (sales receipts). The KKT check or the sales receipt, which is an attachment to the KKT check, must indicate the brand and state registration number of the machine that was serviced (see the letter of the Office of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 04/12/2006 N 20-12 / 29007).
When settlements with legal entities, CCP should be used. If the driver (freight forwarder) pays for parking services as an individual, i.e. on its own behalf, then the mentioned receipt will be the document confirming the payment of the expenses incurred. If the driver (freight forwarder) acts on the basis of a power of attorney issued by the organization, then the payment of expenses can only be confirmed by a cash register check and an invoice.
Expenses for technical inspection. Admission of vehicles intended for participation in road traffic on the territory of the Russian Federation, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 15 of the Federal Law of 10.12.95 N 196-FZ \\ "On road safety \\" is carried out by registering vehicles and issuing relevant documents, including a coupon for passing a state technical inspection. Vehicles in operation on the territory of the Russian Federation and registered in accordance with the established procedure are subject to compulsory state technical inspection (clause 1 of article 17 of Law N 196-FZ).
Technical inspection of the vehicle is carried out when purchasing (registering) a car, and then at a frequency determined by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 1998 N 880 \\ "On the procedure for conducting a state technical inspection of vehicles registered with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs Russian Federation \\ "and the order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated 03.15.99, N 190 \\" On the organization and conduct of state technical inspection of vehicles \\ ".
The fee for conducting a state technical inspection, paid in connection with the acquisition of a vehicle that is an object of fixed assets, is the cost of its acquisition, construction and manufacture and should be included in its initial cost (see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 5, 2006 N 03-06 -01-04 / 138).
It seems that the payment for the technical inspection in the subsequent periods of operation of the car should be included in the composition of other costs associated with production and (or) sale, in accordance with cl. 11 p. 1 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Naturally, you must have a passport, a charter registration certificate, a copy of it, an application for registration, an information letter from Goskomstat, a certificate of the presence of premises (own or rented), as well as an extract from the order "On putting a car on the balance of the organization." 3 After that, you can put the car on balance, that is, put it into operation. Include all expenses for the state registration of the vehicle in the initial cost, that is, take it to account 08 in the company's balance sheet. After registration, transfer the car to account 01, which contains the fixed assets in operation. Remember that it is prohibited by law to operate a car without state registration. 4 The car should be on the balance sheet of the organization as long as it is used in the course of its activities.
Fixed asset balance sheet
Personal passport of a representative of a legal entity. All copies must be notarized. Material costs at this stage: 1.
MTPL registration - 9690 p. 00 kopecks 2. Payment of registration fees (license plates, production of the Vehicle Registration Certificate) 364 rub.
66 kopecks. Details for payment of registration fees (MREO OGIBDD SEAD): Department of Finance
Moscow OKATO 45286585000 KPP 770701001INN 7707089101 r / s 40201810000160100046AK IMB "Bank of Moscow" BIK 044525219k / s.
30101810500000000219 KBK 2060100DKAU31502 Keeping the car on the balance sheet of the enterprise 2.1 Transport tax Annually no later than January 20 of the year following the expired tax period, the organization is obliged to submit a tax return to the tax authorities at the location of the vehicles.
Car registration in accounting
Remember that fixed assets are recorded only at their original cost, which is written off gradually using depreciation.
Such cost includes all costs associated with the acquisition, net of VAT.
If the fixed asset came from the supplier, make the posting: D08 K60 - the cost of the fixed asset was paid to the supplier. This entry is made on the basis of an invoice, delivery note or other document.
If assets enter the organization in the form of an investment in the authorized capital, make the entry: D08 K75.1 - the receipt of fixed assets from the founder is reflected on the account of the authorized capital.
4 After the fixed assets have arrived, they must be put into operation.
To do this, draw up an order (instruction), and then, based on it, issue an act of acceptance and transfer of the OS into operation (form No. OS-1, No. OS-1a or No. OS-1b).
Car on the balance sheet of the enterprise
The question is what problems may arise. :-) Thanks in advance for reading. qwer 09/27/2004, 16:21 #
Attention
If the question is like this: So that my personal car, which I now drive (it is in transit, respectively), was on the balance sheet of my organization.
That is, so that in the certificate of registration of the vehicle in the field owner, the legal entity is indicated. person .: I am ready to pay all expenses myself (well, accordingly, the organization can reimburse them by deducting expenses from my salary). That is, the question of whether to put the car on the balance sheet or not is not worth it.
Important
The question is what problems may arise. :-): Thanks in advance for reading. \u003d\u003d\u003d no problem there.
Arrival of vehicles at the enterprise
The company accountant will perform the following actions:
- reflects Borisov's debt to pay for his share in the authorized capital: Dt 75 Kt 80 - 800,000 rubles;
- Borisov transferred a Volvo car as payment for the share: Дт 08 Кт 75 - 800,000 rubles;
- the received car was put into operation: Дт 01 Кт 08 - 800 000 rubles.
- When received free of charge - the market price of the car on the date of its acceptance for registration and the cost of services for its delivery, registration and preparation for use.
To determine the market price of the transferred object, you can use the information contained in the media, data from statistics bodies, manufacturing organizations, prices determined in expert opinions. Example LLC "Solnyshko" under a donation agreement received from the only participant a LADA Granta car worth 250,000 rubles.
3 ways to make a vehicle if there are no documents for the car
- Car registration with the traffic police
- How the car is registered with the traffic police
- How to register a car with the traffic police according to the new rules?
- New rules
- How to register a car with the traffic police: order
- How to register a car with the traffic police, and how to save money?
We register the car: what documents are needed? need and other papers: What documents do legal entities present? Legal entities provide the following papers to the traffic police: Refusal of registration: reasons The main reasons why the applicant may be denied registration of the car are listed in the Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs No. 1001: Registration of the car with the traffic police In total, the cost of registration of the car in 2018 year will cost 2850 rubles.
What documents do you need to have with you to register a car?
Accounting for cars at the enterprise should be carried out in analytics for each classification group, by location and by source of purchase.
This accounting procedure is ensured by the data contained on the cards opened for each inventory object, and synthetic accounting for account 01. The standard form of the card is the OS-6 form. Enterprises that have a small number of fixed assets are allowed to keep their records in the inventory book by places of registration and classification groups.
Results When registering a car, it is necessary to pay special attention to the correct formation of its value and documentary registration.
Auto on balance in ooo
In this case, for registration, the new owner of the car must be provided to the inspector: Registration of the car with the traffic police Second, re-registration will be required if the owner's personal data has changed (for example, the name or place of registration).
Let's consider the listed issues in more detail. How to register a car with the traffic police, and how to save money? These include: In addition, the car itself will be required for registration: a traffic police officer will inspect it to verify the numbers of the body, frame and other numbered elements.
Having received his signature in the application, you can safely hand over the documents - and get your hands on the PTS with the entered registration data, a car registration certificate (STS) and a set of numbers.
Registration of a new car has an important feature.
When registering a car for the first time, you need to get numbers for it (state registration plates).
2 tbsp.
Add to favoritesSend by mail Accounting for a car in accounting has a number of features in comparison with other fixed assets. From the proposed article, the reader will learn how to correctly register a car, depending on the source of its receipt. Classification and appraisal of cars Documentation and analytical accounting of the receipt of a car Results Classification and appraisal of cars Based on the provisions of PBU 6/01 "Accounting for fixed assets", approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 30.03.2001 No. 26n, the car belongs to fixed assets (OS) The exceptions are cars purchased for resale (in which case they are a commodity) and vehicles manufactured in the enterprise (in which case they are accounted for as finished goods). Find out which property belongs to the fixed assets of the enterprise here.
The hourly limit is set in 2013. You can contact any department of the MREO traffic police. Nissan X-Trail I 2 4. Transfer of money, receipt of a car, preparation for registration. To travel by car, you must be included in the insurance. To do this, you can either ask the previous owner to add you for the first time, or you can already issue new insurance before buying. For registration, you must have: 1. Purchase and sale agreement + photocopy or 3rd copy of the agreement (remain in the traffic police); Registration of a used car In this case, the traffic police officer will simply refuse to register the car, and the buyer will receive a lot of problems, for example, the need to undergo an examination. Moreover, if the sale and purchase agreement will be concluded directly at the traffic police, you don't even have to sign the agreement (the traffic police officer just needs to make sure of the seller's identity). However, it is better to have a written agreement.