How to calculate depreciation for fixed assets. Depreciation calculation using formulas. Example of depreciation on a straight-line basis
Compensation for unused vacation: ten and a half months go in a year When an employee who has worked in the organization for 11 months is dismissed, compensation for unused vacation must be paid to him as for a full working year (Clause 28 of the Rules, approved by the NKT USSR on April 30, 1930, No. 169) ... But sometimes these 11 months are not so worked up.< … Налог на прибыль: перечень расходов расширен Подписан закон, который внес изменения в перечень расходов, относящихся к оплате труда. Так, работодатели смогут учитывать в «прибыльной» базе затраты на оплату услуг по организации туризма, санаторно-курортного лечения и отдыха на территории России для работников и членов их семей (родителей, супругов и детей). < …
Accrual of depreciation on a straight-line basis and its features
Important
So, knowing the initial price of the object and the value of the accrued depreciation, the accountant receives the value of the object at the time of calculation. It is called residual. The accountant should make such a calculation on a monthly basis - the tax on the property of the enterprise directly depends on this indicator, the illiterate calculation of which hits the company's profit and creates problems in relations with the tax inspection. Therefore, it is so important to correctly calculate depreciation for each object.
There are linear and non-linear methods for calculating depreciation. Companies and organizations are legally given the right to independently choose the method of calculating the depreciation of property. IN accounting policy of the company, the application of the depreciation calculation method is fixed.
The law establishes the right to switch from one depreciation method to another only once every five years.
Linear depreciation calculation: example
Primary cost of an object The primary cost of an object is used as the basis for calculation, which is calculated by adding up all the costs of its purchase or construction. If a revaluation of the property value was carried out, then such an indicator as replacement value is used for the calculation. 2. Operational period The operational period is established by studying the classification list of fixed assets, differentiating them into depreciation groups. If the object is not recorded in the list, then the period of its operation is assigned by the organization, depending on:
- predicted time of use;
- expected physical wear and tear;
- expected operating conditions.
Depreciation and examples of its calculation
Features of the calculation They begin to calculate depreciation from the beginning of the month following the month when the object is entered into the production process. For example, even if the property is purchased and commissioning is dated March 1, then depreciation should be charged from April 1. The same rules apply to objects received free of charge.
Info
According to the same principle, depreciation is terminated: from the 1st day of the month following the month in which the amount of depreciation equaled the original cost of the object. There are other reasons for the termination of depreciation, for example, when an object is liquidated, retired or mothballed due to a need arisen. When leaving the mothballed state (by written order of the company's management), depreciation of fixed assets is also charged from the beginning of the month following the one in which the facility was resumed.
The procedure for calculating depreciation of fixed assets in a linear way
With the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (work), accrual depreciation charges produced on the basis of a natural indicator of the volume of production (work) in reporting period and the ratio of the initial cost of the object of fixed assets and the estimated volume of production (work) for the entire period useful use object of fixed assets. Example. We bought a car worth 60 thousand rubles, its carrying capacity is more than 2 tons, guaranteed mileage is 400 thousand km. For the first year, the mileage was 40 thousand km. Consequently, the amount of depreciation deductions based on the ratio of the initial cost and the estimated volume of production will be: Solution: (40 x 60: 400) \u003d 6 thous.
Prednalog.ru
Attention
Accruals of depreciation deductions for fixed assets during the reporting year are carried out monthly, regardless of the method of calculation in the amount of 1/12 of the calculated annual amount. In the case of commissioning an object of fixed assets during the reporting year, the annual amount of depreciation is the amount determined from the first day of the month following the month of acceptance of this object to accounting, before the date of the annual accounts. Example. In April of the reporting year, an object of fixed assets with an initial cost of 120 thousand rubles was put into operation and accepted for accounting.
rub. Usage period - 5 years, annual rate depreciation - 20%. With the linear method, the depreciation of this object in the first year of use will be: Solution: (20 x 8: 12) \u003d 13.33%, i.e. 16 thousand rubles; (120 x 13.33: 100), where 8 is the number of months of operation of the facility in the first year.
Linear depreciation method for fixed assets (example, formula)
Solution 120 x 20: 100 \u003d 24 thousand rubles. With the diminishing balance method, depreciation deductions are determined based on the residual value of the object of fixed assets at the beginning of the reporting year, the depreciation rate and the acceleration factor established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. Example. An object of fixed assets was purchased for 120 thousand rubles. with a useful life of 5 years. The object's annual depreciation rate, calculated based on the useful life, is 20%.
This rate is increased by an acceleration factor of 2 to 40% (20 x 2). Hence, the annual amount of depreciation deductions is: Solution (120 x 20: 100) x 2 \u003d 48 thousand rubles. In the first year of operation, the annual depreciation is determined based on the original cost of the object.
In the second year of operation, depreciation is calculated at 40% of the residual value, i.e.
An example of calculating depreciation using a linear method. depreciation of fixed assets
Add to favoritesSend by mail The linear method of calculating depreciation of fixed assets is probably the simplest and most convenient in calculations. More on the linear method and the formula used to calculate depreciation later in our article. Linear method of calculating depreciation of fixed assets - the essence of the method Calculation of depreciation linear way - example Transition from non-linear to linear depreciation method Linear method of depreciation of fixed assets - the essence of the method Depreciation when choosing the straight-line method is charged every month for each fixed asset separately, depending on its useful life (p.
2 tbsp. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Depreciation calculation in ms excel
With the method of writing off the cost by the sum of the number of years of the useful life of the object, depreciation deductions are determined based on the initial cost of the object of fixed assets and the annual ratio, where the numerator is the number of years remaining until the end of the object's service life, and in the denominator is the sum of the number of years of the object's service life ... Example. An object of fixed assets was purchased for 120 thousand rubles. The useful life is 5 years. The sum of the service life is 15 years (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). In the first year of operation of the specified object, depreciation may be charged in the amount of 5/15, or 33.3%; in the second year - 4/15, i.e. 26.7%; in the third year - 3/15, i.e. 20.0%; in the fourth year - 2/15, i.e. 13.3%; in the fifth year - 1/15, i.e. 6.7%.
Suspension of operation of an object: how to calculate depreciation Let us recall the example of calculating depreciation in a linear way and add it: the object was put into operation on September 25th. This means that depreciation is charged in the amount of 3000 rubles. the accountant will start in October. Consider a situation when a fixed asset is mothballed for a certain period of time.
Let's continue the previous example with new operating conditions of the facility. Due to unforeseen circumstances, the head of the company decided to suspend the participation of this object in the production process, and he issues an order to withdraw the object from the working process for 6 months, for example, from May 1 to October 31. In this case, the depreciation of the equipment is suspended.
The calculation is made as follows: depreciation is charged for April and a break is made for 6 months. From November 1, depreciation will resume.
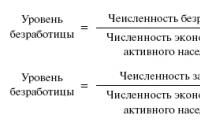
Depreciation rate formula The annual depreciation rate is expressed as a percentage of the primary (replacement) value of the property and is calculated by the formula: K \u003d (1: n) * 100%, where K is the annual depreciation rate; n is the service life in years. If you need to know the monthly depreciation rate, then the result is divided by 12 (the number of months in a year). 4. Formula for calculating the accrual of depreciation With the linear method of calculating depreciation, the calculation formula is: A \u003d C * K / 12, where A is the amount of monthly depreciation charges; С - the primary value of the property; K - depreciation rate, calculated according to the formula in the 3rd paragraph. If you need to calculate the annual amount of depreciation deductions, then dividing by 12 (the number of months in a year) is not necessary or it is enough to divide the initial value of the property by its useful life.
How to calculate depreciation in a linear way examples of accounting problems
- simplicity of calculations, no need to do lengthy calculations and understand complex formulas;
- the value of the property is evenly transferred to the finished product;
- depreciation is calculated for each object;
- this method is used in tax accounting;
- no regular recalculations are required;
- suitable for depreciation of real estate.
Along with the advantages, there are a number of disadvantages due to the peculiarities of production:
- the deterioration of the initial condition of the equipment over time is not taken into account;
- obsolescence is not taken into account;
- not suitable for large organizations that use equipment unevenly, that is, when some machines are idle;
The negative consequences of using the linear method are inferior to the pros.
. Depreciable property property, results of intellectual activity and other objects of intellectual property that are owned by the taxpayer, are used by him to generate income and the cost of which is repaid through depreciation is recognized. Depreciable property is property with a useful life of more than 12 months and an initial cost of more than 40,000 rubles.
Not subject to depreciation land and other objects of nature management (water, subsoil, other natural resources), material productive reserves, goods, objects of capital construction in progress, securities and other property.
Damping property is registered at its original cost, determined in accordance with Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and is allocated to depreciation groups in accordance with its useful life. The useful life is determined by the taxpayer independently as of the date of commissioning of the depreciable property. Taxpayers have the right to include in the expenses of the reporting (tax) period the cost of capital investments in the amount of no more than 10% (no more than 30% - in relation to fixed assets belonging to the third - seventh depreciation groups) of the initial cost of fixed assets. This benefit does not apply to fixed assets received free of charge. If taxpayers exercise this right, then the corresponding items of fixed assets, after their commissioning, are included in depreciation groups at their initial cost less depreciation bonus... In the event that these fixed assets are sold within five years from the date of commissioning, the amounts of expenses previously taken into account when forming the tax base are subject to restoration and inclusion in the tax base.
Depreciation methods
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for two methods for calculating depreciation:
- linear method;
- nonlinear method.
The depreciation method is set independently for all objects of depreciable property and is reflected in the accounting policy for tax purposes. A change in the depreciation method is allowed from the beginning of the next tax period... In this case, the taxpayer has the right to switch from the non-linear method to the linear depreciation method no more than once every five years.
Depreciation is charged separately for each depreciation group (subgroup) using the non-linear depreciation method, or separately for each item of depreciable property when using the linear depreciation method.
Regardless of the depreciation method established by the taxpayer in the accounting policy for tax purposes, the linear depreciation method is applied to buildings, structures, transmission devices, intangible assets included in the eighth to tenth depreciation groups.
With respect to other objects of depreciable property, regardless of the date of putting the objects into operation, the method of depreciation is applied, which is established by the taxpayer in the accounting policy for tax purposes.
When using the linear method of calculating depreciation, the amount of depreciation accrued for one month is determined as the product of the original (replacement) cost of the depreciable property and the depreciation rate determined for this object. The depreciation rate is determined by the formula:
K \u003d 1 / p - 100%,
- TO - depreciation rate as a percentage of the original (replacement) cost of the depreciable property;
- p - useful life of the given object, expressed in months.
When calculating depreciation using the non-linear method, the total balance of each depreciation group is monthly reduced by the amount of depreciation charged for this group. The amount of depreciation charged for one month for each depreciation group is determined based on the product of the total balance of the corresponding depreciation group at the beginning of the month and the depreciation rates:
A \u003d Bk / 100,
- AND - the amount of depreciation charged for one month for the corresponding depreciation group;
- IN - the total balance of the corresponding depreciation group;
- to - depreciation rate for the corresponding depreciation group.
For the purpose of applying the non-linear depreciation method, the following depreciation rates are applied.
Depreciation group - Depreciation rate (monthly):- First - 14.3
- Second - 8.8
- Third - 5.6
- Fourth - 3.8
- Fifth - 2.7
- Sixth - 1.8
- Seventh - 1.3
- Eighth - 1.0
- Ninth - 0.8
- Tenth - 0.7
Methods for calculating depreciation of fixed assets
In accordance with Regulation on accounting of fixed assets and Methodological guidelines amount of depreciation charges for any method of depreciation is determined taking into account the useful life of fixed assets.
See further: Depreciation of fixed assets is performed by one of the following methods of depreciation:- in a linear way;
- by way of decreasing balance;
- by the method of writing off the cost according to the sum of the numbers of years of the useful life;
- method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products.
The application of one of the methods for a group of homogeneous objects of fixed assets is carried out during the entire useful life.
Linear depreciation
When linear way the annual amount of depreciation is determined based on original cost object of fixed assets and depreciation ratescalculated taking into account.
Example... An object worth 120,000 rubles was purchased. with a useful life of 5 years. The annual rate of depreciation is 20%. The annual amount of amortization deductions will be 24,000 rubles. (120,000 * 20/100).
Diminishing balance depreciation
When diminishing balance method the annual depreciation amount is determined based on residual value object of fixed assets for beginning of the reporting year and depreciation ratescalculated taking into account the useful life of this object and the acceleration factor established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. The acceleration factor is applied according to the list of high-tech industries and efficient types of machinery and equipment approved by federal executive authorities.
By movable propertythat constitutes an object of financial leasing and attributed to the active part of fixed assets, an acceleration coefficient of not more than 3 can be applied in accordance with the terms of the lease agreement
Example... An item of fixed assets was acquired for the cost of 100 thousand rubles. with a useful life of 5 years. The annual depreciation rate is 40. The depreciation rate calculated based on the useful life of 20% is increased by acceleration factor 2 (100 thousand rubles / 5 \u003d 20 thousand rubles) (100 * 20 thousand rubles / 100 thousand rubles * 2) \u003d 40.
IN first year of operation the annual rate of amortization deductions is determined taking into account the initial cost formed upon posting the object, and will amount to 40 thousand rubles. In second year operation, depreciation is charged at 40% (100 * 40/100) of the residual value, i.e. the difference between the initial cost of the object and the depreciation amount accrued for the first year ((100 - 40) * 40/100) and will be 24 thousand . rub. IN third year operation - in the amount of 40% of the difference between the residual value of the object formed at the end of the second year of operation and the amount of depreciation accrued for the second year of operation, and will amount to 12.4 thousand rubles. ((60 - 24) * 40/100), etc.
When the residual value of fixed assets will reach 20% of the original value, this balance is fixed, the monthly amount of depreciation is determined by dividing the fixed residual value of fixed assets by the number of months remaining until the end of the useful life (Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Depreciation by the method of writing off the cost according to the sum of the number of years of useful life
When method of writing off the value by the sum of the number of years of useful life the annual amount of depreciation deductions is determined taking into account original cost object of fixed assets and annual ratio, where the numerator is the number of years remaining until the end of the object's service life, and the denominator is the sum of the number of years of the object's service life.
Example... An item of fixed assets was acquired for the cost of 150 thousand rubles. The useful life is set at 5 years. The sum of the numbers of years of service life is 15 years (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). In the first year of operation of the specified object, depreciation can be charged in the amount of 5/15, or 33.3%, which will amount to 49.95 thousand rubles, in the second year - 4/15, which will amount to 39.9 thousand rubles, in the third year - 3/15, which will amount to 30 thousand rubles. etc.
Depreciation by the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of production
With the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of production (work), depreciation is calculated based on the natural indicator of the volume of production (work) in the reporting period and the ratio of the initial value of the fixed asset item and the estimated volume of production (work) for the entire useful life of the fixed asset item.
Example... A car with a carrying capacity of more than 2 tons, with an estimated mileage of up to 400 thousand km, costing 80 thousand rubles was purchased. In the reporting period, the mileage is 5 thousand km, therefore, the amount of depreciation, taking into account the ratio of the initial cost and the estimated volume of production, will be 1 thousand rubles. (5 * 80/400).
Reflection in accountingDepreciation deductions accrued for fixed assets are reflected in accounting in the reporting period to which they relate, and are charged regardless of the organization's performance in the reporting period.
The amount of accrued depreciation is reflected in accounting on the debit of accounts for accounting for production or circulation costs (except for fixed assets leased) in correspondence with the credit of the account for depreciation (account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets").
Figure: 4.3. General scheme of correspondence of accounts when calculating depreciation of fixed assetsAccrual of depreciation deductions for fixed assets during the reporting year is made on a monthly basis, regardless of the method of accrual used in the amount of 1/12 of the calculated annual amount. The beginning and end of depreciation is from the first day of the month following the month of commissioning or, respectively, of disposal of the fixed asset. After the end of the useful life of property, plant and equipment, depreciation is not charged.
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the straight-line method is a straight-line write-off of the cost of the depreciable property during its useful life, established by the organization when the object is accepted for accounting.
When applying the straight-line method, the amount of depreciation accrued for one month, in relation to an object of depreciable property, is determined as the product of its original (replacement) cost and the depreciation rate determined for this object.
Clause 5 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that when the nonlinear method is applied, the amount of depreciation calculated for one month in relation to the depreciable property is determined as the product of the residual value of the depreciable property and the depreciation rate determined for this object.
In relation to fixed assets, taxpayers can apply special increasing and decreasing coefficients provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to the basic rate of depreciation.
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, increasing coefficients are provided for:
§ depreciable fixed assets used to work in an aggressive environment and (or) extended shifts. In this case, the taxpayer has the right to apply a special coefficient, but not higher than 2. An aggressive environment is understood as a combination of natural and (or) artificial factors, the influence of which causes increased wear (aging) of fixed assets during their operation. Also, to work in an aggressive environment is equated with the presence of fixed assets in contact with an explosive, fire hazardous, toxic or other aggressive technological environment, which can serve as a reason (source) for initiating an emergency.
§ depreciable fixed assets, which are the subject of a finance lease agreement (lease agreement). In this case, the taxpayer, for whom this fixed asset must be accounted for in accordance with the terms of the financial lease agreement (lease agreement), is entitled to apply a special coefficient to the basic rate of depreciation, but not higher than 3. These provisions do not apply to fixed assets related to the first, the second and third depreciation groups, if depreciation on these fixed assets is calculated using a non-linear method. Taxpayers who transferred (received) fixed assets, which are the subject of a lease agreement concluded before January 1, 2002, are entitled to depreciate this property using the methods and norms that existed at the time of transfer (receipt) of the property, as well as using a special coefficient not above 3.
§ taxpayers - agricultural organizations of an industrial type (poultry farms, livestock complexes, fur farms, greenhouse plants), which have the right to apply a special coefficient to the basic depreciation rate, chosen independently, taking into account the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in relation to their own fixed assets, but not higher than 2.
§ taxpayers - organizations with the status of a resident of an industrial-production special economic zone, have the right to apply a special coefficient to the basic depreciation rate in relation to their own fixed assets, but not higher than 2.
Example 4.
In February 2006, the organization put into operation an item of fixed assets, acquired in the same month for 236,000 rubles, including VAT of 36,000 rubles. This fixed asset belongs to the fourth depreciation group and the organization, when the object is accepted for accounting, has a useful life of 6 years (72 months). The fixed asset is used in the production process under conditions of increased shifts, in accordance with the Decree how?
"The norms of depreciation allowances for machines and equipment are established based on the operating mode in two shifts (with the exception of continuous production equipment, forging and pressing equipment weighing over 100 tons, for which the norms are established based on the operating mode in three shifts, and logging equipment, for which the norms are established based on the mode of operation in one shift) ".
and applies a special multiplier of 1.4. The organization depreciates on a straight-line basis.
The monthly depreciation rate for this fixed asset, calculated based on the deadline useful use of the object, and a special multiplying coefficient will be 1.94% ((1/72 months) x 100% x 1.4).
The amount of monthly depreciation deductions taken into account when taxing profit will be equal to 3,880 rubles (200,000 rubles x 1.94% / 100%).
Accrual of depreciation at rates lower than those established by paragraph 10 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is allowed by decision of the head of the organization - the taxpayer. The decision on whether the organization will apply reduction factors when calculating depreciation rates should be fixed in the organization's accounting policy.
The use of reduced depreciation rates is allowed only from the beginning of the tax period and throughout the entire tax period.
According to clause 9 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for passenger cars and passenger minibuses, the initial cost of which is, respectively, more than 300 thousand rubles and 400 thousand rubles, the basic depreciation rate is applied with a special coefficient of 0.5.
Example 5.
In January 2006, the organization put into operation a passenger minibus, the initial cost of which is 470,000 rubles (excluding VAT). The minibus, in accordance with the Classification of fixed assets, belongs to the third depreciation group, the organization, when accepting the object for accounting, set the useful life equal to 3.5 years (42 months). Depreciation for income tax purposes is charged on a straight-line basis.
The estimated useful life is 42 months, the monthly depreciation rate, taking into account the reduction factor, will be 1.19% ((1/42 months) x 100% x 0.5).
The amount of monthly depreciation deductions taken into account for profit tax purposes will be 5,593 rubles (470,000 rubles x 1.19% / 100%).
The amount of depreciation accrued over the useful life of the fixed asset will be 234,906 rubles, while its initial cost is 470,000 rubles.
End of the example.
From the given example, it can be seen that when using decreasing factors and applying the straight-line depreciation method, the organization will not be able to fully write off the cost of this fixed asset to production costs or sales costs.
Clause 11 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that taxpayers who use reduced depreciation rates do not recalculate the tax base for the amount of uncalculated depreciation against the rates provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for tax purposes.
A somewhat different situation arises when taxpayers, when calculating depreciation, apply a non-linear method of calculating depreciation. When using the non-linear method, the organization will be able to charge more depreciation as an expense than when using the straight-line method.
Having calculated the amount of depreciation charges over the entire useful life of the object, we get the amount equal to 299,105.43 rubles. When using the non-linear method, the organization will also not be able to write off the entire value of the fixed asset. However, the amount of depreciation charged using this method is greater than the amount of depreciation charged when using the straight-line depreciation method, which is RUB 234,906.
End of the example.
On the basis of clause 9 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the reduction factor is applied by organizations that received or transferred cars and passenger vans for lease. The specified property is included in the composition of the corresponding depreciation group and the basic depreciation rate is applied to this property taking into account the special coefficient applied by the taxpayer for this type of property.
If the parties under the lease agreement provide for the use of a multiplying coefficient in the amount of no more than 3, then the coefficient applied to the basic depreciation rate will be calculated as the product of the established multiplying coefficient by 0.5.
For more details on the procedure for the valuation of fixed assets, the way of receipt, types of repairs and methods of disposal of fixed assets, you can find in the book of JSC "BKR-Intercom-Audit" "Fixed Assets".
Linear depreciation is widely used due to its simplicity. It is applied in mandatory to items of fixed assets that belong to the eighth, ninth and tenth depreciation groups (buildings, structures, housing stock, vehicles, transfer devices). As for the rest of the groups of fixed assets, any method of depreciation can be applied to them. But it is worth remembering that the chosen method of accrual cannot be changed during the entire period of accruals for this object.
Features of the linear method
If the organization has chosen the straight-line method to calculate depreciation on fixed assets, this means that over the entire useful life of the property, which is established by the organization, taking into account the fixed asset, the cost will be written off evenly. In this case, the amount of depreciation accrued for a month will be determined as the product of the original cost of the property and the depreciation rate, which is determined for a specific object.
The depreciation rate is determined by the following formula: K \u003d (1 / n) x 100%
Here K is the depreciation rate, expressed as a percentage of the original value of the property, and n is the useful life of the property, expressed in months.
The amount of depreciation charged for the month is: A \u003d C x K
Here A is the amount of depreciation deductions per month, C is the initial cost of an item of fixed assets, K is the depreciation rate in%.
Linear depreciation means that the physical depreciation of the property occurs evenly and equally throughout the entire period of use. Of course, this primarily applies to stationary structures, since during the operation of equipment, the time of use and the conditions of use are of great importance. For example, obsolescence cannot occur at a uniform rate throughout the life of a fixed asset. But if we take into account that there may not be accurate information about the rate of depreciation of a particular property, then the linear method, characterized by a uniform write-off, will be the simplest for accruals.
How do I calculate depreciation in a linear fashion?
To calculate the depreciation of a fixed asset, you need to know the useful life of the property. It can be determined by examining the depreciation groups of fixed assets or you can set the useful life yourself (if the specific property is not in the depreciation groups). The useful life is determined based on the expected useful life, wear and tear and operating conditions of the equipment.

Let's perform a linear depreciation on the example of a machine. Let's say that its cost is 250,000 rubles. According to the classification of fixed assets, this machine belongs to the third depreciation group, and the useful life of such property is from three to five years. The organization has set a useful life of five years for a particular machine. This means that the annual depreciation rate will be 20% (100% / 5). From this it follows that the amount of depreciation for the year will be: 250,000 x 20% / 100% \u003d 50,000 rubles.
Used fixed assets
The linear depreciation method can also be used for property that has already been in use. In this case, the useful life of the fixed asset will need to be determined as the difference between the useful life, which was established by the previous owner, and the number of years (or months) that this property has been in operation. In particular, such a norm has been adopted in relation to property that is contributed as an authorized capital or by way of succession during the reorganization or liquidation of organizations. Once the useful life is documented, depreciation can be made either based on the useful life or on the remaining useful life.
Disadvantage of the linear method
Straight-line depreciation is a straight-line basis. But for equipment that is used in production, a decrease in performance is characteristic after a certain period of operation. Gradually, the equipment will wear out, fail more often, which means that the cost of maintenance and repair will increase. Such expenses cannot be ignored, but depreciation will still be written off evenly, since there is no other straight-line method.
Individual entrepreneurs have the right to apply only straight-line depreciation intangible assets and fixed assets that are used in business.
This refers to their attribution to depreciation groups. Methods for calculating depreciation are carried out in accordance with the "Procedure for accounting for income and expenses and business transactions for individual entrepreneursapplying OSNO, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation No. 86n / BG-3-04 / 430 dated August 13, 2002 ". For LLCs and individual entrepreneurs, Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Amount of depreciation is determined monthly for each object separately. Depreciation begins from the next month, after the month of commissioning or acceptance for accounting of an economic object. Depreciation ends in the month of write-off, sale or transfer of an item of fixed assets or intangible assets.
Linear method for calculating depreciation for individual entrepreneurs
Linear depreciation method implies that the initial cost of the item is expensed on a straight-line basis over its useful life. For this, the depreciation rate is determined.
Depreciation rate formula: K \u003d (1: n) x 100%,
where K is the depreciation rate (%);
n is the useful life of the object (months).The amount of accrued depreciation for the month is: A \u003d C x K,
where A is the amount of depreciation deductions per month;
С - the initial cost of the depreciation object;
K - depreciation rate (%).An example of calculating depreciation in a linear way:
The individual entrepreneur purchased a computer worth 25,000 rubles in March 2011 and put it into operation in the same month. The object has a useful life of 2 to 3 years (from 24 to 36 months) and belongs to the second depreciation group. The individual entrepreneur assumed a useful life of 36 months.
Total:
Monthly depreciation rate: (1: 36) x 100% \u003d 2.78%
Amount of depreciation per month: RUB 25,000 x 2.78% \u003d 695 rubles.
Amount of depreciation included in expenses in 2011: 695 rubles. x 9 months (from April to December) \u003d 6255 rubles.If an individual entrepreneur has acquired a fixed asset that was in operation, then he has the right to reduce the useful life by the number of months of operation from the former owner. Depreciation is calculated in the same way.
Depreciation is charged regardless of the results of financial activities until the cost is fully repaid or the ownership of the fixed asset is terminated. And it is included in the expenses of the tax period to which it belongs. The method of depreciation is established in the accounting policy of the organization.
Along with straight-line depreciation, organizations can also use non-linear methods for calculating depreciation:
- Decreasing balance method.
- The method of writing off the value by the sum of the number of years of useful life.
- The method of writing off the cost is proportional to the volume of products.
Details and examples of depreciation are described in this video: