Annual depreciation rate 12. Annual depreciation rate. Depreciation methodology
PRACTICAL LESSON No. 1.
Payment depreciation charges.
The student must:
know:
depreciation of fixed assets.
be able to:
calculate depreciation charges.
Methodical instructions
Depreciation fixed assets (fixed assets) - this is a gradual transfer of the value of fixed assets in the process of their operation to the cost of manufactured products. Economically, depreciation compensates for the wear and tear of fixed assets and ensures their safety in monetary terms. In other words, depreciation - the monetary expression of the depreciation of fixed assets in the process of their productive functioning.
The amount of the cost of depreciation of fixed assets for a period of time is called depreciation deductions. The amount of annual depreciation charges depends on the value of fixed assets and on the time of their operation. In practice, it is more convenient to calculate depreciation charges using the depreciation rate.
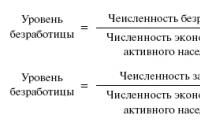
The rate of depreciation, or depreciation rate , Is the ratio of the amount of depreciation deductions to the value of fixed assets (fixed assets), expressed as a percentage.
The most common depreciation method is the straight-line method, in which the depreciation of fixed assets is charged in equal parts throughout their entire service life.
With the linear (straight-line) method of depreciation, the annual depreciation rate for full restoration (renovation) is determined by the formula:
Because  then
then 
Where H and - the annual rate of depreciation deductions,%;
P from - the initial cost of the object of fixed assets, rubles;
L from- - liquidation value of fixed assets, rubles;
D eat - the cost of dismantling the liquidated fixed assets and other costs associated with the liquidation, rubles;
T and - depreciation period (service life of the object), years.
The monthly depreciation rate is 1/12 of the annual depreciation rate.
Depreciation deductions for fixed assets begin from the first month following the month when the object is accepted for accounting, and are carried out until the cost of the object is fully paid off or it is written off from accounting in connection with the termination of ownership or other property rights.
Annual depreciation charges are calculated in one of the following ways:
- "In a linear way"
based on the initial cost of fixed assets and the depreciation rate according to the formula: 
If the liquidation value of fixed assets and the cost of dismantling the liquidated fixed assets and other costs associated with liquidation are not specified or are unknown, then the depreciation rate for full restoration (renovation) with a linear method of calculating depreciation deductions is determined by the formula:

For instance: An object worth 620 thousand rubles was acquired. with a useful life of 5 years.

2) Annual amount of depreciation charges:

- "Diminishing balance method" , based on the residual value of fixed assets and the depreciation rate according to the formula:

ABOUT from - residual value of fixed assets ( OS \u003d P from - Wear),rub.,
Wear - the amount of previously accrued depreciation (depreciation), rubles.
then 
The depreciation rate for the diminishing balance method is determined by the formula: 
For instance:
An item of fixed assets was purchased for the cost of 500 thousand rubles. with a useful life of 5 years. The acceleration factor is 2.
1) Annual rate of depreciation charges:

2) Annual amount of depreciation charges: 1st year - 
5th year - remaining amount
-
"By the method of writing off the cost by the sum of the number of years of useful life"
based on the initial cost of fixed assets and depreciation rates. 
The depreciation rate is calculated as an annual ratio, where the numerator is the number of years remaining until the end of the object's service life ( T a.ost), in the denominator - the sum of the numbers of years of the object's service life ( Σп) according to the formula:

For instance:
An item of fixed assets was purchased for the cost of 1,500 thousand rubles. The useful life is 5 years.
1) The sum of the numbers of years of service life:
2) 1st year - Annual rate of depreciation charges: 

2nd year
Amount of annual depreciation charges: 
3rd year - Annual rate of depreciation charges: 
Amount of annual depreciation charges: 
4th year - Annual rate of depreciation charges: 
Amount of annual depreciation charges: 
5th year - Annual rate of depreciation charges: 
Amount of annual depreciation charges: 
- "by the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (works)" , based on the initial cost of fixed assets, the volume of production in kind in reporting period and depreciation rates per unit of production (volume of work) for the entire useful life of fixed assets.
The depreciation rate per 1 unit of the expected volume of production (work) for the entire useful life of fixed assets is determined by the formula:
 ,
,
and the amount of annual depreciation deductions in the current year: 
For instance:
A car with a carrying capacity of more than 2 tons with an estimated mileage of 400 thousand km was purchased at a cost of 1800 thousand rubles. In the reporting period, the mileage is 5 thousand km. Decision
Depreciation rate per unit of production:
 %
%
Amount of depreciation charges for the reporting period:
For a group of similar objects of fixed assets, the selected method is applied throughout the entire useful life. During the reporting year, depreciation deductions are charged monthly, regardless of the applied method of calculation, in the amount of "/ 12 of the annual amount.
Basic production assets (OPF), being in the production process for a long time, are subject to physical and moral deterioration.
Under physical(material) wear and tear means the loss of their original qualities by means of labor.
The level of physical depreciation of fixed assets depends on: the initial quality of fixed assets; the degree of their exploitation; the level of aggressiveness of the environment in which fixed assets function; the level of qualifications of service personnel, etc. Taking these factors into account in the work of enterprises can significantly affect the physical condition of fixed assets.
A number of indicators are used to characterize the degree of physical wear and tear of fixed assets.
Depreciation ratefixed assets (Kf) is defined as follows:
where And - the amount of depreciation of fixed assets for the entire period of their operation, rubles;
The coefficient of physical depreciation of fixed assets can be determined on the basis of data on their actual service life. For objects whose actual service life is below the standard, the calculation is carried out according to the formula:
TPI - useful life (standard service life) of fixed assets.
For objects for which the actual service life is equal to or exceeded the standard, the factor of physical wear is calculated using the following formula:
Kf \u003d  ,
,
where Tf is the actual period of use of fixed assets;
TV - the possible residual life of fixed assets (most often it is determined by an expert).
Expiry factor fixed assets in a consolidated manner characterizes their physical condition at a certain date and is calculated according to the formula:
where Comp is the residual value of fixed assets, rubles;
First - the initial cost of fixed assets, rubles.
In addition to the physical wear and tear of OPF, there are also mowear and tear, the essence of which is that one or another type of OPF is devalued even before its complete physical wear and tear.
Distinguish between obsolescence of the first and second kind (type).
Obsolescence of the first kind is caused by a reduction in the cost of production of the fixed assets themselves in the industries producing fixed assets.
The degree of obsolescence of the first kind (Km1) can be determined by the following formula:
Km1 \u003d  ,
,
where Sv and Cn are the replacement and original cost of fixed assets, respectively.
Obsolescence of the first kind does not lead to losses, since it reflects the savings in the costs of past labor and represents the effect of increasing accumulation.
Obsolescence of the second kind occurs as a result of the appearance of similar types of fixed assets with greater productivity.
The degree of obsolescence of the second kind (Km2) can be determined as follows:
Km2 \u003d  ,
,
where Wu and Vn are the productivity (production) of obsolete and new equipment, respectively.
At each enterprise, the process of physical and moral depreciation of fixed assets must be controlled in order to prevent their excessive wear and tear, especially of their active part, as this can lead to negative economic consequences for the enterprise.
Depreciation of fixed assets
Depreciationis a process of gradual transfer of the value of fixed assets to manufactured products in order to form a special amortization fund money for the subsequent complete restoration (renovation) of fixed assets.
Depreciation deductions are included in the cost of manufactured products. The initial data for calculating the amount of depreciation deductions are:
The amount of the initial cost of fixed assets;
Useful life (depreciation period).
According to Art. 256 of the Tax Code, depreciable property is property that is owned by the taxpayer, is used by him to generate income and the cost of which is repaid by means of depreciation.
Depreciable property is property with a useful life of more than 12 months and an initial cost of more than 20,000 rubles.
Depreciation rate
Depreciation rate - the state-established annual percentage of repayment of the cost of fixed assets. The depreciation rate determines the amount of annual depreciation charges.
The depreciation rate is the ratio of the annual depreciation to the original cost of the means of labor, expressed as a percentage. The calculation of the depreciation rate (N) is carried out according to the following formula:
H \u003d  ,
,
where Sperv is the initial cost of this type of fixed assets, rubles;
Slikv - the liquidation value of this type of fixed assets, rubles;
T - useful life, years.
The level of the depreciation rate is determined by the accepted useful life of various types of fixed assets. The choice of its value is due to a number of factors: the pace and directions of technical progress, the capabilities of the production apparatus for the production of new types of equipment, the relationship between needs and resources in various types of fixed assets, etc.
Depreciation methods
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for two methods of depreciation: linear and non-linear.
Accrual of depreciation on an object of depreciable property starts from the 1st day of the month following the month in which this object was put into operation.
The accrual of depreciation on an object of depreciable property is terminated from the 1st day of the month following the month when the cost of such an object was completely written off, or when this object was removed from the depreciable property of the taxpayer for any reason.
Straight-line depreciation method applies to buildings, structures, transmission devices and intangible assets included in the eighth to tenth depreciation groups, regardless of the timing of the commissioning of these facilities.
Accrual of depreciation in relation to an object of depreciable property is carried out in accordance with the depreciation rate determined for this object based on its useful life.
When applying the straight-line method, the amount of depreciation accrued for one month in relation to an object of depreciable property is determined as the product of its original (replacement) cost and the depreciation rate determined for this object.
where K is the depreciation rate as a percentage of the original (replacement) value of the depreciable property;
Thus, the straight-line depreciation method allows the costs of the depreciable property to be accounted for evenly throughout the useful life.
When applying non-linear depreciation method,its monthly amount will be calculated not separately for each property (as with the linear method), but for the depreciation group as a whole.
The amount of depreciation charged for one month for each depreciation group is determined by the following formula:
A \u003d B (k / 100%),
where A is the amount of depreciation calculated for one month for the corresponding depreciation group;
B - the total balance of the corresponding depreciation group;
k - depreciation rate (in percent) for the corresponding depreciation group.
In this case, in order to apply the non-linear method, the following depreciation rates are applied (Table 4.1).
The total balance is calculated as the sum of the residual value of all depreciable property items that belong to this depreciation group.
Depreciation is not linear way continue to accrue until the total balance of the group is less than 20,000 rubles. After that, the value of the total balance of the group can be included in non-operating expenses.
Table 4.1.
Depreciation rates
|
Depreciation group |
Depreciation rate (monthly) |
|
Fourth |
In order to create financial conditions for accelerating the introduction of scientific and technological achievements into production and increasing the interest of enterprises in accelerating the renewal and technical development of the active part of fixed assets (machinery, equipment, vehicle) enterprises have the right to apply accelerated depreciation method active part of production fixed assets, put into operation after January 1, 1991.
Accelerated depreciation is a target method faster than the standard service life of fixed assets, the full transfer of their book value to the costs of production and circulation.
Enterprises can apply an accelerated method of calculating depreciation in relation to fixed assets used to increase the output of computer technology, new advanced types of materials, instruments and equipment, and expand product exports in cases where they massively replace worn-out and obsolete equipment with new, more productive ones.
With the introduction of accelerated depreciation, enterprises use a uniform (linear) method of calculation, while the rate of annual depreciation deductions for full restoration, approved in accordance with the established procedure (for the corresponding inventory object or their group), increases, but not more than twice.
Accelerated depreciation allows you to speed up the process of updating fixed assets at the enterprise; to accumulate sufficient funds for technical re-equipment and reconstruction of production; reduce income tax; maintain fixed assets at a high technical level.
There are the following accelerated depreciation methods: method of diminishing balance and method of depreciation by writing off the value by the sum of the number of years of useful life.
With the diminishing balance method, the annual amount of depreciation deductions is determined based on the residual value of an item of fixed assets at the beginning of the reporting year and the depreciation rate calculated based on the useful life of this item and the acceleration factor, not more than 3.
With the method of calculating depreciation by writing off the cost according to the sum of the number of years of useful life, the annual amount of depreciation is determined based on the initial cost or replacement cost (in case of revaluation) of the fixed asset and the ratio, in the numerator of which is the number of years remaining until the end of use of the object, and in the denominator - the sum of the numbers of years of the useful life of the object.
Since January 1, 2009, Federal Law No. 224-FZ of November 26, 2008 has canceled the possibility to apply an accelerating depreciation rate (no more than 3) for leased items of 1-3 depreciation groups. At the same time, small and medium-sized leasing companies will suffer the most, as they will lose the benefits of taxation of leasing transactions for a number of inexpensive equipment (cars, personal computers, a significant part of innovative equipment, agricultural machinery, etc.).
Depreciation rate formula
The essence of depreciation
The depreciation rate for fixed assets includes the amount of depreciation accrued as a percentage of the existing book value of the fixed asset.

Wear types
All fixed assets are gradually subject to depreciation, which is the gradual loss of the fixed asset of its use value. There are 2 types of wear:
- Physical wear and tear (decrease in use value as a result of wear of parts, negative influence of aggressive environment, nature, etc.),
- Obsolescence (decrease in cost regardless of physical wear and tear).
To better understand the depreciation formula, it is necessary to distinguish between two kinds of obsolescence:
- The first kind, which is a loss of initial value due to an increase in labor productivity in the industry of manufacturing fixed assets,
- The second kind, which occurs due to the development of more progressive or economical technology. Due to obsolescence of the second kind, the relative usefulness of obsolete fixed assets decreases.
Basic concepts
To study the formula for the depreciation rate, you should understand some concepts:
- The depreciation object is a fixed asset located in the organization on the basis of ownership (operational management or economic management).
- Useful life includes the average life span of a particular type of item.
- The depreciation rate is the annual percentage of the reimbursement of the value of fixed assets, which is set by the state. In the Russian Federation, uniform depreciation rates are applied, the indicator of which is determined for each type of fixed asset.
Depreciation rate formula
In order to implement accounting The depreciation rate formula can be calculated in two ways:
- According to the first method, the depreciation rate formula is as follows:
NA \u003d (PS - LS) / (AP PS) * 100%
Here HA is the depreciation rate,
PS - initial cost (rubles),
Medicines liquidation value (rubles),
AP - amortization period (years).
- According to the second method, the depreciation rate formula sets the indicator based on the service life of a certain object (expressed in years):
HA \u003d (1 / T) * 100%
Here HA is the depreciation rate,
Т - service life of the OS object (years).
The second formula is used in accounting and for tax purposes.
Amortization rate
The following depreciation rate formula is also used to calculate taxes:
HA \u003d (2 / Tm) 100%
Here HA is the depreciation rate,
Тm is the service life of the corresponding OS object (determined in months).
Examples of problem solving

Example... An object worth 120 thousand rubles was purchased. with a term of use of 5 years. The annual rate of depreciation is 20%. Hence, the annual amount of depreciation deductions is:
120 x 20: 100 \u003d 24 thousand rubles.
With the diminishing balance method, depreciation deductions are determined based on the residual value of the object of fixed assets at the beginning of the reporting year, the depreciation rate and the acceleration factor established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Example... An object of fixed assets was purchased for 120 thousand rubles. with a useful life of 5 years. The object's annual depreciation rate, calculated based on the useful life, is 20%. This rate is increased by an acceleration factor of 2 to 40% (20 x 2). Hence the annual amount of depreciation deductions is equal to:
(120 x 20: 100) x 2 \u003d 48 thousand rubles.
In the first year of operation, the annual depreciation is determined based on the original cost of the object. In the second year of operation, depreciation is calculated at 40% of the residual value, i.e. (120 - 48) x 40 \u003d 28.8 thousand rubles. etc.
With the method of writing off the cost by the sum of the number of years of the useful life of the object, depreciation deductions are determined based on the initial cost of the object of fixed assets and the annual ratio, where the numerator is the number of years remaining until the end of the object's service life, and in the denominator is the sum of the number of years of the object's service life ...
Example... An object of fixed assets was purchased for 120 thousand rubles. The useful life is 5 years. The sum of the service life is 15 years (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). In the first year of operation of the specified object, depreciation may be charged in the amount of 5/15, or 33.3%; in the second year - 4/15, i.e. 26.7%; in the third year - 3/15, i.e. 20.0%; in the fourth year - 2/15, i.e. 13.3%; in the fifth year - 1/15, i.e. 6.7%.
Accruals of depreciation deductions for fixed assets during the reporting year are carried out monthly, regardless of the method of calculation in the amount of 1/12 of the calculated annual amount.
In the case of commissioning an object of fixed assets during the reporting year, the annual amount of depreciation is the amount determined from the first day of the month following the month when this object was accepted for accounting until the date of the annual reporting.
Example... In April of the reporting year, an object of fixed assets with an initial value of 120 thousand rubles was put into operation and accepted for accounting. The term of use is 5 years, the annual depreciation rate is 20%. With the linear method, the depreciation of this object in the first year of use will be:
(20 x 8: 12) \u003d 13.33%, i.e. 16 thousand rubles;
(120 x 13.33: 100), where 8 is the number of months of operation of the facility in the first year.
With the method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of production (work), amortization deductions are calculated based on the natural indicator of the volume of production (work) in the reporting period and the ratio of the initial value of the object of fixed assets and the estimated volume of production (work) for the entire useful life of the object of fixed assets.
Example... A car worth $ 60,000 was bought.
Depreciation calculation using formulas
rubles, its carrying capacity is more than 2 tons, the guaranteed mileage is 400 thousand km. For the first year, the mileage was 40 thousand km. Consequently, the amount of depreciation charges based on the ratio of the initial cost and the estimated volume of production will be:
(40 x 60: 400) \u003d 6 thousand rubles.
In case of disposal of an object and its write-off from accounting (or full repayment of the value of this object), depreciation charges for the object of fixed assets cease from the first day of the month following the month of disposal and write-off of this object or full repayment of the value of the object.
In 2002, in connection with the introduction of part two Of the Tax Code RF introduced a number of changes to the procedure for the depreciation of fixed assets. A new procedure for calculating depreciation for tax purposes has been established. Fixed assets are classified as depreciable property.
For tax purposes, depreciable property is property with a useful life of more than 12 months and an initial cost of more than 10,000 rubles. According to Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, land and other objects of nature use (water, subsoil and other natural resources), as well as inventories, goods, objects of unfinished capital construction, securities), as well as property of budgetary organizations, with the exception of property, are not subject to depreciation, acquired in connection with the implementation of entrepreneurial activities and used to carry out such activities.
For the purposes of taxation of enterprises and organizations, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation established that taxpayers accrue depreciation independently using one of the following methods:
1) by a linear method;
2) nonlinear method.
When applying the linear method, the depreciation rate for each object of depreciable property is determined by the formula:
K \u003d (1 / n) x 100%
nonlinear:
K \u003d (2 / n) x 100%
where K is the depreciation rate as a percentage of the original (replacement) value of the depreciable property; with non-linear - to the residual value;
n is the useful life of this depreciable property, expressed in months.
T.I. Yurkova, S.V. Yurkov
Enterprise economy
Electronic textbook
MODULE 2.4. CUSHIONING OF FIXED ASSETS
Depreciation of fixed assets, reflected in the accounting records, accumulates during their entire service life in the form of depreciation charges on the accounts for depreciation. In each reporting period, the depreciation amount is written off from the depreciation accounts to the accounts for accounting for production costs. Together with the proceeds from the products and services sold, the depreciation is credited to the settlement account of the enterprise where it is accumulated.
Accrual of depreciation on a straight-line basis and its features
Depreciation deductions are spent directly from the current account to finance new capital investments in fixed assets.
Depreciation Is a systematic process of transferring the value of the means of labor as they wear out to the product produced with their help. Depreciation is a monetary expression of physical and moral depreciation of fixed assets. The amount of depreciation accrued during the operation of fixed assets should be equal to their initial (replacement) cost.
Objects for amortization are objects of fixed assets that are in the organization on the basis of ownership, economic management, operational management.
Depreciation is not charged for the following types of fixed assets:
· For items of fixed assets received under a gift agreement and free of charge in the process of privatization;
· Housing stock (except for objects used to generate income);
Objects of fixed assets, the consumer properties of which do not change over time ( land and objects of nature management).
Depreciation policy is an integral part of the economic policy of any state. By setting the rate of depreciation or useful life, the procedure for calculating and using depreciation charges, the state regulates the rate and nature of reproduction in industries.
Useful life Is the average service life of objects of this type.
Depreciation rate Is the annual percentage of fixed assets reimbursement established by the state.
In Russia, unified depreciation rates are used for calculating depreciation. The depreciation rate is defined for each type of fixed assets.
The depreciation rate for full recovery is calculated by the expression

where Hin - the annual depreciation rate for full restoration; FROMfirst - the initial cost of fixed assets; L - the liquidation value of fixed assets; D - the cost of dismantling fixed assets being liquidated and other costs associated with liquidation; Tand - useful life.
The depreciation rates are differentiated by groups and types of fixed assets. They also depend on the conditions in which the fixed assets are operated.
So, for buildings, they range from 0.4 to 11%, for power and working machines and equipment from about 3 to 50%, for heat exchangers in the production of plastics with a non-aggressive environment - 6.7%, for the same devices used in production of plastics with an aggressive environment - 10%.
The depreciation rate is related to the useful life of an item of property, plant and equipment. It can be assumed that the useful life is the reciprocal of the depreciation rate.
During the useful life of an item of fixed assets, the accrual of depreciation charges is not suspended, except when they are under reconstruction or modernization by the decision of the head of the organization. The accrual of depreciation is also suspended for fixed assets transferred, by decision of the head of the organization, to conservation for a period of more than three months.
Depreciation on the value of newly received fixed assets begins on the first day of the month following the month of their receipt. For retired fixed assets, depreciation ceases from the first day of the month following the month of their retirement
Test control
1. Depreciation of fixed assets2. The useful life is3. The depreciation rate is set depending on
We figured out the concept of depreciation. Learn how to calculate depreciation of fixed assets. From 2002 to the present, the following methods of depreciation have been used in accounting: linear depreciation method, diminishing balance method, proportional to the volume of production method, and also a method based on the sum of the number of years of useful life. In the article, we will analyze these 4 methods for calculating depreciation deductions with examples.
The calculation of depreciation of fixed assets involves the use of the original or residual value and depreciation rates of fixed assets. Initial is the cost at which the object is accepted for accounting upon receipt at the enterprise. Read more about the receipt of fixed assets. The residual value of fixed assets is the difference between the original cost and the accrued depreciation.
General formula for calculating depreciation deductions:
Cost (initial or residual) * depreciation rate / 100%.
It is very simple to calculate the rate, for this you need to divide all depreciation (taken as 100%) by. Then you can calculate the amount of depreciation for the past year, that is, multiply the original cost by the rate and divide by 100%. How do I calculate the depreciation charge per month? To do this, it remains only to divide the amount received by the previous action by the number of months in a year.
Depreciation deductions cover part of the cost of fixed assets at the expense of profit, gradually transferring it to income from goods produced and sold.
State regulatory bodies establish standard indicators for depreciation deductions, which depend on the type of fixed assets and the conditions for their use in production. For example, for production facilities, the norm is from 3% to 11%, for buildings - from 0.4% to 11% in the reporting period.
Factors that determine the rate of depreciation
The amount of deductions is determined in accordance with the requirements of RAS or IFRS (for companies operating in accordance with international standards). The total depreciation rate depends on three factors.- The original cost of the assets to be depreciated. The price that the entity paid when purchasing the asset. Due to inflation, fixed assets are regularly revalued to ensure that depreciation rates are presented fairly. For example, the factory building was purchased in 1980 at a price of 1,000 rubles, after which it was revalued due to the denomination of the national currency, inflation, reconstruction.
- Residual value of buildings and equipment. The price at which an asset can be sold before its useful life. For example, a new woodworking machine has a lifetime of 25 years, but the company plans to sell it in 5 years. The indicator reflects the degree of moral or physical obsolescence of the asset.
- The standard life of the asset (the length of the depreciation period). The number of years during which fixed assets are usable. For example, the lifespan of a wooden building is 30 years; the company purchased it 10 years after its construction. The amortization period will be 20 years.
The method of depreciation of each group of fixed assets is determined by the scientific and technical policy pursued at the state level. Due to the strong wear and tear of industrial buildings and structures in the Russian Federation, accelerated depreciation was created. Book value the active part of production (machine tools, transport, lifting equipment) is a cost item, the operating period is halved. Small businesses are allowed to write off up to 50% of the value of buildings and production facilities that have been used for more than three years.
Methods for calculating the rate of depreciation
The annual amount (rate) of depreciation is calculated depending on the expected date of disposal and the level of utilization of fixed assets.- Linear calculation of depreciation is used for poorly worn fixed assets with a long service life - buildings, industrial facilities. The amount of deductions is inversely proportional to the period of operation of the facility (in months or years). For example, a machine has been in use for 10 years (120 months). The monthly rate will be 1/120 or 0.8% of the property value.
- Depreciation calculation using the declining balance method. The amount of deductions is equal to the product of the residual value of the asset (at the time of accrual, taking into account the revaluation), the depreciation rate and the acceleration factor established by the company's accounting department.
- Price write-off calculation based on the number of years of use. The amount of deductions is equal to the quotient of dividing the original price of the object by its service life.
- Depreciation is charged in proportion to the amount of goods produced. The rate of deductions is calculated as the ratio of the initial price of fixed assets and the estimated volume of production.
Fixed assets registered by the company, through depreciation deductions, gradually transfer their considerable cost to production costs. Several methods for calculating depreciation have been legally approved, but there are no strict guidelines for the mandatory application of any particular method. However, there are a number of approved Provisions and Instructions that state the recommended version of the depreciation calculation formula for each specific group from the List of asset qualifications.
Depreciation methods
Based on the theses of the Legislation of the Russian Federation, depreciation property includes equipment, the duration of productive operation of which exceeds a period of 12 months, and the initial cost is determined in the amount of 40 thousand rubles. Land, natural resources, objects of unfinished capital construction, securities have no wear and tear, and therefore are not subject to depreciation.
There are several calculation methods:
- Non-linear.
Linear way
The linear method is the most common due to its elementary and unpretentiousness. At the first stage of work, the depreciation rate is determined using the formula for calculating the depreciation of fixed assets:
NAO \u003d 1 / service life in months x 100%
The annual rate of amortization deductions is determined as a percentage.
CAM \u003d PS x NAO / 100%,
where the initial cost of the fixed asset is reflected in the PS.
Based on the calculations obtained, monthly values \u200b\u200bof norms and amounts of depreciation deductions are found. This method is used to depreciate directly for each inventory number of property that is registered with the organization.
Depreciation is charged monthly in equal installments.
The depreciation rate does not change during the entire period of operation of the facility.
Assessment of technological equipment 550 thousand rubles. Refers to the 4th depreciation group, the operating period is 84 months (7 years).
Depreciation rate \u003d 100%: 7 \u003d 14.29% per year
Amount \u003d 550,000 x 14.29%: 100% \u003d 78,595 rubles. in year
Depreciation deductions every month \u003d 78595/12 \u003d 6550 rubles.
Non-linear depreciation methods
The non-linear option for depreciation, in turn, is subdivided into several more areas:

The declining balance method is characterized by an accelerated depreciation process based on the residual value of the property.
UOAO \u003d OS x NAO x KU / 100%,
- OS - residual value;
- KU - acceleration coefficient.
The cost of the property is 300,000 rubles. The service life is 5 years. Acceleration factor fixed in accounting policy, is equal to 1.5.
Depreciation rate \u003d 100%: 5 \u003d 20%  Depreciation of fixed assets according to the formula of the cost write-off method based on the sum of the number of years of useful life is determined by the formula:
Depreciation of fixed assets according to the formula of the cost write-off method based on the sum of the number of years of useful life is determined by the formula:
AOChL \u003d PS x CHLO / CHLPI,
CLO - the number of years that remain until the end of the service life,
CHLPI - full term useful use of fixed assets.
The initial cost of the fixed asset is 400,000 rubles. The second depreciation group, the service life is 3 years. According to the method of writing off the value of fixed assets in proportion to the volume of output, works and services rendered, the formula for calculating depreciation takes the following form:
AOVP \u003d FOP x PS x / PO,
FOP - the volume of products actually produced for a specific reporting period,
PO - the planned volume of production for the entire period of useful use of the equipment.
This method of accrual is fixed in the acceptance certificate (form OS-1).
The initial cost of the car is 430 thousand rubles. The expected mileage is 500 thousand km.
PS / expected mileage \u003d 430,000 / 500,000 \u003d 0.86 rubles / km

Wear
During the period of operation, fixed assets are exposed to the external environment and other negative influences, therefore, over time, moral and physical deterioration of the equipment used appears.
Physical deterioration implies a decrease in the level of the original technical characteristics of fixed assets and depends on many factors:
- The initial state of fixed assets;
- Operation level;
- The presence of an aggressive environment;
- The skill level of the service personnel.
The economic essence of obsolescence is that production assets depreciate before the end of their useful life. Continuous development of production leads to the occurrence of obsolescence due to:
- Reducing the cost of production of fixed assets,
- The release of similar equipment with greater productivity.
Increasing and decreasing coefficients
Businesses can use various ratios that speed up or slow down the depreciation process. Firms reflect the choice of indicators provided for in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in accounting policies.
For equipment used in corrosive atmospheres or in conditions of extensive use, multiplying factors are applicable. When calculating depreciation of fixed assets according to the calculation formula, increasing coefficients are applied in the amounts approved by law.
The organization, according to the decision of the head, can also apply reduction factors. According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, special efficiency factors are applied to vehicles received or leased. For example, minibuses intended for passenger transportation with an acquisition cost of more than 400 thousand rubles are depreciated at k \u003d 1/2.
All changes regarding the use of additional coefficients are fixed in the accounting policy of the enterprise and are valid throughout tax period... Recalculation of depreciation of fixed assets according to the calculation formula during the reporting period is not allowed.