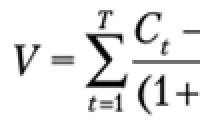Accounting for the receipt and disposal of intangible assets. Accounting for intangible assets Accepted for accounting nma posting
Accounting for acquisitions and disposals intangible assets carried out on the balance sheet. 04 "intangible assets". Let us consider how transactions on the acquisition of an asset, its use and disposal are reflected in the accounting.
Documenting the receipt and disposal of intangible assets
The documentary evidence of the receipt of property in the production process of the company is the acceptance certificate f. No. OS-1. The capitalization of intangible assets is accompanied by the registration of an analytical account card f. № intangible assets-1, which records information about each object separately, as well as the reasons for its liquidation or disposal.
Official recommendations on the registration of the movement of intangible assets have not yet been determined, therefore companies have the right to develop the necessary forms on their own, relying on the instructions of the current regulatory legal acts, for example, the Law "On Accounting", dictating the presence in the document required details, reflecting the period of use of the asset, its value, depreciation rates, dates of acceptance and decommissioning, etc.
It is on their basis that the accounting for depreciation and disposal of intangible assets is carried out.
Particular attention is required when registering the transfer of ownership of an asset, since the acquisition of rights to dispose of property subject to patent protection (for example, an invention) must be confirmed license agreements with the corresponding registration in the Patent Department. Often, accounting for the acquisition and creation of intangible assets involves the registration of special forms of protection that determine internal rules operation and protection of such property in order to prevent the disclosure of industrial secrets.
Accounting for the receipt of intangible assets
Intangible assets are considered to be received:
- purchase;
- exchange;
- gratuitous transfer;
- creation of an asset on its own or by third-party contractors;
- contribution to the company's management company.
The costs of creating an intangible asset are reflected in the account. 08-5 "Acquisition of intangible assets". It accumulates all the expenses incurred by the company in the formation of the initial cost of this asset. Introducing intangible assets into operation intangible assets is recorded in the debit of the account. 04.
Acceptance of intangible assets for accounting: postings
The following accounting entries are common to all types of intangible assets acquisition:
- D / t 08-5 K / t 60, 70, 75-1, 76, 98-2 - a set of costs associated with the acquisition or manufacture of intangible assets
- D / t 04 K / t 08-5 - the asset is accepted for accounting.
In the case of the creation of intangible assets, the receipt of intangible assets is formalized by entries:
- D / t 08 K / t accounts involved in the formation of the cost of intangible assets - staff salaries, deductions to the Social Insurance Fund, the cost of materials, energy, etc. (70, 69, 76, 10, etc.). Upon completion of the creation of an asset, its value is transferred to the debit account. 04.
Accounting for the receipt of intangible assets as a share in the authorized capital of the company is reflected in the records:
- D / t 75 K / t 80 - debt of the founder to the management company;
- D / t 08 K / t 75 - receipt of the asset in the enterprise;
- D / t 04 K / t 08 - intangible assets commissioning;
- When buying an asset, VAT is allocated, which is accounted for on the account. 19 "VAT on purchased values".
Example
The company acquired the right to software... The price under the agreement was RUB 472,000, incl. VAT RUB 72,000 The specialist's consultations cost the company 29,500 rubles. (including VAT 4500 rubles) In this case, the receipt of intangible assets from suppliers is reflected in the records:
Operation
Sum
Supplier invoice acceptance
Payment of the invoice for the purchase of the program
Consultant cost
Payment of invoice for consultations
VAT credited (72,000 rubles + 4500 rubles)
Commissioning (400,000 rubles + 25,000 rubles)
The receipt of intangible assets on a gratuitous basis uses account 98 “Income bud. periods "with a sub-account of gratuitous receipts. Gratuitous receipt of intangible assets into the company is reflected:
- D / t 08 K / t 98
As the depreciation is calculated, the depreciation amount, reducing the cost of the object on the debit account. 98, goes into credit account. 91, which means the recognition of profit on other income:
- D / t 98 K / t 91.
Accounting for disposal of intangible assets
The cost of intangible assets, the use of which has become impractical for various reasons (lack of income, complete wear or the need to sell), should be written off. The disposal operation is accompanied by a corresponding order of the company's management. If the reason for disposal is the obsolescence of the asset, then a commission created at the enterprise analyzes the situation and draws up an act to write off intangible assets.
Upon liquidation of an asset with residual value, the difference between it and discount price the asset is debited to the account. 91, defining a loss. A fully depreciated object does not create a loss upon liquidation.
Example
Morally outdated and the intangible asset object with an initial value of 100,000 rubles must be liquidated. The amount of accrued depreciation by the date of liquidation was 85,000 rubles. Disposal of intangible assets is documented by entries:
Intangible assets can be sold, assigned, transferred free of charge or into the statutory funds of other companies. Income from the sale of tangible and intangible assets is reflected in the effective accounts 91 and 99.
Example
The firm sells the right to use the asset with an initial cost of RUB 150,000 that it owns. Depreciation accrued - 100,000 rubles. The purchase price under the contract is 295,000 rubles. (including VAT - RUB 45,000). The sale of intangible assets is drawn up, postings:
- these are materials that do not have material, or physical form and which are used in the work of production, in the performance of any services, and so on. In this article, we will consider the purchase of intangible assets and their entry into the enterprise.
Intangible assets can be applied to an enterprise only in the following cases:
- In case of purchase.
- If created independently or with the help of additional services.
- In the case of entering into the authorized capital.
- In case of gratuitous receipt.
Intangible asset purchase transactions
When assets arrive at the enterprise, they are included in the accounting for actual cost... Fixed assets are included in the same way. This price includes the exclusive rights to intangible assets, as well as to its presence in the contract or patent, other documents and all attached costs.
These costs may include duties, some taxes, some services (consultations), customs duties and services of other organizations. These costs do not include VAT. From full cost costs are calculated by VAT and reimbursed from the budget.
In the process of introducing accounting for intangible assets, a special account 04 was set aside, which is called "Intangible assets". The debit of this account provides data on the receipt of the object, and the credit, on the contrary, gives data on the write-off of objects.
Before intangible assets go to account 04, they go through debit account 08, which reads “Investing in fixed assets". To do this, in account 08 you need to open a special sub-account "Acquisition of intangible assets".
An example of the acquisition of intangible assets
The company receives, following the contract, its exclusive right to the trademark. The contract indicates the cost of 500,000 rubles, if you add VAT, you get 590,000 rubles. In order to register the contract, we paid a fee of 12 thousand rubles. Also, a fee of 2 tr was paid for the fact that changes were made to the register of trademarks. How, then, should the transactions for the purchase of HMA be drawn up?
Intangible assets: example of purchase transactions
| Debit | Credit | Description | Sum |
| Payment for the exclusive right to a trademark | 590 000 | ||
| The cost of the exclusive right to a trademark without VAT | 500 000 | ||
| VAT cost for the purchase of an exclusive right | 90 000 | ||
| VAT deduction | 90 000 | ||
| Payment of the fee for the registration of the contract | 12 000 | ||
General issues of synthetic and analytical accounting intangible assets we considered in. In this material, we present the main entries for intangible assets in accounting.
Intangible assets: transactions when purchasing an asset
Recall that intangible assets are recorded at their original cost. The order of its formation depends on the method of receipt of objects, and we talked about this in. The accounting records generated at the same time depend on the way intangible assets enter the organization. Here are some typical ones below. We note right away that the initial cost of intangible assets is formed according to the debit of account 08 "Investments in non-current assets". And then, when the object is accepted for accounting, it is debit to account 04 "Intangible assets" (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Account debit 04 - Account credit 08
When accepting intangible assets for accounting, this entry is always applied, it does not depend on the method of receipt of the asset. The latter affects only the transactions on the formation of the initial value of the intangible asset on account 08.
So, when purchasing an intangible asset for a fee, the wiring is usually as follows:
Debit account 08 "Investments in non-current assets" - Credit account 60 "Settlements with suppliers and contractors"
However, even if intangible assets were purchased, transactions are not always limited to settlements with suppliers and contractors. Indeed, the initial cost may include various duties:
Account debit 08 - Account credit 76 "Settlements with by different debtors and creditors "
And even interest on loans and borrowings, when the acquired intangible asset is recognized as an investment asset (clause 10 of PBU 14/2007):
Debit of account 08 - Credit of accounts 66 "Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings", 67 "Settlements for long-term loans and loans "
The IA object was created by the organization itself
When an object of intangible assets is created by the organization itself, the composition of the accounting records is usually more varied. For example, the following postings can be generated:
| Operation | Account debit | Account credit |
|---|---|---|
| Assessed wage employees involved in the creation of intangible assets | 08 | 70 "Payments to staff on remuneration" |
| Assessed insurance premiums from payments to such employees | 08 | 69 "Calculations for social insurance and providing " |
| Reflected expenses on travel related to the creation of intangible assets | 08 | 71 "Settlements with accountable persons" |
| Reflected duties and fees associated with the creation of intangible assets | 08 | 76 |
| Remuneration was awarded to intermediary organizations, as well as organizations for information and consulting services related to the creation of an intangible asset | 08 | 60 |
| Depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets that are used to create new intangible assets has been charged | 08 | 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets", 05 "Depreciation of intangible assets" |
Intangible assets received as a contribution to the authorized capital
Upon receipt of an intangible asset as a contribution to the authorized capital at a cost agreed by the founders and not exceeding the amount determined by an independent appraiser, an accounting entry is made:
Debit account 08 - Credit account 75 "Settlements with founders"
Intangible assets received free of charge
When an intangible asset enters the organization under a gift agreement, an entry is formed at its market value:
Account debit 08 - Account credit 98 "Deferred income"
And as the depreciation of intangible assets is accrued in the amount of the accrued depreciation, future income is written off to other income current period:
Debit account 98 - Credit account 91 "Other income and expenses"
Intangible assets received under an exchange agreement
When acquiring intangible assets under an exchange agreement, each party to the transaction must reflect both the sale of its assets transferred in exchange and the posting of the values received in return.
Let's consider these operations using an example. An organization acquires the exclusive right to a computer program in exchange for its goods. total cost goods is 230,000 rubles, incl. VAT 18%. The cost of goods is 162,000 rubles. The acquired program is not subject to VAT (subparagraph 26 of paragraph 2 of article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The exchange is recognized as equivalent.
Accounting records from the acquirer of intangible assets, we present in the table:
Intangible assets depreciation transactions
When calculating amortization of intangible assets, accounting records may be as follows:
Debit of accounts 20 "Main production", 26 " General running costs", 44" Expenses for sale ", 08" Investments in non-current assets ", 97" Prepaid expenses ", etc. - Account 05 credit
The debit account depends on where the intangible asset is used and what is provided for. For example:
- account 20 applies when intangible assets are used in the manufacture of products, performance of work or provision of services;
- account 26 - when using the asset for management purposes;
- on account 44, the amortization of intangible assets will be taken into account by trade organizations;
- account 08 is required when intangible assets are used when creating a new object of intangible assets or in the process of creating an object of fixed assets;
- account 97 can be used when an intangible asset is used in the development of new industries or units.
Transactions when writing off intangible assets
At the time of writing off an object of intangible assets from the accounting records, first of all, it is necessary to close the depreciation account (account 05). And then it should be written off already residual value intangible assets. The write-off transactions depend on how the item is disposed of.
In the above example, when the goods are changed to an object of intangible assets, the seller of intangible assets must record the disposal of the object. Suppose his asset was also listed in intangible assets, its initial cost was 195,000 rubles, and the depreciation accrued at the time of disposal was 19,000 rubles. Recall that the asset is being exchanged for goods worth 230,000 rubles, which will be the selling value of intangible assets.
Let us present the transactions for the disposal of intangible assets and receipt of goods in exchange in the table:
| Operation | Account debit | Account credit | Amount, rub. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reflected income from the sale of intangible assets | 62 | 91, subaccount "Other income" | 230 000 |
| Depreciation of retired intangible assets written off | 05 | 04 | 19 000 |
| The residual value of the intangible asset was written off (195,000 - 19,000) | 91, subaccount "Other expenses" | 04 | 176 000 |
| Goods are capitalized | 41 | 60 | 194 915 |
| VAT charged on goods is included (230,000 * 18/118) | 19 "VAT on purchased values" | 60 | 35 085 |
| Accepted for deduction input VAT | 68 | 19 | 35 085 |
| Reflected offset on exchange operation | 60 | 62 | 230 000 |
If it is not exchange operation, and a regular sale, then receivables the buyer of intangible assets will be closed, for example, as follows: Debit of account 51 "Current accounts" - Credit of account 62. And, accordingly, transactions on the posting of goods and offset of mutual debt will not be reflected.
The transfer of intangible assets free of charge is reflected in other expenses also at the residual value:
Debit account 91, subaccount "Other expenses" - Credit account 04
We will also show the transfer of intangible assets as a contribution to the authorized capital of an LLC with an example. Suppose the parent organization contributes a trademark to the authorized capital. The deposit price is agreed by the founders in the amount of market price and is 325,000 rubles. The initial cost of the object was 116,000 rubles. The property has not previously been depreciated. Disposal records will be as follows:
If a shortage of intangible assets is identified as a result of inventory, its residual value is charged to the debit of account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables": Debit of account 94 - Credit of account 04
And then, in the absence of guilty persons, these losses are written off to other expenses: Debit of account 91, subaccount "Other expenses" - Credit of account 94
If the guilty persons are identified, then, depending on whether they are employees of the organization or other persons, postings are made accordingly:
Debit of account 73 "Settlements with staff on other operations" - Credit account 94
Account debit 76 - Account credit 94
The non-current assets owned by the enterprise are divided into fixed assets, which we talked about in detail, and intangible assets, which we will talk about now.
The main difference between intangible assets and fixed assets is that the former have no physical form and are created as a result of intellectual activity. Intangible asset (intangible asset) is an exclusive right to the result of intellectual activity.
An example of intangible assets is the exclusive right to:
- Computer programs, databases;
- Inventions, models;
- Integrated circuits topology;
- Breeding achievements;
- Know-how;
- Trademarks;
- Brand names;
- Commercial designations;
- Business reputation of the organization.
I repeat once again, intangible assets are not the result of intellectual activity itself, but the exclusive right to it.
To be called an intangible asset, an object must simultaneously satisfy 4 of the following conditions:
- It is planned to be used for a long period (over a year);
- Used for the purpose of obtaining economic benefits;
- Purchased for use, not for resale;
- You can reliably determine its value.
Receipt of intangible assets to the enterprise
First of all, we note that it is necessary to accept the object on the basis of an act of acceptance and transfer, after which it is necessary to enter an accounting card on it in the form of IA-1 (similar actions are carried out with).
Documents that confirm the acquisition of intangible assets can be documents such as patents, an agreement on the alienation of exclusive rights, certificates, a license agreement, etc.
An enterprise can buy an intangible asset (purchase for a fee), create it on its own or with the help of third-party organizations, receive it as a contribution to authorized capital from the founders, and also receive it as a gift (free of charge).
Let us dwell in more detail on each of these 4 methods of receiving an object of an intangible asset, consider what postings must be made in accounting in this case.
Purchase of intangible assets for a fee (purchase)
For accounting of intangible assets, 04 accounting account is used. Received intangible assets are recorded on the debit of this account at their original cost. Acceptance for accounting on account 04 is carried out through an auxiliary one, on the debit of which all costs for the acquisition of an object are collected: directly the cost of the exclusive right to this object and the costs of its use in the future, payment of various duties, taxes, customs duties, consulting and information services, third party services.
As for VAT on all these costs, it should be noted that not all intangible assets are subject to this tax.
VAT does not need to be allocated for the following intangible assets - the exclusive right to programs and databases, inventions, models, know-how, integrated circuits.
For other assets, it is necessary to separate from the sum of all costs that form the initial cost, the amount of VAT and send it to deduction.
Purchase transactions for intangible assets
On account 08 we open an additional subaccount 5 "Acquisition of intangible assets". We will collect all costs on the debit of this account, after which we will send them to the debit account 04 in one transaction, so we will form the initial value of the intangible asset.
Postings:
Creation of intangible assets
You can create an intangible asset independently, with the help of employees of your own enterprise, or you can order a third-party organization that specializes in this.
No matter how the intangible asset is created, it is also necessary to collect all the costs associated with its creation on the debit of account 08, and then transfer them to the debit of account 04.
If the process of creating intangible assets occurs with the help of one's own forces, then the salaries of employees involved in this process, insurance premiums calculated and paid from this salary can act as expenses. Also, expenses can be attributed to depreciation of equipment used in research and development and other work.
If third-party organizations are involved, then the payment for their services acts as an expense.
After the expenses are collected on debit 08, a posting is made to accept the object for accounting D04 K08.
Introducing intangible assets into the Criminal Code
If the intangible asset is entered in the form, then we involve the account of accounting for settlements with the founders and carry out the postings:
- D08 K75 - the initial cost of intangible assets is reflected
- D04 K08 - the asset is accepted for accounting
Gratuitous receipt of intangible assets
Upon receipt of an intangible asset under a gift agreement, it must be evaluated at the average market value as of the current date, in order to know at what cost to accept it and from what to calculate depreciation in the future. Read about the amortization of intangible assets.
Third-party appraisal organizations may be involved for the assessment.
To account for gratuitously received intangible assets, you need to use accounts 98 "Gratuitous receipts".
Accounting entries for intangible assets received under a gift agreement:
- D08 K98 - reflects the market value of the asset obtained after the appraisal.
- D04 K08 - the object is accepted for accounting.
In the future, when calculating depreciation, you need the amount depreciation charges write off also with account 98 wiring D98 K91 / 1.
Intangible assets are property that does not have a physical form, but represents for the enterprise In addition, they, like fixed assets, are aimed at making a profit in the course of financial activities... Accounting for this group of funds is somewhat different from collecting information about the rest of the property. We will get acquainted with the peculiarities of its organization and the structure of the assets themselves in this article.
Specific signs
What are intangible assets? What belongs to them? A novice accountant is probably tormented by such questions. If the image of material property looms immediately, then how to imagine something else?
Let's analyze the main conditions for classifying funds in the group of intangible assets. So, representatives of this category must meet the following criteria:
- have no physical form;
- be used in the production and implementation processes of the enterprise or for management needs;
- be in circulation for 12 months or more;
- make a profit in the present or forecast time;
- comply with the requirements of the documentary legislation;
- be able to transfer ownership to another natural or legal person.
The enterprise itself, for the use of intangible assets in its activities, must have ownership of them.
Classification of intangible assets by type
With the growth of scientific technologies, the number of types of immaterial forms of property increases. A dozen years ago, only exclusive copyrights were included here, but now the group has about 7 categories, including:
- The right to use natural resources.
- Property rights.
- Commercial designations (use of brands, names).
- Property objects in the industrial sector.
- Copyright.
- Goodwill.
- Other intangible assets (in particular, some costs).
It should be borne in mind that, as intangible assets, it is not the result of research and intellectual work that is recognized, but the exclusive right to use it for commercial purposes.
Intellectual property
The results of intellectual activity are also intangible assets. What belongs to them? Mostly patent or copyright assets. The first category includes rights arising in the scientific and design field. It:
- new inventions;
- industrial designs;
- technical models;
- names and trademarks.
The second category includes property created on the basis of the objective ideas of a certain author. These are works of art, software, databases, integrated circuit layouts and other assets.

The main difference between copyright and patent law lies in the way it is recognized, which is reminiscent of in this case the relation of the part to the whole. If a patent is issued for any invention and protects the work itself, then copyright is assigned only to the form of expression of the subjective view of different owners on the same idea.
Organization costs of a legal entity
It would seem, what is common between the costs and assets of the enterprise? In some cases, they can be reflected in the composition of intangible assets. To do this, it is enough to comply with several conditions:
- expenses must be made during the preparation of documents for the creation of an enterprise until the moment of its registration with regulatory authorities;
- they are aimed at paying for the work of legal consultants, paying off registration fees and other costs for the legal establishment of a legal entity;
- the amount of expenses must be included in the authorized capital of the organization.
Funds that meet these criteria can be safely included in intangible assets. All further expenses related to changes in accounting policies, stamps, seals and other documents are attributed to general expenses.
Goodwill
The classification of intangible assets provides for the formation of such property as business reputation. It is considered only if there is a sale of the enterprise. Goodwill is understood as the difference between a market and a company, taking into account the accumulated reputation (positive or negative). It turns out that goodwill has its own price, which means that it is sold and bought in the same way as any other property.

In the case of the formation of a positive business reputation, they speak of an additional amount of the premium that must be paid to the seller, since in the future, the presence of goodwill will bring economic benefits to the new owner. A negative characterization of a company in the market can lead to problems and difficulties that hinder operations and profit. This is due to poor management staff, lack of a well-established sales system, marketing plan, regular customers and connections, and for other reasons. This situation reduces the value of the enterprise and requires a discount from the seller.
Depreciation rules
It has already been clarified what intangible assets are, what belongs to them, what are their specific features. Realizing that this property is equated to fixed assets, the question should be asked: is it depreciable? Since intangible assets have no physical form, how will they wear out? Basically, depreciation takes the form of obsolescence. When determining the amount of deductions, one should rely on the following rules:
- Assess the cost and term useful use intangible assets.
- Depending on the specific situation and the provisions of the accounting policy, calculate the amount using one of three methods: linear, decreasing balance, production.
- Deductions are made from the 1st day of the month following the registration of the asset.
- On intangible assets non-profit organizations depreciation is not charged.
To collect accumulations of depreciation amounts, account 05 is used. This is a passive accounting account: the credit is charged, and the debit is written off. When compiling the balance sheet, the credit balance is used in calculating the intangible asset indicator.
Description of depreciation methods
Different types of intangible assets require an individual approach to their assessment and depreciation. Linear way is universal for any property, regardless of its useful life, the amount of profit and other indicators. The method is often used in cases where it is impossible to determine the exact operating period, and it is difficult to predict the receipt of possible economic benefits in the future. The method assumes that the total amount of depreciation is evenly distributed over the months.

They are used for intangible assets, the profit from which will be greatest in the first years of operation. The amounts are unevenly distributed but remain constant over the same period. For the calculation, the acceleration factor is used, which is regulated accounting policies... The indicator of the residual or market value is multiplied by a fraction: the numerator is the coefficient, the denominator is the period of the remaining operation, determined in months.
The production method is the most flexible approach depending on the financial result obtained. The amounts are calculated in direct proportion to the volume of manufactured / sold products with the participation of intangible assets.
Initial cost of intangible assets
To register property, you need to know exactly the value of its value. Like other non-current assets, intangible assets are reflected in accounting at their original cost as at a certain date. The actual amount that had to be spent on the manufacture or purchase of intangible assets includes:
- accounts payable directly related to the creation / purchase of property;
- the net worth of the asset itself.
If there are difficulties in assessing self-made intangible assets, you should carry out comparative analysis with similar products on the market.

In the future, the company has the right to revalue the property in accordance with the instructions of the accounting policy. In the event of a decrease in the price of an intangible asset, the initial cost changes. The difference between market and actual cost write off to the financial results of the enterprise.
Service life of intangible assets
After determining the initial cost, it is necessary to establish the useful life of the intangible assets. The basis is the duration of the property rights to own intangible assets. In other cases, they rely on the possible period of profit. Major intangible assets fall into two categories:
- with an indefinite operational life;
- with a limited period of use.
If everything is clear with the second type, then for the first it is recommended to stop at 20 years. The determination of the operational period must necessarily be based on an analysis of the possible profit, since the period is used to calculate depreciation.
Accounting for intangible assets
To collect and group information about property that does not have a real form, two accounts are used: 04 and 05. The latter, as is already known, is created to accumulate depreciation charges. Account 04 collects all data on the types, costs and processes occurring with intangible assets. This is an active inventory account whose debit balance is reflected in financial statements... In addition, the company uses accounts 19.2 and 48 to characterize VAT and the sale of intangible assets.

A prerequisite for organizing the accounting of intangible assets is the maintenance of analytical accounts for each group or individual units of property. The following sub-accounts can be used as an example:
- 04.1 "Intellectual Property".
- 04.2 "The right to use natural resources".
- 04.3 "Deferred costs".
- 04.4 Goodwill.
- 04.5 "Commercial designations".
- 04.6 "Other intangible assets".
Analytical accounting data must be indicated in the annual reporting (form No. 5) in the section describing the composition of non-material property.
Correspondence with other accounts
Knowing what intangible assets are, what they refer to, we can assume with which accounting accounts the account 04 will interact. Based on the characteristics of the active account, debit transactions characterize the acceptance of intangible assets for accounting through purchase, receipt, exchange. The related accounts become 04 and 08, 50-52, 55, 75-76, 87-88. Writing off intangible assets in special cases of sale, liquidation, exchange leads to an entry in the credit of account 04. In this case, interaction with the debit of accounts 06, 48, 58, 87 takes place.
Accounting for intangible assets
The act of acceptance of intangible assets is a document on the basis of which the receipt of property is recorded. The order of reflection of intangible assets differs depending on the method of obtaining them:
- Purchase - the acquisition of assets for a fee stipulated by the agreement between the seller and the buyer. The expenses that should be included in the initial cost are collected in the debit of account 08. After the intangible assets are ready for commissioning, the data is written off to account 04 by posting Dt 04 Kt 08.
- Barter is a mutually beneficial and equal exchange between entities economic relations... The accountant writes down the account assignment Dt 08 Kt 60/76, characterizing the receipt of intangible assets through the fulfillment of obligations to the other party to the exchange. If the process is accompanied by a surcharge or additional costs, they are reflected in the debit 08 of the account. After the calculation and the start of use, the posting is similar to the first paragraph: Dt 04 Kt 08. The transfer of intangible assets is recorded in the credit of inventory or inventories and in the debit of account 46, 47 or 48.
- In the process of organizing an enterprise, intangible assets can be obtained from the founders. An example of posting looks like this: Дт 04 Кт 75.1.
- When intangible assets are transferred free of charge into the possession of the company, the amounts are credited to account 87.3 at the current market value of the object. Account 04 is debited.
- A prerequisite is the allocation of VAT, which occurs on accounts 68 "VAT" and 19.2. The process of acquiring intangible assets is accompanied by the posting of Dt 19.2 Kt 60/76 or other current accounts. After accepting assets to accounting VAT amount in equal shares write off within six months: Дт 68 "VAT" Кт 19.2.
- VAT on intangible assets purchased for economic and other needs outside of production is taken into account in a slightly different way. The tax is covered by own sources financing: Dt 29, 88, 96 Kt 19.2.
- Acquired intangible assets for production purposes exempted from VAT are included in the initial cost of the tax amount.
Disposal of intangible assets in accounting
Property of this type can be written off from account 04 in cases of sale, gratuitous transfer, liquidation or redirection to the capital of other enterprises. These are the main reasons why intangible assets are disposed of. Regardless of the method of debiting, the 48th account with an active-passive structure is used. The debit records the value of the initial cost of intangible assets, the amount of VAT on them, as well as the costs of disposal. The credit indicates the accumulated depreciation, as well as the amount of income from sales or other benefits.

Turnovers on account 48 allow you to highlight financial results from the process: income in case of excess of the loan turnover over the debit turnover and vice versa. The data is written off to the corresponding account - 80, 84, 83, 98 (depending on the reason for the intangible assets leaving the balance sheet).
Characteristics of a business transaction |
||
Income from the sale of intangible assets was attributed to the increase in the authorized capital. |
||
The loss from the sale of the property right is attributed to the decrease in the initial capital. |
||
The income from the gratuitous receipt of intangible assets is attributed to it. |
||
A production patent was transferred free of charge against the uncovered loss. |
||
Reflected the positive difference between contractual and book value Intangible assets to be transferred as a contribution to the capital of a third-party company. |
||
Income from the investment of intangible assets in another organization is written off to the authorized capital in equal shares. |
Intangible assets are no less important for the successful operation of an enterprise than other types of non-current assets. It is this type of ownership that becomes a unique advantage in the market for a company over competitors.