On account 02, depreciation of the main. What is investment in non-current assets
Active or passive account 02
According to the Chart of Accounts, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, account 02 - Depreciation of fixed assets - is used to collect and systematize information about the depreciation accrued during the use of fixed assets.
Since depreciation is charged on the credit of the account, the question of whether account 02 is active or passive has a simple answer. This is, of course, a passive account, which accumulates depreciation deductions that reduce book value OS. With account 02 in accounting correspond accounts on which expenses are taken into account, thus, these expenses increase.
Depending on where and why the fixed assets are operated in the course of the economic activity of a business entity, the amount for the reporting period of depreciation is included in certain expenses:
- industrial (Dt 20, 23, 25, 29),
- implementation (Dt 44),
- general business (Dt 26),
- others (Dt 91),
- capital investments (Dt 08).
And the fact that account 02 is passive does not mean at all that it will be reflected in the liabilities side of the balance sheet. According to paragraph 35 PBU 4/99, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated 06.07.1999 No. 43n, the balance sheet must contain the indicators made in the net assessment. And this means that the amount accumulated according to Kt 02 is a value that regulates the residual value of fixed assets.
How to fill in the balance sheet for account 02
Analytical accounting for accounts. 02 is maintained for each of the fixed asset inventory items in order to obtain reliable information on depreciation accumulations. Building analytical accounting starts with the opening of sub-accounts. After that, it is formed turnover balance sheet on account 02, and the loan balance at the end of the accounting period is reflected in the accounting - balance sheet (in a special way in the asset, as described above).
As usual, to form such a register, special databases are used (for example, "1C: Accounting"), with which it is easy to sum up the totals and detailed balances for accumulated depreciation charges in the context of each inventory object. This is quite consistent with the requirements prescribed in paragraph 32 of PBU 6/01, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n.
The opening credit balance in the register is the total value of the depreciation accumulated at the beginning of the accounting period. Outgoing credit balance - a similar value, but at the end of the period. The debit turnover is the written off depreciation upon disposal of fixed assets, and the credit turnover is the accrued depreciation.
The credit final balance of account 02 is subtracted from the debit balance of account 01 "Fixed assets" when filling out line 1150 of the balance sheet.
Total for the year depreciation charges is determined by one of the existing methods listed in paragraph 19 of PBU 6/01. The amount of depreciation for each inventory item is determined based on its useful life. Everything property objects can be classified as one of 10 depreciation groups according to the Classifier, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 01.01.2002 No. 1.
Don't know your rights?
Basic postings on account 02
sch. 02 corresponds with many accounts, reflecting certain operations carried out with the OS. Traditional postings on account 02 look like this:
Dt 02 Kt 01 - write-off of accumulated depreciation;
Dt 02 Kt 02 - depreciation is placed on a separate sub-account (for example, for fixed assets leased out);
Dt 02 Kt 79 - depreciation was written off on property allocated from the parent organization to the branch;
Dt 02 Kt 83 - an increase in additional capital due to a reduction in depreciation of fixed assets;
Dt 08 Kt 02 - the amount of depreciation of fixed assets used in the modernization (reconstruction) of other fixed assets, is included in non-current assets;
Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44, 79, 91) Kt 02 - increase in expenses due to accrued depreciation;
Dt 83 Kt 02 - an increase in depreciation as a result of an additional assessment of fixed assets;
Dt 97 Kt 02 - depreciation of fixed assets that are used when starting a new production (costs must be allocated for future periods).
Depreciation of fixed assets is taken into account on account 02. Here it is accumulated in the context of each inventory object, and then written off in correspondence with cost accounts, increasing their amount. In the balance sheet, depreciation is reflected in the asset balance, reducing the book value of fixed assets.
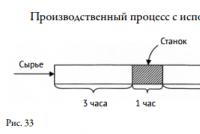
Depreciation- this is a systematic process of transferring the value of the means of labor as they wear out to the product produced with their help. Depreciation is a monetary expression of the physical and obsolescence of fixed assets. The amount of depreciation accrued during the operation of fixed assets should be equal to their original (replacement) cost.
The depreciation process is specified in the Accounting Regulation "Accounting for Fixed Assets" PBU 6/01, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Finance Russian Federation dated 30.03.2001 N 26n. On January 1, 2002, Chapter 25 came into force tax code RF. It provided for other ways of calculating depreciation of fixed assets for calculating corporate income tax.
In the new chart of accounts, account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” is intended to account for depreciation and accumulation of depreciation. This is a regulatory passive account on which two sub-accounts are opened:
02.1 "Depreciation of fixed assets recorded on account 01.1";
02.2 "Depreciation of fixed assets accounted for on account 03".
The credit balance on account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets" reflects the amount of accumulated depreciation of fixed assets that are listed on accounts 01 "Fixed assets".
When accepting an item of fixed assets for accounting (tax) accounting, organizations independently determine depreciation rates in accordance with the chosen method of its accrual within the established ranges of useful lives. Depreciation on fixed assets is charged monthly.
Depreciation rate - the share (in percent) of the cost of an object to be included in production costs with a specified frequency over the useful life or attributed to the appropriate sources.
Currently, depreciation is charged on fixed assets in one of the following ways:
straight-line depreciation method;
non-linear depreciation method;
method (method) of decreasing balance;
method of writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products (works, services);
method of writing off the cost by the sum of the numbers of years of the useful life.
A prerequisite is that the use of one of the methods of depreciation for a group of homogeneous items of fixed assets is carried out during the entire useful life of the items included in this group.
The useful life of an item of fixed assets is determined by the organization when accepting the item for accounting. This period is determined based on:
the expected life of this facility in accordance with the expected productivity or capacity;
expected physical wear and tear, depending on the operating mode (number of shifts), natural conditions and the influence of an aggressive environment, the repair system;
regulatory and other restrictions on the use of this object (for example, the lease term).
In the tax accounting of fixed assets, in accordance with Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciable property is distributed into depreciation groups in accordance with its useful life. In total, 10 depreciation groups have been established, which are differentiated depending on the useful life.
In cases of improvement (increase) of the initially adopted normative indicators of the functioning of an item of fixed assets as a result of the reconstruction or modernization, the organization reviews the useful life of this item.
Accrual of depreciation deductions for an object of fixed assets begins on the first day of the month following the month in which the object was accepted for accounting (tax) accounting. Accrual of depreciation on the object of depreciable property is terminated from the 1st day of the month following the month when the full write-off the value of such an object or when this object has retired from the depreciable property of the taxpayer for any reason.
During the useful life of an object of fixed assets, the accrual of depreciation deductions is not suspended, except when it is transferred by decision of the head of the organization to conservation for a period of more than three months, as well as during the restoration of an object, the duration of which exceeds 12 months.
Accrual of depreciation deductions for fixed assets is made regardless of the results of the organization's activities in reporting period and is reflected in the accounting of the reporting period to which it relates.
In accounting, depreciation is reflected on the credit of account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets" in correspondence with the debit of the accounts of production costs or sources of financing:
debit 20 "Main production";
debit 23 "Auxiliary production";
debit 25 "General production costs";
debit 26 " General running costs»;
debit 29 "Service production";
debit 44 "Distribution costs";
PBU 6/01 contains a list of fixed assets, the cost of which is not redeemed, i.e. depreciation is not charged (for such fixed assets, as well as for fixed assets of non-profit organizations, depreciation is calculated at the end of the reporting year according to the established depreciation rates, and the movement of depreciation amounts on these objects is accounted for on a separate off-balance sheet account). These include:
objects housing stock(residential houses, hostels, apartments, etc.);
objects of external improvement and other similar objects (forestry, road management, specialized structures for navigation, etc.);
productive livestock, buffaloes, oxen and deer;
perennial plantings that have not reached operational age.
Starting from the financial statements for 2002, purchased books, brochures and similar publications, as well as fixed assets worth no more than 10,000 rubles. per unit is allowed to be written off to production costs (sales costs) as they are released into production or operation. And in order to ensure the safety of these objects in production or during operation, the organization must organize proper control over their movement.
Also, fixed assets are not subject to depreciation, the consumer properties of which do not change over time - land plots and objects of nature management.
The accrual of depreciation of fixed assets that are not used in production activities is reflected at the expense of own sources, formed from the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
Formation procedure accounting entries based on the recognition of certain accounts accounting active, passive or active-passive. Accordingly, an increase in various accounting objects can be reflected not only exclusively in the debit or credit of any account. On separate accounting accounts, an increase in accounting objects can be reflected both in debit and in credit of the same account, depending on the situation. And what account is account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” ()?
02 account: active or passive?
The characteristics of account 02 are contained in the Instructions for the Application of the Chart of Accounts for Accounting for the Financial and Economic Activities of Organizations (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
This account summarizes information on depreciation accumulated during the operation of fixed assets.
The accrued depreciation is reflected in the credit of account 02 in correspondence, as a rule, with accounts for recording production costs or sales expenses:
Debit of accounts 20 “Main production”, 26 “General business expenses”, 44 “Sales expenses”, etc. – Account credit 02
But, of course, these are not the only debit accounts. In posting D 91 - K 02, the accounting account shows that depreciation is included in other expenses. Such a posting can be, for example, if depreciation of leased equipment is accrued (when such a lease is not systematic) (clause 11 PBU 10/99).
Given that the depreciation of fixed assets is accumulated on the credit of account 02, this accounting account is passive. But it is important that at the same time in the passive balance sheet it is not reflected. After all, the balance sheet is formed in a net assessment (clause 35 PBU 4/99). In relation to fixed assets, this means their reflection in the balance sheet according to residual value. In other words, the book value (shown in the debit of account 01) is reduced by the credit balance of account 02 by reporting date.
As for analytical accounting on account 02, it is maintained for individual inventory items of fixed assets.
How is account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets" closed?
Considering that account 02 is passive, the reduction (write-off) of the amount of accrued depreciation is made in the debit of this account. How to close 02 account? Upon disposal of fixed assets (sale, write-off, gratuitous transfer, etc.), the amount of depreciation accumulated at the time of disposal is written off as follows (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit of account 02 - Credit of account 01 "Fixed assets"
As a result of such operations, for example, the balance sheet on account 02 will reflect not only credit, but also debit turnover.
Speaking of synthetic account 02, it is important not to confuse it with sub-account 02 to other accounts. For example, account 68.02 in accounting has nothing to do with depreciation. After all, account 68 - “Calculations on taxes and fees”, and 02 in this case- sub-account to account 68, indicating the type of tax. As a rule, account 68.02 reflects information on settlements with the budget for VAT.
Closing account 02 "Depreciation of fixed assets"
DEBIT 01 sub-account "Retirement of fixed assets" CREDIT 01
- the initial cost of the object being retired has been written off;
DEBIT 02 CREDIT 01 sub-account "Retirement of fixed assets"
— the amount of depreciation accrued on the retiring object was written off;
DEBIT 91 sub-account "Other expenses" CREDIT 01 sub-account "Disposal of fixed assets"
- the residual value of the retiring object is written off (the initial cost of the object minus the accrued depreciation).
Thus, on account 01 the residual value of the retiring object is formed. In this case, it will be equal to zero if the object is completely depreciated. That is, in such a situation, the initial cost of the fixed asset is equal to the amount of accumulated depreciation and there is no balance on account 01.
A similar entry is made when depreciation is written off for missing or completely damaged fixed assets. Closing of account 02 for other reasons is not provided.
Note: when closing account 02, account 01 will appear on transactions with fixed assets that are used directly in the activities of your company. If we are talking about property that was rented out exclusively, then account 03 “Profitable investments in material values". After all, it is on this account, according to the Instructions to the Chart of Accounts, that such assets are supposed to be taken into account.
If depreciation is charged excessively, then if an error is detected in current year the overcharged amount is reversed (for accrual postings, see here).
How is account 02 maintained in the accounting of a Russian enterprise? To answer the question, you must refer to the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order No. 94n dated October 31, 00. In accordance with the instructions for its use, c. 02 “OS depreciation” is intended to summarize information on depreciation accumulated during the use of fixed assets. Let's figure out how to close an account 02 and make postings on the main typical transactions.
Account characteristics 02
In the accounting of the company, all operations of financial and economic activities are carried out on the corresponding accounts. The accountant approves the working chart of accounts of the enterprise in the appendix to accounting policy depending on the economic sector of the business. To account for the amount of accrued depreciation, account 02 is used - active or passive? Since depreciation is charged on credit in correspondence with expense accounts, and debit is written off, account. 02 is passive, unlike, for example, account 68. 02 - in accounting it is considered active-passive.
The structure of the account 02:
- Credit opening balance - the amount shows the amount of depreciation accumulated at the beginning of the period.
- Debit turnover - means the amount of depreciation written off upon disposal / write-off of fixed assets.
- Loan turnover - means the amount of accrued depreciation on fixed assets.
- Credit closing balance - the amount shows the amount of accumulated depreciation at the end of the period
At the same time, it is necessary to organize reliable analytical accounting for inventory items of property in order to obtain complete information about the accumulated wear on the OS. For this, sub-accounts are opened, then a balance sheet is formed on account 02, and the balance as of the end of the reporting / tax period is reflected in the balance sheet of the organization in a special way. Despite the fact that c. 02 - passive, when filling out accounting, the balance of the account does not fall into the liability of the balance sheet. The balance of the account "Depreciation" is taken into account when calculating the residual value of fixed assets \u003d Initial cost (balance account 01) - depreciation (balance account 02).
Account 02 is also analyzed for the purpose of calculating property tax when determining indicators average annual cost(Article 375 of the Tax Code). In this case, the main register is OSV on account 02 or journal-order.
Note! Should not be confused with. 02 and MC account 02. These are two different accounts. The first is intended to reflect depreciation, the second is considered off-balance sheet and is used to summarize information on workwear put into operation. The maintenance of such additional accounting is due to the need to control the organization's property, already deducted from the balance sheet, but still used in activities.
Account 02 - typical postings:
- D 20 (25, , 26, 44, 91) K 02 - depreciation was charged on fixed assets used for production purposes (general production; auxiliary production; for the sake of managerial or general business needs; in trading companies; for leased properties).
- D 02 K 01 - reflects the write-off of depreciation accrued during the operation of the fixed asset.
- D 02 K 83 - reflects an increase in the additional capital of the company due to a reduction in depreciation of fixed assets.
- D 02 K 84 - reflects the recovery of depreciation accrued in previous periods.
- D 02 K 91.1 - write-off of depreciation upon disposal of fixed assets is reflected.
- D 83 K 02 - additional depreciation is reflected due to the revaluation of fixed assets.
How to close account 02 "Amortization"
sch. 02 is closed only when the asset is written off the balance sheet, that is, when the property is sold, its gratuitous transfer, liquidation and other disposal. Earlier than the specified moment. 02 will always have a balance, since the initial cost of the fixed asset is not transferred to the company's expenses all at once, but gradually. Since this account is passive, closing is carried out on the debit of account 02 in correspondence with accounts 01 (with full depreciation) or 91 (if the object is not fully depreciated).
Conclusion - in this article, we have decided which account 02 is active or passive, and how the depreciation of fixed assets in the organization is formed.