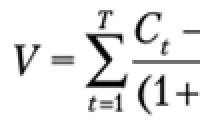End of the tax period. Tax period according to vat. Reporting period codes
The tax period for income tax, as well as for all other taxes, is the period at the end of which the tax base is determined and the amount of tax payable is calculated (Article 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition to the tax period for profits, reporting ones have been established. In this article, we will talk about the duration of all these periods, as well as how they are reflected in the tax return.
Tax period for income tax
The tax period for income tax is defined as a calendar year (clause 1 of article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, this is the time period from January 1 to December 31.
But this is in the general case, and there are exceptions to it, which include the creation or liquidation (reorganization) of an organization in the middle of the year.
So, for a newly created organization, the first tax period for income tax, by virtue of paragraph 2 of Art. 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there will be a period of time:
- from the date of its creation (state registration) until the end of this year ( for example, from May 26 to December 31 of the current year);
- or from the date of creation until the end of the next calendar year, if the organization was registered in December ( for example, from December 15 of last year to December 31 of the current year).
If a foreign organization, whose activities do not lead to the creation of a representative office, independently recognizes itself as a tax resident of the Russian Federation, then in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the first tax period for income tax for it will be the period:
- from January 1 to the end of the calendar year, if she recognized herself as a tax resident from that date;
- from the date of submission of the application to the end of the calendar year, if she recognized herself as a tax resident from the date of submission of the application.
- from the date of submission of the application until the end of the calendar year following the year in which the specified application is submitted, if the application is submitted in the period from December 1 to December 31.
For a liquidated or reorganized organization, the last such period for income tax will be the segment (clause 3 of article 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- from the beginning of the year to the date of completion of the liquidation / reorganization ( for example, from January 1 to June 25 of the current year);
- either from the day of creation until the day of liquidation / reorganization ( for example, from January 15 to October 22 of the current year- for an organization that was created and liquidated / reorganized within one year; or from December 23 of the current year to June 25 of the next - for an organization that was created in December of this year and liquidated / reorganized by the end of the next).
Income tax reporting periods
According to the results of the reporting periods, advance payments for income tax are paid, tax returns are also submitted (clause 1 of article 55, clause 2 of article 285, clause 1 of article 289 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes 2 types of reporting periods for income tax (let's conditionally call them quarterly and monthly). They depend on what method of calculating advances on profit the organization has chosen - the usual quarterly or according to the actually received profit.
For ordinary advances, the reporting periods are (clause 2 of Art.285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 1st quarter;
- half a year;
- 9 months.
With advances calculated from the actual profit (clause 2 of article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- month,
- 2 months,
- 3 months and so on until the end of the year.
For example, January, January-February, January-March, etc.
Period codes for income tax (21, 31, 33, 34, etc.) for the declaration
The tax or reporting period for income tax is required to be indicated in the "profitable" declaration - on the title page. The periods are coded, their codes are given in Appendix 1 to the Procedure for filling out the declaration (approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 19, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected]).
|
Name |
|
|
Used in declarations for the consolidated group of taxpayers (CTG) and designate the first quarter, half year, 9 months and a year according to the CTG |
|
|
Indicate quarterly reporting periods: I quarter, half a year, 9 months and a year, respectively |
|
|
Monthly reporting periods: 1 month, 2 months, 3 months, and so on - until the end of the year |
|
|
The code indicates the last tax period during the reorganization (liquidation) of the organization |
|
|
Indicated by the responsible participants of the consolidated group of taxpayers who pay monthly advances based on actual profit |
Correctly sOur material "Checklist for completing the income tax return for the 1st quarter of 2019" will help you to fill out the income tax return.
Outcomes
The tax period for income tax is a year. The duration of the first and last tax period in the life of the organization is determined according to the rules of Art. 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the income tax return, the reporting and tax periods are indicated in accordance with the codes specified in Appendix 1 to the Procedure for completing the declaration.
In tax returns, the tax period code must be indicated. The numerical designations of the periods depend on the type of declaration. What codes to set when reporting taxes, we will figure it out in this article.
The tax period code contains two digits. In addition to declarations, such a code is put down in bills for payment of taxes. Thanks to these codes, the inspectors of the Federal Tax Service determine the reporting period for the submitted declaration. Also, such a code will make it clear to the Federal Tax Service that the company is being liquidated (upon liquidation, its own code is put).
Types of tax periods:
- month;
- quarter;
- half a year;
- 9 months;
The tax period code is fixed on the title page of the declaration or other reporting form. Usually, payers can find all the codes for a particular declaration in the order of filling out the declaration (in the appendix). For example, for the profit tax declaration, the period codes are prescribed in the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 19, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected]
If the tax is considered on an accrual basis, returns are submitted in the periods listed below with codes:
- quarter - 21;
- the first half of the year - 31;
- 9 months - 33;
- calendar year - 34.
Fill out and send reports to the IFTS via the Internet and the first time. For you 3 months Kontur.Externa free of charge!
Try
If the return is submitted monthly, the codes will be as follows:
For consolidated groups of taxpayers, their codes have been approved: from 13 to 16 (where code 14 corresponds to half a year, and 16 - to a year).
The coding for the monthly reporting of consolidated groups starts with code 57 and ends with code 68.
When liquidating a company, you need to put code 50.
For property tax, other codes are used:
21 - I quarter;
17 - half a year;
18 - 9 months;
51 - I quarter during reorganization;
47 - half a year during reorganization;
48 - 9 months upon reorganization.
Simplified codes
When submitting the annual declaration under the simplified tax system, code 34 is applied.
There are also special codes for the simplified tax system:
95 - the final tax period when the tax regime is changed;
96 - the last tax period before the end of activities on the STS.
Codes for UTII
When filling out the UTII declaration, payers must use the following codes:
21 (51) - I quarter (I quarter during liquidation);
22 (54) - II quarter (II quarter during liquidation);
23 (55) - III quarter (III quarter during liquidation);
24 (56) - IV quarter (IV quarter during liquidation).
You can always check the code by opening the corresponding appendix to the procedure for filling out the declaration. Usually all codes are tabulated.
The national budget is the main financial instrument to support the existence and development of the country. Today, as before, the main, even the main source of its formation is the receipt of various taxes and fees. The taxation system in Russia provides a clear understanding of its basic concepts. It is important to understand the types of fees, the main elements. One of the significant points in this topic is the tax period.
Concept
Taxes refer to one of the types of financial relations between the state and society, aimed at forming the country's budget. The appearance of the fees under consideration can be attributed to the moment of the beginning of the development of civilization, the need for them appeared due to the first social needs. Since then, the creation of new forms of the state each time is accompanied by the transformation of the taxation system. Thanks to this, today a stable, almost perfect tax system has been formed. It has its own rules and concepts.
Taxes are of national importance. Therefore, their concept and accrual are regulated by legislative acts. The Tax Code is an important legal instrument that determines the entire taxation procedure in Russia. It is in this that the basic definition of the fees in question is given. Taxes are levied in compulsory payments, both from the ordinary population and from various commercial elements. They are directed in favor of the authorities, for the formation of central and local budgets. 
Types of the main taxes of the Russian Federation
All fees are classified according to the affiliation of the authority that collects them. There are the following types of taxes.

Mandatory elements of taxation
As elements of taxation are concepts, principles and procedures for calculating and transferring fees. More specifically, this is the very basis of the system. Without it, a lawful ordered tax relationship between the state and the payer will not work.
The list of elements of the tax system is listed in article 17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and contains the following basic concepts.
- Subject of taxation, in other words, a person who is obliged to pay fees.
- The object of taxation is the one for the use of which one has to pay tax. For example, income, property, the sale of a specific product, and so on.
- Tax base refers to the value or physical assessment of an item.
- A tax period that determines the time over which fees are calculated.
- The rate is that part of the cost of the object that will have to be paid to the state budget.
- The procedure for calculating and paying taxes.
Period - as an element of taxation
An important essential element in the topic under consideration is the definition of the tax period. It occupies a special significance in the general scheme of relations for two reasons.
- Determines the period of time during which the object of taxation is formed. This is necessary to calculate the amount of fees.
- Its calculation is directly related to the due date.
The tax period represents the period over which a specific base is established and the total liability is calculated. It is a calendar year or other tax-specific periods, after completion, which indicate the total size of the tax base and the amount paid.
It is necessary to distinguish between two different concepts - tax and reporting periods. The reporting period is an accounting concept that determines the time for which it is necessary to reflect in the reporting registers all business and financial transactions of an organization. Moreover, both periods can coincide. Several reporting periods can exist in one tax period.
The period for calculating the tax and when paying the fee is of great importance. Any organization transfers the amount from the current account. An individual does this by crediting the amount of the fee to the account of the tax authorities. During the operation, the documentation must be filled out correctly. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately indicate the tax period in the payment order or receipt. 
Periods for some fees
For most taxes, the calculation period is standard. It is one calendar year. For some specific types of income, the period of time for determining the base and calculating the amount is different. For example, the VAT tax period is like a calendar quarter. Each element in the calculation for various types of fees, including their tax periods, is spelled out in specific articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, reporting periods are defined for each fee. So, for example, the tax period for income tax is established in the law based on the calculation of the calendar year. But there are three reporting periods: month, quarter and 9 months.
Tax period code is a two-digit number that is used when submitting reports to the IFTS. The need for its use is due to the machine processing of tax reports. A code is put in a special column and serves to determine the period for which the tax is paid. Different taxation systems have different codes. This is done on the basis of the code book.
How the tax period is determined: code in tax accounting
There are periods of time for which you need to report and provide a calculation of the tax base, they are called tax periods:
- month,
- quarter (from first to 4),
- half a year (first, second),
The main reporting is submitted based on the results of work for the year. The tax period is indicated in the declaration: code 34.
Separate codes are assigned to the quarters, the code starts with a two, then comes the number denoting the ordinal number of the quarter. For quarterly reporting, codes from 21 to 24 are used. So for the first quarter - code 21, tax period 22 for the second quarter, 23 for the third, tax period 24 for the fourth quarter.
Some taxpayers report monthly. Please note that there are different codes for individual taxpayers and for a consolidated group. If payment is made by a consolidated group, then encryption is accepted from 13 to 15, from a quarter to a year. The periods from January to December are stamped from 57 to 68.
Tax period when calculating income tax
When paying quarterly advances, the following coding is used: tax period 21 - the first quarter, tax period 31 - the first half of the year, 33 - nine months. From 35 to 46 codes, the months from January to December are indicated.
Tax period 50 is put down by taxpayers when submitting reports before the termination of activities, or reorganization. It is calculated from January 1 until the moment of actual liquidation, or from the moment of opening and until the moment of liquidation, if the company has existed for less than a year.
Tax period: code when calculating property tax
When reporting on this tax, it is not always necessary to submit interim reports, as a result of this, payment is made immediately for the year. The coding will be the same as for reporting other taxes.
When drawing up reports, use coding 21 (tax period - quarter), half a year - tax period - code 31, when calculating tax for 9 months, tax period 33 is indicated.
When liquidating an enterprise, codes 51, 52, 53 are used, they mean a quarter, half a year, 9 months.
Codes for reporting according to the simplified tax system
Organizations that are on the simplified tax system submit an income report to the IFTS once a year. An advance payment of the received profit is made on a quarterly basis. The year is divided into reporting periods in the same way as for income tax, but separate reporting on them is not required. The standard period is indicated in the declaration, the year, the tax period is 34.
For individual entrepreneurs, code 96 is applied, which is applied upon termination of the activity of an individual entrepreneur for the final reporting period and code 95, it is used for closing reporting in connection with a change in the tax regime.
Tax period codes for UTII
Reporting is done on a quarterly basis, with the following designations used:
- Quarter - 21,
- tax period 2 quarter - 22,
- tax period 23 - for the III quarter,
- tax period code 24 - used for reporting for the fourth quarter.
All large organizations engaged in commercial activities are required to pay tax to the state. The main one is the direct tax on the company's profits. Accountants of organizations must enter information and submit declarations on time. For the submission of information, there is a certain tax period for income tax.
Companies engaged in any entrepreneurial activity, receiving income, are required to calculate tax, which is paid to the budget. spelled out by law and is one for all.
- 2% - contributed to the federal budget.
- 18% - goes to the regional fund.
However, local authorities can set a different rate for the company, but not less than 13.5%. Depending on which tax rate the organization uses, income tax is charged.
Income tax = (Income - Expense) * 20% (standard rate).
The concept of "tax" can be characterized as follows: it is a direct tax, the amount of which depends on the direct activities of the company. What financial result was revealed, what profit was received.
The tax period for income tax is the reporting period. Depending on the activities of the enterprise, it can also be different.
When is the reporting period
The tax reporting period is prescribed by the Tax Code (Article 285). Each organization must submit income information to the tax authority. For this, there are certain periods of time for which the organization pays tax.
The reporting period for direct tax organizations is a calendar year. At the end of the year, having calculated the earned profit, the accountant calculates the amount that must be paid to the state budget. In order not to confuse the two concepts, the reporting and tax period, we will draw up a table:
Calculation of tax for companies with a specific activity
The tax legislation prescribes the conditions for calculating tax for enterprises with certain activities. Such enterprises include:
- Banking organizations.
- Pension funds are non-state.
- Securities trading organizations.
- Foreign companies that have a special tax rate.
- Intermediary (clearing) organizations for the sale of securities.
- Organizations that are a management company on the basis of a partnership agreement.
These enterprises have their own tax rate and, accordingly, make their own tax calculation.
Every entrepreneurial activity sooner or later comes across such a concept as profit maximization.
Profit maximization concept
The terminology itself denotes the achievement of the maximum profit by the enterprise. The company decided to get the maximum profit in a short time using all possible means. Any organization is faced with maximizing profits in the short term.
This can be achieved by maneuvering profit and loss alternately, in the shortest possible time.
In the short term, the opportunities are fixed. If an enterprise is engaged, for example, in the release of some kind of product, then maximization in the short term is used to determine the technical capabilities.
For a short interval, the capacities are constantly fixed, increasing profits and reducing costs. It does not always happen that by increasing capacity, an enterprise can make a profit in a short time. To calculate the ratio of profit and loss, a certain formula is used:
(TC): TR - TC = MR,
where it turns out that TR> TC.
This is the ratio of gross income and total income, at which it is noticeable whether the enterprise is profitable or not.
The maximum profit indicators should be higher. If the indicator is less, it means that the company incurs losses in the short term.
The calculation for minimizing costs is similar:
(TC-TR) TR is gross income. TC - gross costs. MR is the marginal revenue. Firms often wonder whether it is worth launching production for the short term. It is worth it if the conditions are met: This process is acceptable if the head of the enterprise has all the prerequisites for business development and positive results have been given in the short term. If the picture is the opposite, then the company should be closed urgently. Losses will snowball down on the enterprise. This can lead to very high debt. These can include both obligations to suppliers and wage arrears. Making a profit by an enterprise is the only thing for which it works and calculates tax. Accordingly, each organization seeks to earn as much as possible and at the same time incur a minimum of losses. Analysts conduct various studies, draw diagrams, and calculate the capabilities of the enterprise. Purposeful well-coordinated teamwork helps to increase the company's income.