The company's current assets are
Being engaged in entrepreneurship, businessmen are not always interested in the details of accounting, considering it a matter of accounting. Acting "at random" for the good purpose of increasing sales or production volume can lead not only to financial problems, but also to unintentional violations of the law. This can lead not only to administrative, but even criminal offenses. The objective of this article is to consider current assets, their features and role in the activities of the enterprise.
We will immediately divide the current and non-current assets of the enterprise. Fixed assets- these are fixed assets (buildings, vehicles, machinery, equipment, etc.), long-term financial obligations, construction in progress, animals, trees, land resources, as well as intellectual property items (patents, software, know-how, copyrights etc.). All these assets are united by the fact that their service life is more than one year. current assets- it is, on the contrary, tangible and intangible assets with a service life of less than one year. The company's current assets are part of the enterprise's balance sheet asset and are reflected in the second section of the financial statement. Current assets are partly formed from the company's own funds, and partly from credit resources.
Abroad, the share of credit resources in working capital reaches 70-75%.
In Russia, due to the high cost of loans, this share is usually below 50%. For material-intensive industries and trade, working capital, as a rule, is very large. Analysis of the structure and optimization of the size of working capital is an integral part of the analysis of the organization's activities both in the process of its work and when making decisions on the sale, purchase and merger.
Let's take a closer look at what current assets are.
The most understandable part of current assets is raw materials and materials for the production of products, as well as goods intended for sale (in trade). All this is "frozen money". Of course, production cannot function normally without stocks of raw materials. However, its quantity should be optimal. An excess amount of raw materials and materials significantly reduces the turnover of current assets (we will consider this issue below). Recommended stock levels can be found in the literature. They depend on the duration of the production cycle, logistics (delivery time, order, payment processing) and the nature of financial interaction with suppliers (prepayment, deferred payments, etc.). The simplest way to calculate the current stock of raw materials is to multiply the daily consumption rate by the delivery interval in days. A safety stock is also needed, which is intended to cover interruptions in deliveries.
In trade, goods are delivered to the store in batches, however, the implementation period for them varies. In addition, for food products, the shelf life should be considered. In small retail outlets, purchases are made "by eye", however, if the volume of sales is large, and the number of items of goods is thousands, then it is better to use specialized computer programs. Such programs, based on the daily sale of each type of product, as well as the timing of its delivery, provide information on the required order time and the optimal lot size. In addition, the program takes into account the minimum volume of the wholesale lot and the loading of vehicles. This allows you to plan financial activities and manage credit resources. Partially stocks of raw materials and materials are formed at the expense of borrowed funds. This is an account payable. It can be in monetary and material form. If raw materials are purchased at the expense of a bank loan, then accounts payable arises. Such debt does not pose a threat to the financial stability of the enterprise, if it is within the planned (reasonable) limits. The danger arises if there is an overdue debt on loans (financial debt). Debt in material form is the raw materials and materials received by the enterprise, but not yet paid. This happens, for example, if the contract with the supplier provides for deferred payments.
Semi-finished products, products in the production cycle, as well as finished products are working capital.
Small inventory, tools and spare parts (consumables) for equipment and machine tools, as part of the working capital that are on the balance sheet, should be written off in a timely manner when they are spent, since used, but not written off, they negatively affect the profitability and turnover of current assets . A significant amount of semi-finished and unfinished products is typical for enterprises with a long production cycle. Particular attention should be paid to the analysis of stocks of spare parts for imported and unique machines and mechanisms. It is very important here to know the timing of the planned replacement of wear parts and not to create a stock of emergency spare parts. All accidents are still unforeseen.
Read also: What is the consumer price index
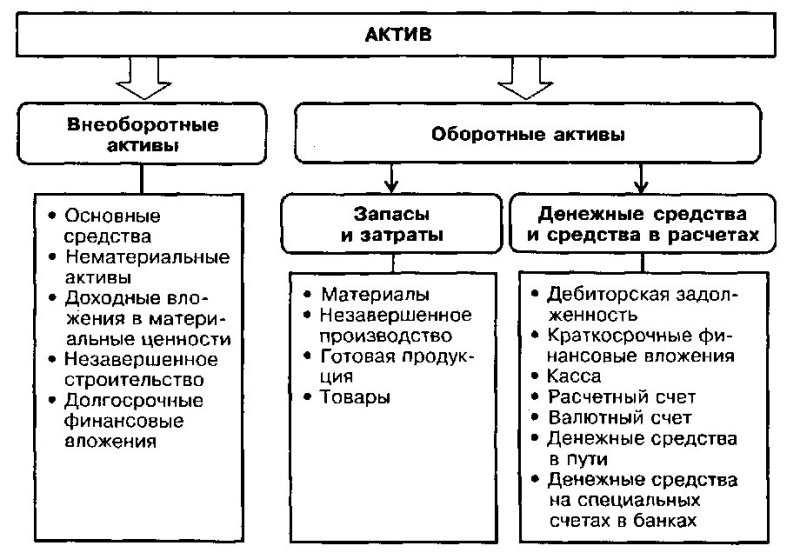
Cash. This is money on accounts (currency and ruble) of the enterprise and cash on hand. This is the most liquid part of working capital. Free cash is often used as financial instruments.
Financial instruments. These include short-term investments in securities with a view to their further resale and short-term bank deposits. Short-term investments and activity on the exchange is an effective means of using temporarily free funds with a professional approach.
Debt of customers and buyers (accounts receivable). This debt arises for shipped, but not paid for goods and services.
Other current assets in the balance sheet are, for example, the amounts of value added tax that are accrued upon shipment of goods or services provided (this is a debit balance), as well as the amount of VAT from advance payment for goods and services. This also includes shortages and losses, as well as defective products. Other current assets also include shares and stakes in other companies that are expected to be sold in the short term.
Which current assets are the least liquid? The least liquid assets (that is, those that are difficult to sell) are the debt of organizations / enterprises in a difficult financial situation, stocks of raw materials for products that have been discontinued, as well as finished products that have limited demand. The most liquid are cash assets, semi-products and finished products, which are in steady demand. Short-term financial assets acquired for the purpose of resale may also be difficult to sell. In analytical work, it is advisable to break down all assets into easily marketable, medium marketable, hard to sell and illiquid, and the analysis should be carried out separately for these groups.
Net current assets are calculated as the sum of the company's own capital and long-term loans, minus the total value of the company's non-current assets. Another method of calculation used is the difference between the total amount of the company's current assets and its short-term debt. The dynamics of this indicator characterizes the financial stability of the organization / enterprise and the efficiency of the use of funds. The higher this indicator, the greater the financial stability and efficiency of the enterprise. However, a negative value of the indicator in itself does not indicate a threat to financial stability. This is often found in the activities of commercial enterprises.






