How is downtime paid due to the fault of the employer
If a business entity is going through hard times for its activities and is not able to fully load employees with work, then the alternative to reducing them or sending them on unpaid leave is simple. With proper design, it allows you to save employees for a period of production difficulties. Downtime is an unpleasant event for the enterprise and for its employees. The company suffers losses, and employees receive payments that are significantly less than their base salary. What is a simple one, how to issue it, what obligations does it form with the employer and what can the employee expect?
Downtime at work
Forced downtime due to the fault of the employer: what does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation say
The suspension of the activities of a business entity due to objective reasons, as a result of which conditions are created in which it is impossible to work, is called downtime. It may be due to circumstances beyond the control of employees, as well as through their fault.
If a person, for objective reasons, cannot conduct activities regulated by internal documentation, then the employer needs to make a decision:
- on transfer to another workplace with the corresponding payments under the item "wages";
- on registration of the suspension of work and the production of appropriate payments to employees in an unfavorable period for the enterprise.
Causes of the situation
Downtime due to the fault of the employer occurs due to the failure to ensure the workload of production in full due to organizational, economic or technical failure. Recognition of the suspension of the activities of a business entity for reasons beyond the control of the employer and employee occurs in the event of force majeure situations, such as disasters, catastrophes, military operations, provided that they are officially confirmed by documents that recognize the assignment of the event to such a category.
The reason for the suspension of the functioning of the subject through the fault of the employee may be his absence from the workplace for a number of disrespectful reasons without warning the authorities. An employee may be accused of suspending the activities of the enterprise if he fails to perform official duties, the result of which determines the production tasks for another person.
Technical and organizational
The lack of raw materials and materials to ensure production, appropriate conditions, without which it is impossible to carry out work, such as electricity, lighting, sewerage, water supply and sanitation, are the fault of the management, which does not conscientiously perform the management functions assigned to it.
It is impossible to conduct activities if the equipment requires repair or the working conditions directly threaten human life and health. In such a situation, the absence of work is the fault of the employer, even if the employee independently refused to perform official duties.
Economic
The economic reasons for downtime are due to the difficulties of the enterprise in the field of financing. They may be due to the failure of the production plan, the loss of customers and the rupture of contracts. All these factors can make it impossible or irrelevant to continue working in full mode.
Read also: Sample application for time off for previously worked time
How to issue
Any circumstances that caused the suspension of activities bring losses to the business entity. Timely and correctly executed forced downtime due to the fault of the employer will help reduce its costs for making the due payments.

Legislative regulation of downtime
After receiving information about the circumstances in which it is impossible to continue production activities, the head of the company should try to solve the problem situation in order to prevent downtime. If this is not possible, then you should deal with the current situation and make a prompt decision to declare downtime. For this it is necessary to carry out a number of activities:
- drawing up by the head of the unit a memo about the circumstances under which it is impossible to continue working;
- identification of the guilty;
- setting deadlines for eliminating the cause of downtime, because otherwise it will have to be recognized as indefinite;
- resolve the issue of where the employee who was touched by the downtime should be;
- transfer of employees to another department or execution of an order for their absence during this period at the workplace;
- drawing up the relevant act;
- registration of administrative documentation and familiarization with it of the persons to whom it concerns;
- notification of the employment service about the event if the issue of suspension of activities is relevant for the entire enterprise;
- appropriate design of the time sheet with a code, the type of which is determined by the circumstances that caused adverse events for production.
An employer cannot force people to work during an officially recognized downtime period. If the head of a business entity did not notify his employees of their special status and made them cut wages for this period, then the employees have the right to complain to the management about his illegal actions.
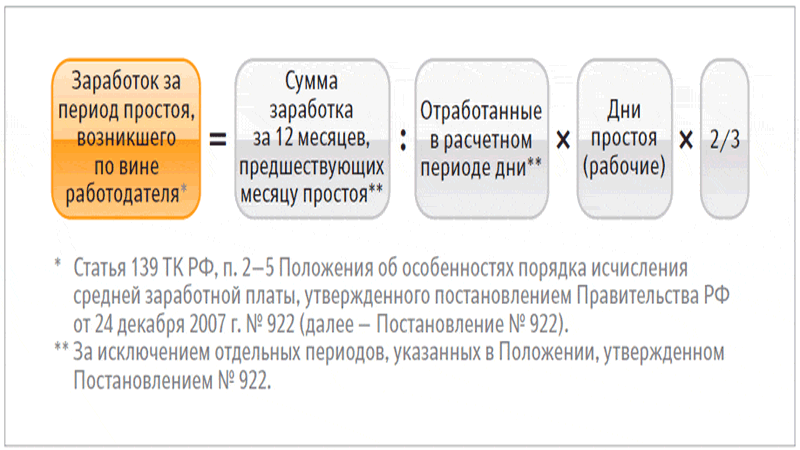
The law provides for the obligation of the employer to pay the employee downtime. The amount of the payout is unlimited by the maximum value. It can be regulated by the internal administrative documentation of a business entity. Downtime due to the fault of the employer is paid in the amount of 2/3 of the average earnings.
If the company's activities are suspended due to the fault of the employee, he is not entitled to any payments, provided that there is an act drawn up by the commission, which documents the fact of identifying and confirming guilt. If none of the parties to the employment relationship is to blame for the circumstances that caused the downtime, then payments are made in proportion to the time of non-fulfillment of official duties. When determining its value, the corresponding part of the bet is taken as a basis.
Payments by an employee for downtime are not classified as compensatory payments, therefore they are taxed on a general basis.
Payments are made to the main employees and part-time employees in accordance with a single general procedure. Even a few hours of downtime fixed within the shift are paid. At the same time, an order for downtime due to the fault of the employer must be drawn up, a sample of which can be found on the Internet.
The law provides for the right of the employer to issue a transfer to another workplace for a time period not exceeding a month. Consent from the employee will be needed only if the person is transferred to a job that requires a lower qualification than it was. Idle time in this situation is not paid, because the person works and his work is paid.






