Debt to the budget for taxes account. Tax debt Tax and levy payable
The obligation of payers to pay taxes is established by the Constitution of the Russian Federation (Article 57 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation), as well as by the Tax Code (subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the payer neglects this duty and does not pay taxes / fees, then there is a debt on taxes and fees, which the tax authorities, in turn, have the right to collect (subparagraph 9 of paragraph 1 of article 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Collection of debts on taxes and fees from organizations and individual entrepreneurs
If the payer has arrears to the budget, the tax authorities make every effort to pay it off. To begin with, a claim is made to pay tax (Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the payer did not respond to the tax authorities' demand and did not pay off the arrears within the time limits specified in the demand, then taxes will be collected in a compulsory indisputable manner: first, at the expense of funds on the payer's accounts (Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), if the IFTS does not have information about the accounts of the payer - at the expense of the payer's other property (clause 7 of article 46, article 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
By the way, in order to ensure the execution of the decision of the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate on debt collection, the tax authorities have the right to suspend operations on the accounts of the payer-debtor (clause 1 of article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Settlement of tax and duty arrears of individuals
An ordinary individual (not an individual entrepreneur), as well as an organization / individual entrepreneur, is required to pay if there is an arrears. If the individual ignored him, then the tax authorities have the right to go to court to collect tax arrears at the expense of money and other property of the individual (Article 48 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Debt on taxes and duties: accounting account
To reflect operations on settlements with budgets for taxes and fees, account 68 "Calculations for taxes and fees" is provided (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Debt on taxes and duties is fixed on credit account 68.
Debt on taxes and duties in the balance sheet
The company's liabilities, including to the budget, are reflected in the liability. Debt on taxes and fees is shown either in section IV "Long-term liabilities" in line 1450 "Other liabilities" (for long-term debt, in respect of which the payer has been granted an installment plan / deferral, investment tax credit), or in section V "Short-term liabilities" in line 1520 "Accounts Payable".
In the period from 2015 to 2016, the FTS did not commission about 50% of capital construction projects included in the Federal Targeted Investment Program (FAIP). This is the basis for concluding additional agreements to state contracts for the extension of the construction period, the Accounts Chamber notes. Violations were also revealed in the regional offices of the Federal Tax Service.
Despite these violations, in 2016 the federal budget received 6.9 trillion rubles. income administered by the Federal Tax Service. This is half of all federal budget revenues, the Accounts Chamber writes.
The press service of the Federal Tax Service explained to RBC that the increase in debt at the end of 2016 is due to the growth of the tax base for property taxes due to the transition to cadastral value instead of inventory value. New rules were introduced to significantly increase tax revenues to regional budgets. According to the Federal Tax Service, in 2016 the amount of property tax for individuals from 28 pilot regions amounted to 27.9 billion rubles. The department reported that the deadline for payment of property taxes was shifted to December 1, 2016, "in connection with which the procedures for collecting the resulting debt were postponed to the beginning of 2017."
Another reason, according to the Federal Tax Service, is the elimination of shadow tax evasion schemes in the alcohol industry. To this end, the department carried out a number of tax audits, during which the largest producers of the alcoholic industry were charged taxes in excess of those paid. Apparently, the absence of their repayment led to an increase in the debt of the entire department, says Oleg Filippov, an expert at the Institute of Sectoral Management of the RANEPA. In his opinion, when taxes are received, there is always a side effect in the form of their delays. “Any action is equal to opposition. The more you push, the more debt will grow, ”he says.
The Federal Tax Service noted that in 2016, as a result of compulsory measures, the budget of the Russian Federation received 769 billion rubles, which is 14% more than in 2015. Interaction with the Federal Bailiff Service allowed the Federal Tax Service to increase the amount of debt recovered by 34%, to 82 billion rubles. “The Federal Tax Service primarily works with legal entities, but how can you make physicists pay - take away the last apartment? If you can close the current account of a legal entity, then there are fewer levers of pressure with individuals, here social work should rather be carried out, "Filippov notes.
From January 1, 2017, the tax authorities were delegated the authority to administer insurance contributions for compulsory pension, social and health insurance. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has been supplemented with Chapter 34 "Insurance Contributions", which establishes the functions of administering these payments by the tax authorities. Previously, these functions were performed by the FIU and the FSS.
According to reports posted on the FTS website, from January to May, 3.1 trillion rubles were transferred to the federal budget. income administered by the Federal Tax Service. The debt to the budget as of June 1 was 1.1 trillion rubles.
From 03.03.2011 N 09AP-2215 2011-AK 4, the organization will not receive a certificate of the absence of debt to the budget, it will receive a certificate in form N 39-1 on the status of tax settlements with debt hanging in the RSB card ...
Tell me in the help of Form 39-1 from the tax office for which column is the tax debt to the budget reflected?
Everything is written - The state of the calculation of taxes (4 columns) if without a minus then this is an overpayment.
Accounting and taxation, 2009, N 12. Reconciliation of calculations with the budget for taxes and fees. 1 shows the balance of settlements of tax arrears with a breakdown by arrears, overpayments, deferred installments ...
How do you work as an accountant if you cannot figure out an ordinary tax certificate? I'm amazed!
"Amounts plus" are overpayments, "Amounts minus" are arrears. So your debts are penny and only on foam
Who has come across and knows? What is the right way and can the company be closed? If debts to the budget for taxes are 300 thousand rubles.
The state has created all the conditions so that individual entrepreneurs do not have tax arrears, and the corresponding payments are timely received to the budget, specialized services have been organized to clarify the amount of debt and its payment.
What is there to know ... you turn to a normal lawyer, he has homeless people / drug addicts. who are ready to take care of everything ... and debts too ...
Sell to the Far East ...
Why didn't you pay so much taxes?
If "as is correct" and according to the law, you will not be allowed to close the enterprise (organization) with debts by the state authorities - tax and off-budget funds.
There are three legal options:
- completely repay the debt and liquidate the company voluntarily;
- apply for bankruptcy (not cheap pleasure), conduct bankruptcy proceedings in accordance with all the rules and exclude the company from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (here either the debts will be paid forcibly, or they will be written off due to the lack of property, but the activities of the bankruptcy administrator will have to be paid in any case);
- sell to another owner and let his head hurt.
Tell me, how is the inventory of accounts payable with the tax budget carried out at the enterprise?
You need to take from the tax office or a reconciliation statement or a certificate of debt. The act will contain your accruals and your payment. The certificate contains only debt or overpayment.
When making an inventory of settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds
there is a reconciliation of accounting data for accounts 68 "Settlements for
taxes and fees "and 69" Settlements for social insurance and
security "with the amounts of taxes calculated in the declarations, as well as with
amounts transferred to pay taxes and fees. Moreover, according to
unpaid taxes on time, it is necessary to check the calculation of penalties and their
payment, as well as penalties.
This should also include arrears in payment of contributions, penalties and fines to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds. According to Article 59 of the Tax Code, arrears on taxes and fees, which cannot be collected due to economic reasons ...
Reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate for taxes must be done.
Penalty for late payment of taxes by individual entrepreneur
Well, first of all, which taxation system should be clarified. Depending on this, we will tell you what and where to pay. And in the pfr you really need to pay fixed payments at the end of the year.
For late payment, a penalty is withheld, not a fine. A fine is levied in the amount of 1000 for late filing of the declaration.
Tax arrears, or rather arrears of Art. 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on taxes is the amount of a tax payment that was not transferred to the state budget within the period established by law. For different taxes, the due date is different.
Whatever system you are on, it's too early to pay))) the declaration is submitted once a year. from January to April inclusive. and the tax is paid the same way.
but with a pension you need to strain yourself up and pay your pension until December 31st.
The income tax was transferred to the budget (part of the debt for the previous month was also paid off) D? K?
Income tax was transferred to the budget Dt 68 kt 51
To approve the attached Regulations on carrying out in 2000 the repayment of overdue tax debts to the federal budget using funds from early repayment of federal loan bonds with a constant coupon yield.
Is the tax debt to the budget considered a short-term liability?
Prompt Tax arrears to the budget refer to liabilities or assets?
Will you get a penny for the deductions to the budget? it's not difficult right there =) passive
Tax arrears to the budget are a passive. The balance sheet is reflected in section 5. SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES on the line tax and levy arrears 624.
It's your debt to liabilities!
Your obligations are all passive
If you must, then this is a liability. And if there is an overpayment, then an asset.
Passive of course
To liabilities.
Transferred to the budget profit tax 15.10 Settlements with the budget Settlement account Д-т 5600 К-т 5600 Credit balance in the part of the subaccount Calculations for income tax shows the amount of debt to the budget i.e. additional amount due to the budget ...
Tax arrears to the budget are a passive. The balance sheet is reflected in section 5. SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES on the line tax and levy arrears (624)
Whose obligation for the company to take a certificate from the tax office about the absence of debt to the budget?
Income tax debts to the budget Electrical equipment Payables to staff
It is immediately evident that the student ... I am writing, but what I am writing I do not see. Oh, poor teachers who listen to this nonsense on exams….
At the same time, tax arrears appear, which are also recorded in this line. The way in which the organization reflects the calculations with the budget for land tax should be recorded in the accounting policy of the company.
There are practically no postings here. Some initial accounts…. Where does this ridiculous statement come from?
How to correctly write an explanation to the tax office about the existing debt to the budget?
Forgive us our debts….
Definition of the item Debt to the budget line 626 reflects the organization's debt to the budget for taxes and fees.
The IFTS does not need your explanations ... only if you ask for a deferred payment, but it is difficult to get it
Why is that? on the basis of which article of the code is required? read the paper tax.
Tell me how to get a certificate on tax calculations, budget debts
Are the tax authorities obliged to make a refund if there is an overpayment to the regional budget and arrears to the federal budget?
Tax authorities and budgetary organizations never make a refund of overpaid amounts. According to the rules, they are required to set off the amount of the overpayment against future payments.
According to the second option, as a rule, a re-account for payments of different purposes is not done. The amount of the overpayment for one appointment will be credited against future payments for the same appointment, and under another item you will have to make an additional payment in the amount of the unpaid amount.
At the final stage, it is necessary to determine the debt to the budget to draw up the forecast balance, which is calculated using the formula Balance of tax arrears at the end of the period Balance of tax arrears at the beginning ...
The tax authority has the right, in the absence of any statements from the taxpayer, to set off the overpayment of tax against future payments or against arrears of interest. When the tax is refunded, they will look at what tax you have arrears (they will pay special attention to the budget - local, regional or federal) In general, when returning it, they ask you to pay off debts for all taxes.
In accordance with Art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, overpaid tax payments are subject to offset or refund at your request (application). Usually, the tax authorities conduct a joint audit and draw up the results with an act (according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax authorities are required to notify you of the overpayment within 10 days) and, based on the data of the reconciliation report, state your desire for offset or refund in writing. If there are arrears on other taxes of the corresponding type, fines and penalties, the offset is made by the tax authorities on their own. As for the deadline for filing an application, three years from the date of the overpayment. In your case, we are talking about a budget of different levels, so offset is not possible. According to the first option: the actions of the tax authorities are competent and legal (Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5). According to the second option: you need to make a VAT refund, and liquidate the debt for income tax.
What will be the accounting entry: income tax arrears transferred to the budget
Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service sent a request for payment of tax, penalty interest. How to reflect in accounting the arrears and penalties on the unified social tax to the federal budget?
Penalties are charged on account D 99, on K 69. (FB subaccount), and you simply pay the arrears, after all, it was formed as a result of your accrual.
Find out your debt. Dear users! We suggest you use one of the following services, about the amounts of accrued and paid tax payments, about the presence of overpayments, pay tax charges, fill out ...
First, check the calculations, maybe not all payments have been credited. If, nevertheless, the tax is right. then the tax (penalty) shall be charged additionally with D20 (26.44) K69 and pay D69 K51.
The amounts of interest and fines do not reduce taxable income D99 K69.
What do the balances on CT count 68.02 and CT count mean? 68.04.01, should they be zero at the end of the period?
This is nothing more than a debt to the budget for certain types of taxes, which are reflected in sub-accounts. They can rarely be zero, except when there are no charges….
If the check of the tax arrears of individuals has shown the existence of such, it must be paid off. Debtors and non-payers were pressed at all times - for example, by the fact that they were not allowed to go abroad. Agree that it's a shame because of the penny debt to the budget ...
This means tax arrears payable to the budget. If at the end of the period the balance on this account is "zero", then this means that there is no debt - but this is rare, usually taxes are paid after the end of the reporting period, so the balance of account 68 is credit.
Tax
Certificate of the absence of debt, or rather, a certificate of the fulfillment by the taxpayer (payer of fees, tax agent) of the obligation to pay taxes, fees, penalties, fines
Debt corporate income tax. Arrears to the budget for local taxes and fees - everything.
Let who buys, he is soared about this. the tax authorities do not give such certificates and no one gives them. You can provide them with a certificate of open accounts from the tax office and an extract from banks for each account, then for all property certificates from the relevant authorities about the absence of the right of third parties or encumbrances. For real estate from the Russian Register, for cars from MREO, etc.
Help solve the problem on boo. accounting
At first glance, it is an unprofitable organization, but it really won't be possible to count .... There is no roll, the cost of materials.
Tax arrears to the budget. Details of the question You can visit the website www.himki.byx.ru to see the organization's debt by the details, to the tax office and how to do it. If it is not possible on the website, then how can it be possible without coming to the tax office?
BALANCE ASSETS: Stocks in the warehouse-26000
3 buyers -5000
Incomplete garage -50,000
Land plot -120000
Cash - 95000
Gasoline -4000
Patent -10,000
Cash desk - 7000
TOTAL: = 317000
PASSIVE BALANCE: Advance payment from buyers -50,000
Z-t before the budget - 30,000
Additional capital -10,000
Credit -20,000
Wages on wages - 40,000
Loan - 20,000
Authorized capital - 100,000
TOTAL: 270,000
To determine the net profit, you need to know how many products are sold at what price, the fact is sold. products. Difference between revenue and fact. cost and VAT will give you profit before tax. Then multiply this profit by the% of tax on profit, get -tax n profit. Profit - income tax = net income.
And if the tax office once refused to liquidate, is it necessary to submit the publication to the Bulletin again?
Che to do something, how to get a quick certificate from the tax office about the absence of debts to the budget
So go to any consulting company that conducts accounting, they just all have garters in the tax office, I think it's a day of work for them, if you don't want to stand in line ...)))
Only if there are established relations with the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate.
The head of the organization provided a loan to pay off taxes and fees arrears to the budget
If issued in submission, then it is necessary
Home gt Clarifications gt Accounts gt Correspondence of accounts Account 68 Settlements with the budget Expert consultation, 1997.
Not. It is necessary to conclude an interest-free loan agreement between the organization and the head of the organization. Acceptance of money at the cash desk is carried out by a credit slip. This money is deposited in the bank.
Please help me solve the problem.
And in no way?
- Inherited on a residential building I will pay income when selling - My sister and I are selling the house.
The asset or liability of the balance sheet reflects the debt of the buyer
We inherited it about 2 years ago. Transaction amount 1,200,000 Will we pay income tax?
- How to Get Rid of Doubtful Accounts Payable - Hello. All of us, probably, have repeatedly faced the problem of extortion of phone numbers by websites. > in
- Trembling creatures and having the right to dostoevsk - Do you think a man should leave in silence, without explanation? Or do we have a right to know? How it turns out You need to understand.
- A trembling creature having the right - Do you trembling creature or do you have the right?) We are all creatures, but not trembling ones, and we have the right only from God ... And how should I decide
- Inherited on a residential building I will pay income when selling - My sister and I are selling the house. We inherited it about 2 years ago. Transaction amount 1,200,000 Will we pay income tax?
- Whether I am a trembling creature or have the right to schismatics - What is set forth in Raskolnikov's article Actually, his theory. that there are trembling creatures, and who has the right 😉 Is it a creature
- How to pay off accounts payable on account 62 - Will the repayment of accounts payable at the expense of retained earnings somehow be reflected in the balance sheet asset ??? Source
- How to Get Rid of Doubtful Accounts Payable - Hello. All of us, probably, have repeatedly faced the problem of extortion of phone numbers by websites. > in
- Dacha amnesty to cut land - Can I, according to the law of the dacha amnesty, cut free plots 5.35 and 6.sotok? I don’t think so. This is a normal self-grabbing. Version
- Dacha amnesty suspended - I think that after the events in "Rechnik" our people will respect the power of the lawyer Medvedev and the leader from the stake Putin. Right? P
- Dacha amnesty prirez - Help the first time I encountered. How to answer this question correctly? Marina wrote everything correctly, but you don't need nature
- Dacha amnesty to cut 4 hundred parts - a plot in snt. How to cut 4 hundred square meters under the dacha amnesty? None of the neighbors claim this land. Am I on for
ON THE ACTIVITIES OF TAX BODIES ON THE SETTLEMENT OF TAX DEBTS AND THE WAYS OF ITS IMPROVEMENT
Obukhova P.A.
One of the mechanisms of influence on the national economy and the formation of financial resources of the state is the tax system, and the collection of taxes and fees characterizes its efficiency. However, persisting non-payments not only reduce the efficiency of tax relations, but also limit the government's ability to finance investment and social projects.
The main reasons for the emergence of tax arrears: inability to work in a market economy, unwillingness to pay taxes, imperfect tax system, non-financing of government orders, etc.
The specifics of settling tax liabilities arrears is determined by the economic essence of tax relations. Tax relations are formed on the basis of economic, financial, property relations, have a public law nature, are based on the power relations between the state and the taxpayer (payer of fees). The state is interested in the prompt and complete fulfillment of tax obligations by legal entities and therefore has created a powerful, specialized system of state coercion (tax, control, legal, security structures).
Tax debt is the amount of tax liabilities due within a specified period and is considered as the total debt, which includes late tax required by law, as well as accrued interest and penalties.
In this case, tax debt should be considered as the concept of “total debt, consisting of settled debt and unsettled debt”.
The settled debt means the debt in respect of which all measures of uncontested collection and in the court have been applied: restructured debt; the amount of debt deferred or deferred on the basis of a decision of an arbitration court or a higher tax authority; the amount of debt suspended pending the adoption of the decision of the arbitration court on the merits; debt collected by the bailiff service; debt in respect of which the bankruptcy procedure was initiated.
Unsettled debt consists of debt that cannot be collected due to a missed deadline and arrears, that is, the amount of tax that was not paid within the prescribed period.
According to the head of the department of corporate governance of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation R. Meshkov, the mechanism for settling tax arrears and other obligatory payments to budgets and state extra-budgetary funds, as well as penalties and tax sanctions, can be implemented by identifying four forms: voluntary-declarative, notification-warning, security, compulsory (see Fig. 1).
The voluntary-declarative form of settlement of tax arrears provides for the declarative nature of the process based on decrees of the President of the Russian Federation and decrees of the Government of the Russian Federation, the methods of this form are applied by taxpayers on a voluntary basis.
The notification and warning form includes the actions of the taxpayer to pay off the debt in accordance with the claims for payment of tax, indicating the amount of arrears, penalties, fines and the deadline for fulfilling the claim, as well as measures to collect tax and ensure the fulfillment of obligations if the taxpayer ignores the claim. In addition, there is also a method for offsetting overpaid or recovered amounts against a taxpayer's debt.
Methods and tools of the security form for the implementation of the mechanism for the settlement of tax arrears ensure the fulfillment of the obligation to pay taxes and fees. An insufficiently clear legislative study of the procedure for applying the provisions of civil legislation on pledges and sureties in the tax sphere, as well as a complete lack of experience in their application, create additional risks for the parties to a pledge or surety agreement. For example, the tax authorities in 2002 - 2009. this form of security for the obligation to pay taxes and fees was not actually applied.
The unconditional requirement of the state is the obligation to pay taxes, which applies to all taxpayers. The taxpayer is not entitled to dispose of that part of his property or income, which in the form of a certain amount of money is subject to contribution to the treasury. Failure to pay the tax on time must be compensated for by paying off the debt on the tax obligation, full compensation for damage incurred by the state as a result of late payment of the tax. Therefore, the method of a security form is applied to the amount of tax not paid in time (arrears) - the accrual of penalties as compensation for losses of the state treasury as a result of shortfall in tax amounts on time in case of delay in tax payment.
Specific methods, tools and procedures are applied by the tax authorities within the fourth form - the compulsory form of implementing the mechanism for settling tax arrears:
- collection orders to the bank for the indisputable write-off from the taxpayer's accounts of the amount owed to the budget system;
- the decision to collect at the expense of property by transferring to the bailiffs of the decisions of the tax authorities, in accordance with Art. 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, court orders and orders of execution;
- bankruptcy procedures - supervision, financial recovery, external management, bankruptcy proceedings.
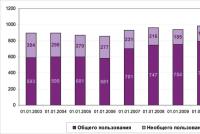
Let us assess the level and dynamics of the tax debt of legal entities in the Tyumen region (Table 1).
Table 1 - Dynamics of tax debts of legal entities in the Tyumen region (thousand rubles) *
* Source: data of statistical reporting in the form 4-NM of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Tyumen region
Analysis of the data in the table allows us to draw the following conclusion: arrears in taxes and fees, as well as accrued penalties and fines to the budget of the Tyumen region as of 01.01.2010 amounted to 4074829 thousand rubles. The total tax liabilities increase annually by 7 - 8%. At the same time, debt indicators in Russia are decreasing. And the share of the settled debt from the total amount of the total debt on tax liabilities for the three-year period under study is approximately 50%.
In connection with the growth of the total debt on tax liabilities to the budget of the Tyumen region, the tax authorities promptly respond to the occurrence of debt and the implementation of the debt settlement mechanism.
The results of the implementation of the mechanism for the settlement of tax arrears are presented in Figures 2 and 3.
From the data presented in the figures it can be seen that in 2010 taxpayers received claims for payment of taxes and fees in the amount of 10,221.5 million rubles. and for 2009 - 9732.2 million rubles. at the same time, in total, 3,722.8 million rubles were repaid under the claims. and 3363.9 million rubles. respectively. Thus, the efficiency of work on claims for payment of taxes in 2010 was 42.9%, and in 2009 it was 40.5%, i.e. efficiency has increased.
In 2010, the regional tax authorities sent collection orders in the amount of RUB 3,715.5 million, and redeemed RUB 1,046.2 million, i.e. the efficiency of debt collection at the expense of taxpayers' funds was 33.4%, which is 1.8 times lower than this indicator in 2009.
In 2010, 60,547 decisions were sent to banks to suspend transactions on taxpayers' accounts, which is 27.7% less than in 2009.
Also, in 2010, the tax authorities of the Tyumen Region issued 18,054 resolutions on the collection of tax from the property of debtors in accordance with the provisions of Article 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for a total amount of 2,733.6 million rubles. In terms of quantity, this indicator is more than for the same period in 2009 by 30.1%, in terms of amount - by 36.8%.
Bailiffs initiated 16,826 enforcement proceedings for the amount of 2864.5 million rubles. The effectiveness of enforcement actions during the application of Art. 47 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as of 01.01.2011 amounted to 15.5%. At the same time, the proceeds from the accounts of bailiffs amount to only 26.0 million rubles. or 0.9% of the amount of the initiated enforcement proceedings.
The main amount of receipts - 403.3 million rubles. is the amount of voluntarily paid off debt by taxpayers after the initiation of enforcement proceedings and after the seizure of property.
Thus, as a result of the measures taken by the tax authorities in 2010 to enforce debt collection from legal entities, the budget system of the Russian Federation received 5233.0 million rubles, which amounted to 7.1% of the amount of tax payments received to the budgetary system of the Russian Federation. In comparison with 01.01.2010, the amount of repaid debt in the region as a whole decreased by 3.1%.
So, as a result of the application of notification - preventive, security and compulsory forms of implementation of the mechanism for the settlement of tax arrears as of 01.01.2011 in the Tyumen region, the efficiency of collection is 60.3%. Moreover, this result is 4.7% lower than the efficiency prevailing as of 1.01.2010.
Methods and tools for implementing the process of settling tax liabilities are indicative for assessing the effectiveness of the tax authorities in this area.
To date, considerable results have been achieved, first of all, a significant increase in the level of indicators characterizing the efficiency of the tax authorities' work on debt settlement. However, the general level of tax discipline in the country, the nature of tax evasion schemes used by unscrupulous taxpayers, which are becoming larger and more sophisticated from year to year, force us to seriously think about the need to use new reserves to improve the efficiency of debt settlement. The main strategic direction for improving such work is the introduction into practice of new forms and methods of debt settlement based on advanced information and analytical technologies.
Particular attention should be paid to increasing the transparency of the Federal Tax Service and simplifying tax procedures, including interaction with the taxpayer. The solution to this problem should be carried out through the development of information technologies, the creation of new and the development of existing electronic services.
It is necessary to create specialized centers for processing and storing documents, as well as a system for managing electronic archives. As a result, the tax authorities will be able to switch to work exclusively with electronic documents.
The next way to improve the work of tax authorities in the settlement of tax arrears is to create commercial incentives for firms with a good tax reputation.
Improving tax culture. Tax culture consists of citizens' understanding of the importance for the state and society of paying taxes (as part of political culture) and knowledge of their rights and obligations to pay them (as part of legal culture).
For the formation of a tax culture in society, it is necessary to more actively use the media - television, radio, periodicals. It is also necessary to pay attention to explaining to taxpayers their rights and obligations. For this, already in the school curriculum it would be necessary to provide for "tax disciplines". But one cannot be limited to one "educational work". Real incentives are needed. For example, the establishment of an "unwritten rule" that prevents persons with a bad tax reputation from accessing the State Duma and other higher authorities.
At the same time, improving the quality and efficiency of the tax authorities' work should not mean its complication.
Literature
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Part One: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of July 31, 1998 No. 146-FZ (as amended on 06/07/2011) // Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation. - 1998. - N 31. - Art. 3824.
- On amendments to part one and part two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and to certain legislative acts in connection with the implementation of measures to improve tax administration: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of July 27, 2008 No. 137-FZ // Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation. - 2008. - No. 41. - Art. 4849.
- On the tax authorities of the Russian Federation: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of March 21, 1991 No. 943-1-FZ // Bulletin of the SND and the Supreme Council of the RSFSR. - 1991. - No. 15. - Art. 492.
- On some issues of the practice of applying the provisions of the legislation on the bankruptcy of absent debtors and the termination of inactive legal entities: Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 67 dated 20.12.2006 // Bulletin of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation. - 2007. - N 2.
- Verstova M.E. The main ways and prospects for improving the methods of ensuring the fulfillment of obligations to pay taxes and fees in modern Russia / M.E. Verstova // Legislation and Economics.
Is the income tax debt to the budget an asset or a liability?
— 2011. — № 3.
- Meshkov R.A. Mechanism for the settlement of tax arrears: forms of implementation and performance indicators / R.A. Meshkov // Tax policy and practice. - 2010. - No. 11.
- Pantyukhov O. V. Clarified requirement for payment of taxes, fees and fines: / O. V. Pantyukhov // Tax disputes: theory and practice. - 2011. - No. 2.
- Tarakanov S.A. The procedure for collecting taxes, penalties, fines from taxpayers - organizations / S.A. Cockroaches // Russian tax courier, 2010. - No. 22.
- Tsygankov V.V. On the collection of taxes and penalties from a taxpayer after the expiry of the limitation period for bringing to tax liability / V.V. Tsygankov // Law and Economics. - 2011. - No. 6.
- Consolidated forms of statistical reporting: information prepared by specialists of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Tyumen region. - Access mode: http://www.r72.nalog.ru.
DISCUSSION OF STUDENT WORKS AVAILABLE ON THE FORUM OF THE SITE "SCIENTISTS OF RUSSIA"
More about student work discussion
Authors of 3 papers (for each section) that received the largest number of positive constructive feedback and questions on the forum will be awarded with RAE diplomas. The authors will also be invited (together with their supervisors) to the RAE conference (Moscow, May 2012) with a report without paying the registration fee. The RAE diplomas will be awarded to the heads of student research papers who have received the largest number of positive constructive feedback on the forum.
To participate in the forum, you must correctly register in the social network "SCIENTISTS OF RUSSIA" and create a topic dedicated to the discussion of this work in the forum.
Participants of the student scientific forum can also post additional materials (SCIENTIFIC TEXTS, PHOTOS AND VIDEO MATERIALS) for discussion on social network blogs. The availability of additional materials will also be taken into account when determining the winners of the competition.
Debt on taxes and duties
Accounts for accounting of arrears on payments to the budget (by type) (6400)
Instructions for the application of the Chart of accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of economic entities
272. Generalization of information on the current obligations of the enterprise for payments to the budget is carried out on account 6410 "Arrears in payments to the budget (by type)".
Accounts receivable asset or liability
273. The credit of account 6410 "Arrears in payments to the budget (by type)" reflects the amount due to the contribution to the budget, in correspondence with accounts receivable, accounts for accounting of expenses of the period, use of profit to pay taxes and fees, settlements with staff on wages. In the final settlement, the previously transferred advance payments of taxes and fees to the budget are reflected in the debit of account 6410 "Arrears in payments to the budget (by type)" in correspondence with the account of advance payments to the budget (4400). The amounts actually transferred to the budget are reflected in the debit of account 6410 "Arrears in payments to the budget (by type)" in correspondence with the accounts for accounting for monetary funds.
Analytical accounting for account 6410 "Arrears in payments to the budget (by type)" is carried out by type of taxes.
274. Correspondence on accounts of accounting of arrears on payments to the budget (by type) (6400)
|
Correspondence of invoices |
|||
|
Debit |
Credit |
||
| Indebtedness to the budget for various deductions, taxes and fees, included in the expenses of the period | |||
| Amounts of VAT and excise taxes were charged on the sale of finished products, goods, work performed and services rendered, as well as on the sale and disposal of fixed assets and other assets | |||
| Funds were returned from the budget or credited against future payments (in case of final recalculations, etc.) |
5110, 5210, 5530, 4410 |
||
| Amounts of personal income tax deductions from wages | |||
| Amounts of tax on income from accrued dividends | |||
| Accrued payments from profit to the budget | |||
| Payments to the budget are actually listed | |||
| VAT related to material resources, goods, works and services is accepted for offset. | |||
| Debts to the budget were repaid by obtaining loans and credits |
6810-6840, 7810-7840 |
||
According to the first part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxes are divided into three groups - federal, regional and local.
Federal taxes are determined by the legislation of the Russian Federation and are uniform throughout Russia.
Legal advice
These include: VAT, excise taxes on certain types of goods (services) and certain types of mineral raw materials, income tax, tax on capital income, personal income tax, unified social tax, state duty, customs duty and customs duties, tax for mining, forestry tax, water tax, environmental tax, federal license fees, etc. Federal taxes and fees are mandatory throughout the Russian Federation.
Regional taxes and fees are established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with the tax code and are obligatory for payment throughout the territory of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. These include: corporate property tax, real estate tax, road tax, sales tax, gambling tax, regional license fees. With the introduction of the tax on real estate in the relevant territory, the tax on the property of organizations, the tax on the property of individuals and the tax on land are terminated.
Local taxes and fees in accordance with the Tax Code are established by regulatory legal acts of local governments and are obligatory for payment throughout the territory of the municipality. These include: land tax, personal property tax, advertising tax, inheritance or gift tax, local licensing fees.
According to the Instruction to the Chart of Accounts, account 68 "Calculations of taxes and fees" is intended to summarize information about calculations with the budget for taxes and fees paid by an organization, and taxes from employees of this organization.
The main business transactions on the debit of account 68 are shown in table 2.10.1.
Table 2.10.1 - Typical transactions for debit account 68
| Contents of operation | Corresponding accounts |
| Dt | CT |
| Reflected offset or refund (deduction) of VAT paid on the purchase of goods, products, accepted works or services rendered | |
| Tax debts paid off in cash | |
| Tax debts paid off by transfer | |
| Tax debts were repaid by transferring funds from a foreign currency account (in cases permitted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | |
| Tax debts were repaid by transferring funds from special accounts in banks | |
| Received a short-term loan to pay off tax debts (without crediting funds to the current account of the borrower) | |
| Received a long-term loan to pay off tax debts (without crediting funds to the current account of the borrower) | |
| Restructuring of tax arrears was carried out |
The main business transactions on the credit of account 68 "Settlements with the budget" are shown in table 2.10.2.
Table 2.10.2 - Typical transactions on credit 68 accounts
| Contents of operation | Corresponding accounts |
| Dt | CT |
| Taxes charged, attributable to capital investments | |
| Taxes charged are attributed to the actual cost of purchased materials | |
| Taxes are charged attributable to the cost of purchased animals for raising or fattening | |
| Taxes charged to the cost of procurement | |
| Taxes charged to the cost of products (works, services) of the main production | |
| Taxes charged to the cost of products (works, services) of auxiliary production | |
| Accrued taxes attributable to general production costs | |
| Accrued taxes attributable to general business expenses | |
| Taxes charged attributable to the cost of goods purchased | |
| Tax accrued attributable to sales expenses | |
| Overpaid taxes refunded | |
| Overpaid taxes refunded in foreign currency | |
| Overpaid taxes have been refunded and credited to special bank accounts | |
| Withheld personal income tax | |
| Taxes have been withheld on the amounts of dividends paid | |
| VAT charged on sales of products (works, services) of conventional industries | |
| VAT was charged on sales of products (works, services) of industries that are not related to ordinary activities | |
| Income tax has been charged for SE entities, current income tax has been charged |
Synthetic accounting of settlements with the budget for credit 68 accounts is kept in the journal-order number 8.
In the context of conducting automated accounting, a corresponding machine chart is drawn up by type of payment.
Analytical accounting for account 68 "Settlements with the budget" is carried out by types of taxes. For individual sub-accounts of account 68, the balance can be both debit and credit. In this regard, account 68 "Settlements with the budget" may have an expanded balance at the end of the month, i.e. and debit and credit.
Date of publication: 2015-02-18; Read: 154 | Page copyright infringement
Bad debt to the budget
Quite often, firms do not pay taxes on time and / or in full. It happens that taxes (as well as fines and penalties) remain unpaid both in terms of uncontested collection and collection in court. This can happen not only because of the omissions of the organization itself, but also due to an oversight of the inspectors who did not demand payment on time.
How to admit ...
For the above reasons, or as written in Art. 59 of the Tax Code, due to the impossibility of collecting due to reasons of economic, social or legal nature, the debt can be recognized as hopeless. The same article provides for the possibility of its cancellation. But for an operating company, such a possibility is purely theoretical.
... and write off
The specific write-off procedure is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 12.02.2001 N 100 (hereinafter - Resolution N 100). This document allows practically only one condition for writing off bad tax debts - the liquidation of the organization in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (as an option, the death or declaration of the deceased of an individual is for entrepreneurs). Even in case of bankruptcy, the debt is written off only in the amount not covered by the debtor's property.
Finance department<*>and tax authorities<**>unequivocally believe that all possible grounds and conditions for writing off hopeless arrears are limited by the specified Resolution. The opinion of the higher courts is similar (see table 1).
<*>Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 26, 2008 N 03-01-10 / 1-12.
<**>Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05/10/2006 N MM-6-19 / 481 @.
Table 1
———————— T —————————————————
Judicial authority ¦ Decisions on the impossibility of writing off the overdue
¦ arrears
————————+—————————————————
Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation ¦Determination of 03.04.2007 N 334-О-О
————————+—————————————————
Supreme Arbitration Court ¦Rules of the Presidium of 06.11.2007 N 8241/07,
RF ¦ from 11.05.2005 N 16507/04
————————+—————————————————
How to work with her
What does the presence of unpaid and unwritten charges bring to merchants? In such a situation, there are more negative sides than positive ones.
The firm saved on budgetary contributions (off-budget funds). In terms of costs, this is good for her, but this plus is the only one. Such savings can "backfire" at the most unexpected moment and entail unpleasant consequences.
If there is an overpayment
The organization has a debt. Like all settlements with the budget, it is reflected in her personal account, which is maintained by the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate. It is not possible to collect it. But it cannot be written off either, since the company works, is engaged in commercial activities, and the conditions provided for by Resolution N 100 are not met. The arrears continue to be registered, and, possibly, the inspectors will try to recover it. Since the deadlines for uncontested collection have already passed, and there is no court decision on payment, the inspectors can go the other way.
Companies often face the budget not only with debts, but also overpayments. The latter is subject to refund or offset against repayment of debts or future payments. And the controllers direct the overpayment to pay off the debt, which is hopeless to be collected, without getting the opinion of the taxpayer. They have grounds for this - the norms of clauses 5 and 6 of Art. 78 of the Tax Code, providing for the right of tax authorities to independently offset their overpayment against arrears and only after that return the amount of overpaid tax or set it off against future payments. This is also the opinion of a number of courts (see table 2).
table 2
—————————————- T ————————————-
Judgments that admit ¦ Judgments that do not allow
self-repayment of the IFTS ¦ self-repayment of the IFTS
debt due to overpayment ¦ debt due to overpayment
taxes ¦ taxes
————————————-+————————————-
Resolution of the FAS Volgo-Vyatsky ¦Definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation
district of 13.12.2007 in the case of 08.02.2007 N 381-O-P
N А82-16458 / 2006-28 ¦
————————————-+————————————-
Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus
District of 11.02.2008 ¦Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of 24.10.2006
N Ф08-477 / 08-156А ¦N 5274/06
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the FAS Volgo-Vyatskiy
¦district of 01/23/2007 on the case
¦N А29-4225 / 2006а
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-West
¦district of 04/19/2007 on the case
¦N A13-6446 / 2006-28
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Far East
¦circle from 20.09.2006
¦N Ф03-А24 / 06-2 / 2029
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District
¦ from 12.01.2006 N Ф09-5950 / 05-С1
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian
¦circle from 03.09.2007
¦N Ф04-5902 / 2007 (37661-А75-26)
————————————-+————————————-
¦Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District
¦ from 31.05.2006 N КА-А40 / 4436-06
————————————-+————————————-
There are also opposite solutions, in which the servants of Themis admit that such "initiative" of the tax authorities is a form of enforced collection of tax payments. And since the period of enforcement has already expired, then such a procedure is inapplicable.
Tax arrears of a budgetary institution
True, this opinion is not widespread everywhere (see table 2).
So, having received notional income in the form of non-payment of taxes and penalties, the firm can incur an expense in the same amount at the most unexpected moment. Moreover, it will be problematic to challenge the actions of the controllers.
If you need a "clean" help
There are also situations in which not only the absence of debt to the budget is required, but also the corresponding certificate:
- obtaining a license to carry out one of the activities related to the production and circulation of ethyl alcohol, alcoholic and alcohol-containing products;
- purchase of federal special stamps;
- obtaining a loan from a bank;
- obtaining permission to engage in foreign trade activities;
- withdrawal from the citizenship of the Russian Federation (for individuals).
The form of a certificate on the status of settlements for taxes, fees and contributions, the procedure for filling out is approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04.04.2005 N SAE-3-01 / 138 @. Reflection in it of outstanding debts to the budget may result in a refusal to obtain the appropriate permit or license.
According to the arbitrators
The majority of taxpayers apply to arbitration courts with a demand to force the Federal Tax Service to write off the debt, which can no longer be collected beyond the statute of limitations and for other reasons similar to it. And if you "fight back" from open claims about the collection of overdue debt (Resolution of the FAS of the North Caucasian District of 18.01.2007 N F08-7191 / 2006-2964A), the accrual of penalties on it (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of 06.11.2007 N 8241 / 07) still succeeds, then the courts will no longer go to write off the debt from the personal account. The opinion of the servants of Themis in these disputes is unshakable: there is Resolution N 100, where everything is indicated. The tax authorities are not entitled to make a write-off decision on their own.
Perhaps the only one in which the arbitrators obliged the inspectorate to write off the company's debt is Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District of 16.09.2004 N A55-230 / 04-29. But this is an exception. The decision of the same court with a similar conclusion (Resolution of August 24, 2004 N A55-3136 / 04-31) was revised by the highest arbitrators on May 11, 2005 (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation N 16504/04) and canceled.
Not all arbitrators support the cancellation of the company's debt "quietly" at the expense of overpayments. The analysis of judicial practice in most of the districts shows an ambiguous opinion on this issue. In addition, the auditors have an ambiguous provision of the Code (see table 2). Therefore, there is no absolute certainty that arbitration will support the firm against the tax authorities if they begin to pay off yesterday's debts with today's overpayment. In most decisions, the courts come to the conclusion that tax arrears can still be repaid by the inspectors on their own, and for fines, only at the request of the taxpayer.
What's the bottom line?
Arrears in taxes and fees can be quite inconvenient. At an unexpected moment, problems may arise with obtaining a loan, the necessary permits for a new type of activity. This state of affairs will not suit every company.
It happens when, entangled in business, calculations, the founders close the company, pay off their debts at a minimum and start the business "from scratch." But we cannot recommend such a recipe as universal. First, the procedure is quite complicated and costly. Secondly, an enterprise of not every form of ownership can be easily closed and reopened. Thirdly, upon liquidation of a company, the FTS may require the repayment of debt at the expense of assets.
Therefore, the easiest and most reliable thing a company can do is to voluntarily pay taxes and keep working.
A.V. Zakhozhiy