Recession in jurisprudence. In simple terms, a recession in the economy - what is it? Consequences of the downturn in economic performance
The life cycle of the economy and business activity of any enterprise, as well as the state as a whole, consists of 4 stages: rise, peak, economic recession (recession) and complete decline (crisis).
A recession is a predetermining stage for the entire economic cycle, because there are two ways out of it: the complete decline of the country with all the negative consequences, and the search for ways to solve problems with entering a new phase of economic growth.
Dear reader! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to know how to solve exactly your problem - contact the online consultant form on the right or call by phone.
It's fast and free!

Recession concept
The state of the state's economy, often coming after the phase of economic growth, and having a non-critical nature of the decline in production, is called a recession.
During this period, the main economic indicators that affect macroeconomic indicators worsen:
- Falling GDP indicators.
- Reducing the volume of industrial production.
- Decreased income of the population.
- Decreased investment attractiveness.
- Decrease in consumer activity.
In other words, a recession is an unfavorable period for the country, during which enterprises decrease in turnover, produce less products, the population receives lower wages and begins to save. Due to the fact that production volumes are falling, less funds enter the budget, which leads to its deficit.
Causes of the recession
The main reasons that lead to a recession in the form of a crisis and an economic downturn on a global scale are:
- The collapse of oil and gas prices, which entails a recession in the economies in countries where these natural resources are the main strategic product.
- Active growth in the cost of commodities, which is provoked by hype and increased consumer demand.
- The issuance of mortgage loans in an unacceptable amount and with a high percentage of risk.
- Decrease in production volumes in all industrial sectors.
- A decrease in wages and other incomes of the population of the country, which entails a decrease in purchasing power.
A recession inevitably results in a crisis or depression, and according to all the laws of economics, it cannot be avoided. But thanks to the work of specialists, analysts, economists and other top minds of the state, this process can be significantly reduced, as a result of which the consequences of the recession will not be so large-scale and negative.
What does a recession lead to?
The recession entails negative consequences not only for the state in which the economy is in decline, but also for the entire world community. Quite often, the economy of one state is so interconnected with the economy of other developed countries that a crisis in it can lead to a global crisis and even a collapse on world stock exchanges.
In international relations, a recession inevitably leads to a fall in stock market indices. The consequence of this is the depreciation of the state currency, and there is a risk of non-payment of the existing external debt.
On a national scale, enterprises that are forced to reduce production volumes due to inefficient consumption of products are the first to suffer.
Untimely payments for delivered goods entail wage and tax arrears. The result of the activities of companies unprepared for the crisis is the recognition of insolvency and bankruptcy.
The private consumer is also feeling the impact of the recession. It is expressed in the reduction of wages, consumer insolvency, the impossibility of making loan payments and the emergence of debt pits.
Types
Recession, depending on the reasons that led to the recession in the economy, is of 3 types and has different manifestations:
- An unplanned recession resulting from such unfavorable factors as the outbreak of war, an unpredictable collapse in world prices for strategic natural resources (gas and oil). The consequence of these processes is the formation of the country's budget deficit and the fall in gross indicators. This type of recession is recognized by leading economists as the most dangerous for the state's economy, since it is rarely possible to predict it in time and respond with appropriate measures.
- A recession that is political or psychological in nature. The reasons for the decline in production and the economy is the distrust of the private consumer, local businessmen and foreign investors. This is expressed in a decrease in consumer activity, a decrease in the volume of financial flows from investors and a fall in stock prices, bonds, vouchers and other securities. The phenomenon of this nature is easy to overcome by restoring consumer confidence through the methods of psychological and financial impact.
- A recession that occurs against the backdrop of a deterioration in macroeconomic indicators and an increase in external debt. The consequences of this dangerous process can be a fall in the value of shares, an outflow of funds and a protracted multi-year period.
Period
A recession is recognized when the period of decline in production and decline in economic indicators exceeds six months and becomes protracted. The duration of the period of recession in economic growth directly depends on the type of recession.
For example, if we are talking about a recession of the economy of a psychological or political nature, then it is not difficult to reduce the negative period - it is enough to restore the trust of business and the population, using loyal principles in the field of lending and social programs.
It is rather difficult to predict the period of an unplanned recession, since it directly depends on global negative factors that a state with a decline in production cannot influence. In this case, the country's analysts can only develop measures to mitigate the consequences as much as possible.
What is a recession in Russia and what does it threaten?
The Russian economy is directly dependent on the indicators of the gas and oil markets, and the rapid decline in prices for strategic natural resources entails the following negative consequences for it:
- Reduction of financial flows that are sent to the budget as a result of the sale of a strategic product.
- Against the backdrop of falling stock indices, the ruble is weakening.
- Incomes of the population are declining as a result of the decline in production.
- Consumer activity is declining due to low incomes of the population and rising prices for goods and services.
In addition to these obvious signs of a recession, the decline in the Russian economy in 2015 is influenced by such an external factor as the sanctions of the United States and some European countries.
The severance of relations between Russian businessmen and international companies jeopardizes the existence and development of the country's leading enterprises, and has an extremely negative impact on the GDP indicator.
According to the forecasts of the country's leading experts, the recession in Russia will last until 2017, unless a strategic resuscitation decision is made at the level of the heads of several exporting states: a reduction in oil production, and as a result, a significant jump in the price per barrel.
What is a money recession?
The process of decline in production and decline in economic indicators has a direct impact on the currency of the state. In Russia, the recession of money is the weakening of the ruble against generally recognized international currencies, which occurred due to fluctuations in world oil prices and a decrease in stock prices of Russian companies.
A further decline in prices for a strategic natural resource in the coming months may significantly depreciate the Russian ruble, and will require an urgent revision of the monetary policy by the Bank of Russia.
However, there are positive aspects of the depreciation of the Russian ruble. The proceeds from exports are in foreign currency, but they enter the budget treasury accounts in rubles, which allows increasing the revenue side of the state budget.
Differences between recession and stagnation
If a recession is defined as a moderate decline in the economy and production, then stagnation characterizes a complete halt in important strategic areas of the economy.
The period of stagnation has the following negative consequences for the country:
- Manufacturing and trade enterprises stop their activities.
- There is massive unemployment.
- The income and standard of living of individuals is declining.
If during the period of recession the process of reformatting the country's economy and the introduction of plans for the further development and re-equipment of the main branches of the state begins, then stagnation does not provide for positive changes and adaptations to new realities.
According to the old unpromising model, the country is living out the last phase of its life cycle, and falls into a deep crisis.
If we compare both phenomena, then a recession has less negative consequences, since it provides for some progress in economic growth.
Despite the fact that the recession has a negative impact on the activities of the macro- and microeconomic entities of the country, it is a barrier, after passing which the state's economy tends to grow, and the companies that survive are waiting for an active stage of development.
The question regarding the concept of recession in the domestic economy may be of interest to every citizen who cares about the situation in the country.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
In this material, we will reveal the concept of a recession, the features of a recession in the economy in 2019, the causes and consequences of this economic process, and also we will figure out whether it is worth being afraid of this process, what it can affect.
General points
In this section, we will consider what a recession is in simple words, what reasons contribute to its development, consider the current state of the economy in the Russian Federation and understand the regulatory regulation of this issue.
What it is
A recession is a negative trend in the state's economy, which is often observed before periods of crisis.
Such an economic phenomenon is characterized, as a rule, by cyclicity, and is considered inevitable for any economy.
During a recession, there is a decrease in the rate of production at the level of the state economy for six months or more.
The process is characterized by zero dynamics of GDP or its significant fall. As a result of the recession, there is a significant decline in business activity, the pace of industrial production is declining, and the pace of economic development is slowing down.
A decrease in gross domestic product implies a decrease in the volume of goods produced and a decrease in the volume of consumption of goods and.
A recession is to be expected after economic booms or production booms, which are caused by the cyclical development of any economy.
The economic cycle, as a rule, has four phases of development - growth, stabilization or stagnation, recession and depression.
During a recession, key economic indicators do not stop growing, but their growth rates are declining for six months or more.
Industrial enterprises produce less products, business activity decreases, as a result of which the income received by enterprises decreases.
Citizens of the country begin to experience difficulties with, lose their jobs, as a result, consumer activity and demand for goods decrease.
This phase of the business cycle typically follows a boom or boom and is often followed by a depression or stagnation.
However, through the use of competent measures and actions on the part of the government, such consequences can be avoided and the economic situation in the state can be stabilized.
The duration of the economic cycle at the global level is 10-15 years, this process can be traced on the basis of the periodicity of the global financial crises of the 70s and 90s, and the last one was the crisis of 2008-2009.
This recession was the longest and lasted seven quarters in a row. Based on Rosstat data, the recession is over, and over the past three quarters since the end of 2016, the economy has been growing.
However, its end does not mean a return to a stable increase in growth rates and does not inspire optimism regarding future development, since even with the best option for an economic forecast for a long period, experts from the Ministry of Economic Development suggest that revenues potentially have the opportunity to return to 2013 indicators only in 2022.
At the same time, revenues are expected to grow much more slowly than the economy, whose growth rate will be within 3.5%. Pension provision in real terms will not increase.
And if in July 2019 the average pension is about a third of citizens, then by 2035 this pension will be about one fifth of the average wage in various regions.
At the same time, areas such as education and healthcare will experience a lack of funding.
For the Russian Federation, the negative moment was the rapid pace of changes in the world market for oil and oil products.
Economic growth in Russia slowed down significantly well in advance of the recession.
In addition to the global crisis, the ongoing redistribution of the oil market in a competitive environment, other factors also influenced the emergence of a protracted recession.
By the end of the 2010s, the Russian economy reached the level at which it was during the period of transformational decline at the turn of the 1980s–1990s.
As a result, the extensive growth of the economy became impossible by attracting unused industrial capacities and the unemployed able-bodied population into the production process.
As a result of such events, there is a decrease in the structural growth rates of the economy, and as a result, there is also a decrease in real growth rates.
According to the new forecasts of specialists from the Ministry of Economic Development, no significant economic breakthroughs are planned until 2035.
The cost of oil will increase only by the amount of dollar inflation, as a result of which the economy will experience stagnation for another 20 years with a maximum growth rate of 1.7% per year.
The government is planning certain economic measures aimed at increasing the rate of economic growth by attracting the able-bodied population to production, stimulating investment activity and labor productivity of citizens.
Causes
Let's consider the key reasons for the recession, which arise based on the level of development of the state economy.
Experts name the following main reasons that have a serious impact on the economy and may contribute to a recession:
| Changes in the competitive environment and market conditions | GDP growth rates may slow down due to hostilities, lower oil prices and other indicators. For example, the key source of replenishment of the domestic budget is the sale of oil and petroleum products. With a significant decrease in the cost per barrel, the state budget deficit immediately appears |
| Decrease in domestic production | As a result of the excess of the amount of imported goods over domestic goods, a decrease in the production activity of Russian enterprises is observed. The population does not see the point and does not want to purchase domestic goods and prefers to purchase imported goods for the same price. As a result, goods produced by domestic enterprises are not in demand, resulting in a recession. |
| Decrease in the income level of the population | What provokes a drop in demand and has a negative impact on the economic situation in the country as a whole |
| Reducing the amount of investment | When a population with a sufficient level of money supply does not trust the state or prefers other profitable and reliable ways of investing finances abroad, then a recession occurs in the national economy. To prevent such a situation, the state must constantly monitor the conditions provided for capital investment and ensure their continuous improvement, thus avoiding the outflow of capital abroad. And as a result, investors will invest in domestic economic spheres |
In a resource-based economy, the reasons for the slowdown in economic growth are the fall in the cost of a barrel of oil, gas and other natural resources.
The cost of raw materials is falling, the budget does not receive enough income, there is a deficit that requires compensation in various ways.
In order to compensate for such a deficit, taxation rates are immediately increased, spending on social spheres (medicine, education, and others) is cut. With such measures, the decline in production rates is further exacerbated.
In industrial economies, a recession occurs as a result of a change in the technological and industrial structure, for example, due to the emergence and implementation of the latest information technologies.
It is not possible to influence these reasons for the recession, since they appear on the basis of the objective laws of the economy, therefore, a recession in individual national economies is an inevitable phenomenon.
Recession and recession in one state can lead to a chain reaction, resulting in another crisis on a global scale.
If banks have issued too large volume of loans to the population, on which significant debts have arisen.
Then banking institutions are forced to increase lending rates, engage in raising finance in the Russian and foreign markets, often through risky operations.
If there are many such banks, the number of loans issued decreases, industrial organizations are not able to take loans and, as a result, they liquidate production for lack of funds.
As a result, unemployment increases, citizens and businesses have loans, banks raise rates, the situation is aggravated, a vicious circle appears.
Force majeure circumstances, such as hostilities or a sharp drop in energy prices, can also lead to a recession.
To get out of such stagnation, measures taken at the state level will be required to support the economy and stabilize the exchange rate.
Normative base
In the event of a recession at the legislative level, new laws are issued or amendments are made to existing legislation, and state strategies for exiting the recession are formed.
These strategies can be developed at the state level, taking into account global changes in the world economy.
Emerging nuances
In this section, we will look at the types of recession, by what signs it can be determined at the level of the national economy, and what consequences a recession can have for various industries and the economy as a whole.
What are the types
Experts distinguish between three types of recession, which we will discuss below:
| Unplanned recession | It can arise due to unexpected incidents and processes in the economy. Such reasons may be the beginning of hostilities, a sharp decline in the cost of oil and other raw materials. As a result, the state budget experiences a deficit, a lack of revenue, and there is a sharp drop in the gross national product. According to experts, this type of recession is extremely dangerous for the economy, since it is not possible to foresee it and choose the best measures to overcome it. |
| Psychological or political recession | Appears due to distrust of consumers, entrepreneurs and investors. Consumer demand for domestic goods decreases, the volume of capital investment decreases, the price of securities falls. This type of recession is easier to overcome, for this you need to restore the confidence of citizens and investors by lowering interest rates or various psychological methods. |
| Recession due to large external debt | As a result, the value of shares falls, there is an outflow of finance from the economy. This type of recession is also dangerous, because it can last for many years. |
What signs can be found
It is possible to determine the development in the state of recession by several characteristic features:
- in the state, the number of unemployed citizens is growing at an insignificant pace or sharply;
- a decline in production rates, but industrial companies continue to function and produce enough goods for citizens;
- falling indices on the stock exchange;
- rising inflation rates;
- significant outflow of capital and investment abroad.
However, all these parameters are not characterized by specific critical values. For example, the inflation rate can grow only by 2-3%.
When all these signs are revealed, we can talk about the fact that a depression has begun in the state.
What are the consequences
The key results of the recession in the national economy are:
- slowdown in the pace and volume of industrial production;
- the collapse of the financial sector;
- reduction in the volume of lending to the population and enterprises;
- increase in interest rates on lending;
- a significant increase in the number of unemployed citizens;
- decrease in the real income of the population;
- falling GDP.
The critical result of the recession is a full-fledged economic crisis. After all, enterprises stop producing products in the same volumes, the population loses their jobs, which leads to an increase in the level of .


As a result of declining incomes, people buy less, and the recession in the economy deepens. The volume of investment in science and the development of modern technologies is decreasing, scientific and technological progress and development are slowing down.
After the decline in industrial production, the stock market falls, and the shares of the largest industrial producers are sharply reduced in value.
Video: collectors. Assignment agreement and agency agreement
This is followed by a high level of inflation, a decrease in citizens' incomes against the backdrop of a constant increase in commodity prices. As a result, the standard of living of the population is significantly reduced.
The state, trying to get out of the situation, forms strategies by increasing state loans, significantly increasing its external debt to creditors.
When the recession contract is formed
The law provides for two ways of assigning debt - assignment of the right to claim and transfer of debt.
In the first method, the debtor's permission is not required, while he must be notified without fail of the fact of a change in the creditor.
In the second option, it is concluded with the permission of the creditor to the fact that from the moment the contract is concluded, the debt will be paid from another person.
Consider the grounds for which an agreement may be required. A citizen has a loan debt to a banking institution, and he wants another organization or citizen to repay his loan.


The first stage will be obtaining permission from the creditor bank to assign the debt. At the same time, the bank has the right to issue a refusal in case of doubts about the reliability and solvency of the new payer.
If you agree to an assignment, such a mark must be made in the document without fail.
Such an action is necessary so that in the process of repaying the debt by another person, he does not declare that your actions are illegal and you are a full-fledged debtor.
As a result of such a statement, the obligation to pay the debt will again return to the first debtor. The inscription “Agreed” or “I agree to transfer the debt” can serve as a required mark in order to protect yourself from negative consequences.
It is also necessary to specify in the contract under what conditions the new payer pays the debt to the creditor. Thus, it is possible to prove to the tax authorities that the transaction is not free of charge.
When studying the fundamental factors of price movement, it is important to take into account the general state of economic development of a particular state at the current time, since the national bank will rely on it when planning its further actions. Among the popular conditions is a recession in the economy, which is currently observed in a number of countries.
Therefore, below it will be described what this phase of the economic situation of the country is and what measures against its background should be expected from the Central Banks, whose task is to support the national currency and domestic producers. Theoretical material and examples will be presented in simple words so as not to leave understatement.
Explanation of the term and the specifics of its use
History shows that the economy of any country always goes through cycles of growth and decline, developing in a cyclical pattern. In this regard, four main stages are noted, namely:
- active development;
- being at the peak of development;
- attenuation;
- reaching the bottom (crisis).
The period of attenuation, when the economy is experiencing problems, and the situation inside the country worsens, moving from the peak of its development to the bottom, is called a recession.
If we turn to the morphology of the word, then it comes from recessus, which is translated from Latin as a retreat. The main signs will be a slowdown in the pace of economic development, a decrease in production volumes, a decrease in wages, a decrease in the working day, and so on. Moreover, this process is usually quite protracted and stretches for at least a year, or even more. If the crisis unfolds at an intense pace, then the word recession is not used, then they say - recession, collapse, etc.
Periods of recession in the economy are inevitable, as the economy, like the ocean, also experiences its own peculiar ebb and flow. Therefore, economists are always ready in advance for a new round of recession, and the Central Bank has a number of mechanisms in its arsenal that help it lead the country out of this period, spurring development.
Finishing the introductory part, it should be noted that the most developed countries of the world are so closely intertwined with each other that the recession of one inevitably leads to problems in the other. Therefore, in the event of a stagnation of the economy of one of the key countries, a chain reaction usually begins, which soon causes a recession in other states due to various reasons. One of the clearest examples of recent years is China. As soon as the PRC entered the recession phase, other countries immediately felt the negative of this phenomenon.

What are the characteristics of this period?
It is not difficult for financiers to notice the slowdown that has begun, as they can observe very characteristic phenomena during a recession in the economy, which are difficult to miss. If above it was briefly indicated by what signs attenuation can be noticed, now we will describe the main signs in more detail.
- The general macro-indicator, which reflects the totality of economic factors, is the volume of the gross product, known by its abbreviation - GDP. If its indicators are falling, then there is no doubt that the country's economy is in a recession phase.
- The second factor will be a slowdown in production volumes, as well as a decrease in the activity of consumers, who are beginning to save more and save more than they spend. These signs are well displayed by a macroeconomic indicator - the level of business activity.
- As soon as the business begins to experience problems, layoffs are launched. As a result, the number of unemployed is growing, and the relevant macro indicators clearly indicate this.
- The slowdown in growth is causing another negative phenomenon - manufacturers and service providers are starting to save money by cutting the wages of their employees. This leads to a decrease in profits for the population, who are again forced to cut their spending, which aggravates the overall situation in the state.
- The last characteristic feature will be inflation. Its change well reflects the presence or absence of economic problems within the country.
Usually all these phenomena are interconnected, since the appearance of one of them causes a chain reaction. Therefore, any of the signs described above eloquently speaks of an urgent problem.
Why is the economy going into recession?
Despite the fact that the state's economy enters a recession stage regularly, obeying cyclical development, the reasons that lead to this are usually completely different. Moreover, they can be both internal and external. Below are the most common negative factors that lead to a recession in the economy, the reasons that damage the state and lead to a halt in economic development.
Scientific and technical progress
It seems strange, but the revolution in the world of scientific and technical progress is not always a joyful phenomenon. Often, progress becomes the cause of a recession, since the introduction of new solutions can cause the old familiar goods or services to be no longer needed. Accordingly, some industries or service sectors may cease to exist, which will cause a large number of unemployed people, a decrease in government revenues, and so on.
Reducing the cost of commodities
For a number of countries whose budget is replenished by exporting raw materials to the world market, a decrease in the cost of energy carriers leads to a recession. A very good example is the fall in oil prices in 2013-2015. Against the backdrop of cheaper black gold, a number of states, including Canada, Russia, Mexico, etc., experienced a strong budget deficit, which led to a deterioration in the economic condition of the country.

Crisis of the banking segment
Suffice it to recall the 2008 crisis in the United States, when American banks, which seemed unshakable and represented the personification of financial stability, suddenly caused a severe economic crisis in one of the most developed economies in the world. The reason was that they easily provided loans to everyone, especially for real estate, as a result of which the volume of loans issued upset the natural balance. At some point, loan holders lost the ability to repay them, which caused the bankruptcy of small financial institutions, while large institutions were forced to insure their risks and tighten requirements. As a result, business began to receive extremely poor working conditions, which caused a general slowdown in production, the service sector, trade, etc.
force majeure circumstances
In some cases, a recession becomes a consequence of force majeure. A good example is the massive earthquake that hit Japan a few years ago. It was impossible to predict it, but the destruction caused was so significant that investors who use the yen as a safe-haven currency for their capital began to withdraw them hastily. The rapid outflow of finance caused a sharp fall in the yen and, as a result, a protracted period of recession.
The consequences of the recession for the country's economy
If we talk about the consequences that a recession causes, then many of them have already been described above, which tells about the recession in the economy and the phenomena that accompany it. However, below is a list of points to keep in mind, as in many ways they provide opportunities for currency speculators to profit, which can be used to their advantage.
- A decrease in production volumes will lead to a shortfall in profits for enterprises, as a result of which the value of their shares falls.
- Reducing the consumption of goods and services. This factor leads to a depreciation of the national currency, as the Central Bank will soften the course of monetary policy in order to neutralize the negative consequences of this phenomenon.
- An increase in the number of unemployed. Few traders do not know how much the monthly publication from the labor market - NFP - affects the US dollar exchange rate. The same applies to other countries - the unemployment rate serves as a significant benchmark for investors, so an increase in the unemployed weakens the currency, and a decrease strengthens it.
- The fall in the number of loans issued by banks and the increase in interest rates on loans also indicate that the conditions for the development of the country's economy are deteriorating, and therefore its currency will become cheaper.
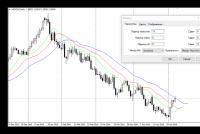
- If some factors indicate the onset of a recession, then we can expect a fall in the state stock market. At this point, you can go short by selling blue-chip stocks or shorting the stock index.
Actions of the National Bank in a Recession
As soon as the first signs of a recession appear, the National Bank of the State begins to gradually put into action certain mechanisms that stimulate the economy and improve conditions for business.
The most common option resorted to by the Central Bank is lowering interest rates. This lowers the rate of the national currency, and quite a lot, which allows traders to make good money at a distance by opening short positions.

In addition, the Central Bank can carry out interventions in the foreign exchange market, preventing the development of particularly protracted and strong trends, when the quotes of the national currency begin to weaken greatly. So, for example, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation acted in 2014-2015, injecting large amounts of money to stop the fall of the Russian ruble against the US dollar.
Knowing the peculiarities of the development of events during a recession, skilled speculators and investors can find many opportunities for themselves that allow them to make good money.
The process of economic growth is, as a rule, cyclical: from boom to recession and from recession to boom (which is called the business cycle).
A recession is a phase characterized by a weak but steady deterioration in economic indicators, primarily a decline. Also, during a recession, it grows, the volume of fixed capital decreases, the total falls slightly, especially for those who receive salaries or business income (as opposed to recipients of government payments and rentiers, whose situation does not worsen).
In some countries, various government agencies officially report the onset of a recession under certain circumstances. For example, in the US, the Business Cycle Committee of the National Bureau of Economic Research defines a recession as "a significant decline in business activity throughout the economy over several months, usually reflected in the deterioration of real GDP, real income, employment, manufacturing and retail trade." In the UK, the recession is recorded by the National Statistical Office with a decline in GDP for two consecutive quarters.
There is a common joke among economists and the business press that explains the difference between a recession and an economic depression: "If your neighbor loses his job, then it's a recession, if you lose your job, then it's a depression."
A well-known paradox is associated with the definition of a recession: given that data on quarterly changes in GDP in developed countries are published with a long delay and can subsequently be significantly revised, the official announcement of the onset of a recession is often made several months after it has already ended. At the time of the announcement of the onset of a recession, the country's economy is either in a state of severe crisis, or at the stage of a new recovery. Accordingly, official recession data are mostly of historical interest and do not reflect the behavior of economic agents. Therefore, a significant role in making economic decisions by the government and entrepreneurs is played by the forecasting of GDP fluctuations, which is based on indirect indicators and is not very accurate. At the same time, in modern economic science there is no consensus on the causes of the recession and ways to accelerate its overcoming.
Economists distinguish several types of recessions - according to the conditional form of the graph of changes in GDP. V recession characterized by a relatively strong and rapid decline in GDP (which, however, does not reach the level of depression) with a pronounced single failure and subsequent rapid recovery to the previous level. U recession is characterized by a relatively long and stable (without up and down movements) stay of GDP at a low level, followed by a rapid recovery. During W recessions there is a short-term “bounce” of the GDP growth graph to the positive area in the middle of the recession, i.e. it is like two V-recessions in a row. Finally, under L-recession refers to a rapid fall in GDP followed by a long, smooth recovery.
Recession is not uncommon in the economies of developed countries. In the United States, more than ten recessions were observed after World War II alone, and in Great Britain at least five. With the growth of globalization, global recessions begin to occur, affecting several countries simultaneously (for example, in 1998, in 2000-2001 and 2008-2009).
There are several main causes of recession, depending on the level of development of the economy.
For resource-based economies, the decline in prices for oil, gas and other exported minerals is the reason for the decline. The price of raw materials falls, the budget receives less revenue, a deficit appears, which is compensated by raising tax rates, reducing spending on social needs (education, medicine, etc.). Such actions further exacerbate the decline in production.
In developed (industrial and post-industrial) states, recession manifests itself as a result of a change in the technological order, for example, due to the emergence and development of information technologies. The technological order is understood as the level of development of technology and technology, the main directions of development of scientific and technological progress.
These reasons for the emergence of a recession cannot be influenced, they arise due to the objective laws of the economy, therefore, a recession at the level of a single national economy will occur sooner or later. A recession in one state can lead to a recession in other economies, which will lead to a global crisis.
There are reasons that arise under the influence of market participants. The recession in the economy may be caused by problems in the banking sector.
For example, commercial banks have issued too many loans that are not repaid. Then financial institutions are forced to raise rates, raise funds in the foreign and domestic markets. In a situation where there are too many such banks, the number of loans issued falls, therefore, enterprises cannot borrow money and, in the absence of funds, stabilize or curtail production. Because of this, unemployment is growing, the population and companies do not repay loans, banks are tightening rules, the situation is entering a vicious circle and getting worse.
Force majeure circumstances, such as a war or a sharp change in energy prices, can plunge the economy into a recession phase. The way out of stagnation is possible only with the participation of the state, which will “inject” money into the economy, supporting various industries and stabilizing the national currency.
Murray Rothbard, a scientist-economist of the mid-20th century, spoke about the essentially similar terms "recession", "depression" and in a humorous form:
In the old days, we suffered from periodic economic crises, the sudden onset of which was called "panic", and the long period after the panic was called "depression". The most famous modern depression is, of course, the one that began in 1929 with a typical financial panic and continued until the outbreak of World War II. After the catastrophe of 1929, economists and politicians decided that this should never happen again. To successfully and without much trouble to cope with this task, it took only the elimination of the word "depression" from use. From that moment on, America no longer had to experience depressions. For when another severe depression came in 1937-1938, economists simply refused to use this terrible name and introduced a new, more harmonious concept - recession. Since then, we have experienced many recessions, but not a single depression. However, pretty soon the word "recession" also turned out to be rather harsh for the refined sensibilities of the American public. Apparently, the last recession we had was in 1957-1958. Since that time, we have had “downs”, or even better “slowdowns”, or even “deviations”.
 The economic situation in the country cannot always be stable, so economists often have to answer the question: what is a recession in simple words. Despite the complex name, as in the case of other economic terms, the essence of the concept lies in the Latin name itself, and a recession is nothing more than a “retreat” or “slowdown”. In fact, this means a moderate, but not yet critical decline in production, following the boom in its growth. We can say that this is the first wake-up call for the country's economy or the early stage of a "disease", which must be treated immediately in order to avoid complications.
The economic situation in the country cannot always be stable, so economists often have to answer the question: what is a recession in simple words. Despite the complex name, as in the case of other economic terms, the essence of the concept lies in the Latin name itself, and a recession is nothing more than a “retreat” or “slowdown”. In fact, this means a moderate, but not yet critical decline in production, following the boom in its growth. We can say that this is the first wake-up call for the country's economy or the early stage of a "disease", which must be treated immediately in order to avoid complications.
What is a recession and its signs
No economy can constantly prosper, and a sharp rise is always accompanied by a fall. As a rule, there is a decrease in the quantity of manufactured products, and its consumption also decreases, while the level of GDP does not increase, but is at a “zero” level and even decreases. This is the first sign of a recession and a call to action as the next phase is a crisis. By the way, a recession is a normal state of the economy, which periodically goes through four alternating phases, which takes from 10 to 20 years.
Let's take a look at its main features:
- a decrease in production volumes and a reduction in jobs, as a result (unemployment);
- rising prices for food and other consumer goods;
- falling stock indices and rising inflation;
- an increase in the number of remittances to other countries;
- a decrease in the number of loans issued, while their size is also decreasing;
- government debt is growing.
We can say that we are dealing with a recession if the inflation rate reaches not yet critical levels of 3-4%. If at the same time the presence of other signs is noted, with a high degree of confidence we can talk about an approaching crisis.
A recession can be of three types: unplanned (resulting from war or other unpredictable events), caused by external debt or growing investor distrust. The main danger is represented by the first two types, since it is not possible to minimize the consequences due to an elementary lack of time.
Causes of a recession in Russia
Among the causes of a recession, the main one is often the inability of the leadership to govern the country, while global economic trends play a significant role in this.
The Russian Federation has experienced this very “slowdown” more than once, and, as it turned out, there are enough reasons for this:
- First of all, this is a great dependence on the situation in the hydrogen market, the sale of which determines the filling of the budget and the level of GDP, respectively.
- Thus, the recession of 2010 in Russia is directly related to the fall in world oil prices, despite the fact that there was practically no growth in production in non-commodity segments.
- Decline in production, and this leads to a decrease in demand in the domestic market and a decrease in the number of export operations.
- An increase in the level of inflation, a decrease in investment attractiveness and an outflow of capital, as a result.
- Devaluation, or depreciation of the national currency in relation to the currencies of other countries, or a decrease in the gold content of the country's monetary unit (ruble).
Despite the fact that a recession is not yet a critical change in the country's economy, measures not taken in a timely manner can lead to the impoverishment of the population, which means that people will start saving. The consequence of this will be a decrease in consumer demand, curtailment of production rates or a surplus of unclaimed goods. A decrease in production leads to a decrease in wages, an increase in unemployment and an outflow of qualified personnel from the country. All countries experience recessions from time to time, but if for some it is painful, in others there are serious deteriorations.
What is happening in modern Russia
 According to many economists, Russia has been in a dangerous situation for some time, because the recession that began in 2014 has progressed, and already in 2015 there was an acceleration of the process. The reason for this was a sharp drop in oil prices, which led to a significant devaluation of the ruble and a decrease in the solvency of the population. To be fair, something similar has happened in other advanced economies.
According to many economists, Russia has been in a dangerous situation for some time, because the recession that began in 2014 has progressed, and already in 2015 there was an acceleration of the process. The reason for this was a sharp drop in oil prices, which led to a significant devaluation of the ruble and a decrease in the solvency of the population. To be fair, something similar has happened in other advanced economies.
Since 2017, when oil prices began to rise, the situation on the Russian market began to improve, which led to an increase in production, the opening of new enterprises and an increase in living standards. The rise in hydrogen prices continues against the backdrop of a reduction in the amount of its production and a decrease in the level of commercial oil reserves. By the way, for some, a recession is a decrease in income and impoverishment, while other enterprising people manage to make good money on this.