The state of economic security of the Russian Federation. Economic security of the Russian Federation. Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation GOU VPO MO
The concept of economic security and its levels. The role and place of economic security in the system of national security. Internal and external threats to economic security. The concept and state strategy of Russia's economic security. Methods for ensuring economic security.
Goals and objectives of Russia's foreign economic policy. The need to protect the domestic market. Methods and tools for protecting the domestic market. Current customs policy and WTO requirements.
Cooperation of the customs authorities of Russia with the customs services of other countries. Russia and the World Customs Organization. The main directions, principles and forms of Russia's participation in international cooperation in the field of customs.
The concept of economic security and its levels .
Economic security in the structure of national security is the main link.
economic security - an economic category characterizing such a state of the economy, which ensures sustainable economic growth, optimal satisfaction of social needs, rational management and protection of economic interests at the national and international levels. of which it consists (resources, natural resources, human resources, production assets, non-production, financial, etc.)
The legal basis for the functioning of the system national security are:
Constitution of the Russian Federation
Federal Law "On Security", "On the State Border", "On State Secrets"
State Economic Security Strategy of the Russian Federation, National Security Strategy until 2020, military doctrine, information security doctrine, etc.
National Security Structure:
President of the Russian Federation. Heads and forms the Security Council, gives sanctions, appoints and dismisses the highest command staff, is the supreme commander
The Security Council is a constitutional body that prepares decisions.
Subjects of economic security:
state,
tax and customs service,
all structures of the market economy
manufacturers
society
Types of economic security:
production and technological
industrial
food
ecological
economic
energy
information, etc.
Levels of economic security:
International (global and regional) - a set of international levels, agreements, in which each state is provided with the opportunity to freely choose and implement its own strategy of social and economic development, without being subject to external pressure, counting on non-interference, understanding and mutually beneficial cooperation from other countries.
Principles of economic security:
Equality of all states
Freedom of choice and development paths
Ensuring state sovereignty over natural resources
Mutually beneficial cooperation in various industries
The principle of peaceful settlement of economic disputes
Special incentives for underdeveloped countries
2. national economic security- the state of the economy and government institutions, which ensures the protection of national interests, socially oriented development of the country, sufficient economic and defense potential, even with the most favorable development of internal and external processes.
3. local- security of certain industries
4.Private- protection of enterprises and individuals, the state of organizational relations, when the stability of the organization is ensured
Internal and external threats to economic security.
External:
brain drain abroad
capital flight abroad
foreign public debt
excessive openness of the economy. The degree of openness is determined by: 1. export quota - the ratio of the value of exports to the value of the gross product; 2. the volume of exports per capita.
Internal:
Growing structural deformation
Decreased investment and innovation security
Destruction of the scientific and technical potential of the country
The effect of a stable trend is the transformation of the country into a fuel and raw materials periphery of developed countries
Strengthening the property stratification of society
Criminalization of the economy and society
The role and place of economic security in the system of national security.
National security-- there is a state of protection of the vital interests of the individual, society and the state, achieved by joint actions of state and public institutions through the flexible use of economic, political and other means both in domestic politics and in international relations.
Based on this, we will understand economic security as part of national security, which ensures the guaranteed protection of national interests, the socially oriented development of the country as a whole, and sufficient defense potential.
A high level of economic security, which is determined by the level of economic development of the country, allows:
to pursue an independent economic policy, in particular, independently carry out major economic activities, without linking this with the receipt of financial or other assistance from abroad;
maintain the stability of the economic standards in force in the country (primarily in terms of the standard of living of the population, their compliance with standards generally accepted in world practice or approved by directive for a specific period of time);
respond with minimal losses to global and regional financial and other crises, sharp geopolitical changes in the world and quickly restore the lost balance;
to provide assistance to other countries, in particular neighboring countries, in the event that the unbalanced economic situation that has developed there may adversely affect the economic interests of the state.
Being part of the national security system, economic security simultaneously forms the basis for the formation of all the elements included in its structure: financial, energy, food, military-industrial. The main indicators characterizing these types are: the volume of GDP, the gross grain harvest, the share of GDP in defense spending, the inflation rate, the share of spending on science, the share of the population with incomes below the subsistence level, the unemployment rate, external and internal debt. There are more than 160 indicators of economic security, after analyzing which one can draw a conclusion about the index of "complex national strength" of the state, the components of which are such components as the ability to contribute to the international community, the ability to survive, the possibility of forceful pressure.
The concept and state strategy of Russia's economic security.
1. STATE STRATEGY OF THE ECONOMIC SECURITY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION (approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608)
Basic provisions:
I. Purpose and objects of the State Strategy for Economic Security of the Russian Federation
II. Threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation
III. Criteria and parameters of the state of the economy that meet the requirements of the economic security of the Russian Federation
IV. Measures and mechanisms of economic policy aimed at ensuring economic security
1. Monitoring of factors that determine threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation
2. Development of criteria and parameters (threshold values) for the economic security of the Russian Federation
3. Activities of the state to ensure the economic security of the Russian Federation
Second half of the 1990s marked by the revival of the attention of state structures and the public to the problems of the country's national security. The formation of a socially oriented market economy necessitated the development and approval of basic concepts in the national security system.
The modern reform of the legal and economic foundations of the Russian state cannot but take into account the interests of national security. This problem becomes especially acute in the context of increasing globalization and in connection with Russia's active involvement in international political and economic processes. Foreign economic aspects of the national security of the country are the most important component of the system of economic security of the state. The more economically developed the country, the more economic resources it has (or controls), the higher its degree of protection from possible threats.
At the present stage, economic security is a guarantee of the country's independence, determines the possibility of pursuing an independent economic policy and creates a condition for stability and success in the context of the globalization of the world economy.
In the period from 1996 to 2005, scientific research was carried out and a number of scientific papers, collective monographs on this issue were published Senchagova V.K., Oleinikova E.A., Grunina O., Guseva G. and others. educational process and special courses are taught on national security and its various aspects. The urgency of the problems of economic security is reflected in the work of all-Russian and international scientific and practical conferences.
The paper considers the general problems of Russia's economic security associated with its activities in the system of international economic relations.
State features are:
the presence of a special system of bodies and institutions exercising the functions of state power;
· the law fixing a certain system of norms sanctioned by the state;
a certain territory to which the jurisdiction of the state extends and in which its population lives.
The life and activities of the people, the state are deployed in various spheres, and in each of them the action of adverse factors, dangers and threats that disrupt the normal life of a person, society and the state is possible. In terms of content, the following types (spheres) of its activity are distinguished: economic, social, political, military, environmental, legal, technological, cultural, intellectual, informational, demographic, psychological, and many others.
The state protects its interests, its territory, its population from external and internal threats.
A threat to the security of the state can be formulated as the possibility of such a development of events that will create (or creates) a danger to the existence of the state, its political and economic independence.
There are the following types of state security:
geopolitical security;
Geopolitical security is the protection and security of state interests guaranteed by constitutional, legislative and practical measures.
political security;
Each state is interested in having a stable internal political situation, in creating an internal state climate conducive to the normal development of all spheres of society and the individual. Political security is the state of security of the country's geopolitical life. The goal of political security is determined by the type of state. The essence of political security is determined by the ability to pursue an independent foreign and domestic policy and to resolve issues of state structure.
· military security;
Military security is the ability to protect the sovereignty, territorial integrity and population of a country from internal and external threats. Military security includes the following areas: state borders, armed forces, deterrence, military education, military science and military industry.
economic security.
The problems of national economic security are increasingly becoming the subject of study by representatives of various sciences. Scientists offer their own definitions, define the essential features of this complex social phenomenon, reveal emerging social connections between related concepts and phenomena. However, there are still many “dark spots” in this area. Until now, there is no unanimity of opinion among the researchers of this problem on the definition of basic concepts, which in practice gives rise to significant difficulties in applying the legislation on economic security. Therefore, it is necessary to start with the development of a conceptual apparatus.
The legal definition of the concept of "economic security" can be found in the Federal Law of October 13, 1995 No. No. 157-FZ "On state regulation of foreign trade activities". In accordance with Article 2 of the said Law, economic security is a state of the economy that ensures a sufficient level of social, political and defense existence and progressive development of the Russian Federation, the invulnerability and independence of its economic interests in relation to possible external and internal threats and influences. Therefore, the state of the economy is the main sign of economic security.
Therefore, in a compressed (concentrated) form, we can say that national economic security is a state of protection of the main national economic interests from internal and external threats.
It is important to emphasize that such concepts as "conditions", "factors", "correlation" characterize economic security from different points of view. Thus, a condition is an environment (environment) in which economic security proceeds (realizes). There are economic, geopolitical, environmental, legal and other conditions. The factor is the reason, the driving force of economic security. The ratio of economic interests is understood as their mutual relationship, location relative to each other.
Economic security is characterized by the level of development of productive forces and economic relations aimed at meeting the needs of the individual, society, state, the presence of minerals, developed infrastructure, skilled labor and its training system, as well as the nature of integration into the system of world economic relations.
The objects of economic security are:
· economic system of the country: producers and sellers of products, works and services;
· natural wealth of the country - agricultural land, forests, rivers, lakes, seas, shelf, minerals.
The subjects of economic security are:
functional and sectoral ministries and departments;
tax and customs services;
Banks, stock exchanges, funds and insurance companies;
Manufacturers and sellers of products, works and services;
Society for the protection of consumer rights.
In Russia, the doctrine of economic security was approved and introduced by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996. No. 608 "The State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)". In pursuance of the provisions of this Decree on December 27, 1996. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1569 “On priority measures for the implementation of the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)” was adopted. These documents define the purpose and objects of the state strategy of economic security, characterize the threats to the economic security of Russia, formulate the criteria and parameters of the state of the economy that meet the requirements of economic security, describe the mechanisms and measures of economic policy aimed at ensuring economic security. As noted in the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation, “in international relations, Russia is faced with the desire of industrialized countries, large foreign corporations to use the situation in the Russian Federation and the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States in their economic and political interests .... Without ensuring economic security, it is practically impossible to solve any of the tasks facing the country, both at the domestic and international levels. By the above Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, a number of federal executive bodies (Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, Security Council of the Russian Federation, etc.) are responsible for developing quantitative and qualitative parameters of economic security criteria, monitoring and forecasting the factors that determine the occurrence of threats to economic security, for conducting research to identify trends and opportunities for the development of threats and the search for optimal ways to overcome them. At the same time, the economic security system should identify situations in which the actual or projected parameters of economic development go beyond the threshold values, develop measures to overcome them (i.e., to exit the country from the danger zone), conduct an examination of the adopted regulatory legal acts, state decisions on financial and economic issues from the standpoint of Russia's economic security.
is the ability of the state to respond adequately in the face of constant destabilizing effects of military, economic, political, informational, demographic and psychological factors, i.e. to implement measures aimed at both eliminating threats and dangers and protecting the interests of an individual and the state as a whole.
The regional aspect of national security depends on changing the goals, objectives and methods (or means) of the state. The state policy for ensuring national security should reflect the role and place of each region in achieving national interests. In turn, regional features predetermine the totality of threats and dangers that affect the security of not only the region, but the country as a whole.
Of particular interest are economic security and its most important component - the regional aspect of economic security. Economic security is characterized by the possibility of the national economy of Russia and its regions ensure stable progressive development and appropriate protection by economic methods of both the subject and the Federation as a whole.
Economic security of Russia
Economic security is the basis of the country's national security.
is the protection of the country's economy from internal and external adverse factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the economy and undermine the achieved standard of living of the population.
The Law of the Russian Federation "On Security" defines the economic security of Russia as the protection of the vital interests of all the inhabitants of the country, Russian society as a whole and the state in the economic sphere from internal and external threats. Economic security is the main component of the national security system. Guarantees of economic security are a prerequisite for sustainable development.
Threats to economic security are such phenomena and processes that adversely affect the economic condition of the country, limit the economic interests of the individual, society, state, create a danger to national values and the national way of life.
Threats to economic security are divided into internal and external.
To internal threats to economic security Russia can be attributed to:
- Strengthening the property stratification of society. According to the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, the income level of the wealthiest Russians is 15 times higher than the income level of the least wealthy citizens.
- Criminalization of the economy and society. Estimates of the scale of the Russian shadow economy usually vary in the range of 20-40% of GDP. This year, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev sets an example and invites all officials to publish tax returns.
- Destruction of the scientific and technical potential of the country. In terms of absolute spending on science, Russia today is approximately 5 times inferior to Germany, 7 times to Japan, and 17.5-100 times to the United States.
to the most significant external threats to economic security Russia can be attributed to:
- Brain drain abroad. Unfortunately, it is Russia that is now the main supplier of highly qualified specialists abroad. And in this case we are talking about the loss of that segment of the population that could provide Russia with a worthy place in the world community of the 21st century.
- Capital flight abroad. The concept of "capital flight" means the illegal export of capital abroad. The data of the Bank of Russia were published: in the last year, 2008, almost $130 billion flowed out of the country.
- Increasing import dependence on food and consumer goods. Today, 80% of the Russian drug market and more than 40% of the Russian food market are imported.
In the interests of a real socio-economic rise in Russia, it is necessary to revise the government's course and carry out reforms in structural, industrial, monetary policy and in the use of foreign economic relations.
The concept of national economic security of Russia
The Need for Security- elimination of undesirable effects leading to cardinal deformations is one of the basic needs of both the individual and the whole society as a whole. In modern conditions, the need for security has become aggravated, since if it is not observed, a number of negative phenomena arise not only for the individual, but also for the entire society - the state.
National security means such a state of the external environment that allows maintaining the normal functioning of the entire state, preserving its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
National security for a long period of time had an exclusively external orientation - the protection of the independence of the state from external interference. The current stage of human development has brought the understanding of national security to a fundamentally different level. Scientific and technological progress has significantly changed the methods and the very essence of military aggression. For example, with the advent of atomic weapons, the conduct of hostilities does not make sense, since as a result of them both the aggressor and the object of aggression will be destroyed. The level of national security increasingly depends not on the specific military power of the country, but on such factors as the level of development of the national economy, the quality of life of the population, the degree of development of social infrastructure, and the size of national wealth. Modern threats to national security have shifted towards terrorism, intercultural conflicts, environmental violations, and the decline of the national economy.
The main component of national security is national economic security, the importance of which in modern conditions is increasingly growing under the influence and integration of the world economy.
National economic security- this is the mode of functioning of the national economy, which allows you to maintain acceptable living conditions for the population - the quality, standard of living and the provision of economic resources in the amount necessary to ensure sustainable economic growth.
National economic security is based on such basic principles as:
- independence of the national economy. Due to the increasing involvement of national economies in the world economy, this principle can only be fulfilled relatively - it is necessary to achieve a state of relative independence of the national economy. The task of the state is to form such a level of development of the national economy that allows it to take a competitive and equal position in the world economy;
- stability of the national economy. The state must create a sustainable growth of the national economy, excluding social upheavals, strengthening the role of criminal structures and creating a security regime for every citizen;
- sustainable growth rates of the national economy. In modern conditions, only constant and sustainable growth can provide an acceptable level of economic security, including the improvement of production, the professionalism of each person.
Economic security is based on the independence, stability and growth of the national economy, which is a prerequisite for its normal functioning.
The concept of the national security of the Russian Federation is a normative legal act that establishes the main provisions of national security, including economic. It was approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of December 17, 1997 No. 1300 (as amended by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of January 10, 2000 No. 24).
The concept of national security of the Russian Federation is a system of basic provisions aimed at ensuring the security of the individual, society and the state in the Russian Federation from external and internal threats in all spheres of life. This legal act determines that the national security of the Russian Federation is understood as the security of its multinational people as the bearer of sovereignty and the only source of power in the Russian Federation.
The following tasks are set for national economic security:
- forecasting the emergence of internal and external threats;
- development and implementation of the necessary measures to reduce the degree of influence of internal and external threats;
- protection of the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Russian Federation;
- development and implementation of economic policy aimed at enhancing economic growth;
- creation of conditions for scientific and technological independence;
- ensuring the security of man and citizen, his rights and freedoms;
- improving efficiency ;
- maintaining the balance of interethnic relations;
- creation of conditions for compliance with the law;
- formation of mutually beneficial relations with other states;
- containment of the country's military potential;
- improvement of the ecological situation;
- integration of the national economy into the world economy;
- formation of a single economic space with the CIS countries;
- protecting the interests of domestic producers on world markets;
- formation of the regime of financial and credit independence of Russia;
- strengthening state regulation of foreign companies conducting economic activities in the country;
- formation of an effective legal framework for the activities of economic entities;
- bringing the national economy out of the crisis.
The basis of national security is national interests - a set of interrelated and balanced interests of the state, society and the individual.
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation GOU VPO MO
"Kolomensky State Pedagogical Institute"
Faculty of History, Department of State and Municipal Administration.
Department of Economics
day department
COURSE WORK
by discipline: Economic theory
on the topic: Economic security of the economy of the Russian Federation.
Performed:
3rd year student
Borodavkina Yu.A.
Supervisor:
Leonova Zh.K.
Kolomna
year 2009
Introduction 3
Chapter 1. Economic policy of the state and economic security 5
1.1. The concept, structure and elements of the concept of economic
state security. 5
1.2 Regulatory framework for the economic security of the Russian Federation 12
Chapter 2. Present and Future of the Russian Economy 16
2.2. The current state of Russia's economic security 20
2.3. Globalization as a threat to economic security 35
2.4. The main directions of increasing the economic security of the country. 37
Conclusion 43
List of references 44
INTRODUCTION
The economic security of the country today has come to the fore among the problems that attract the close attention of specialists of various profiles, including representatives of special services. Such attention is by no means accidental. It is connected, first of all, with the fact that the economic sphere of the state is pivotal and determines the viability of other spheres. The influence of the economic sphere on others is more tangible than the influence of these spheres on it. Accordingly, economic security is dominant in relation to other types of security.
It used to be that economic security was the prerogative of the state security agencies. Undoubtedly, law enforcement agencies, special services, including the FSB of Russia, are an important link in ensuring the economic security of the state. But the structure of the economy itself must ensure security, the implementation of the conditions of which is possible only if Russia's national interests are observed when conducting economic reforms and taking into account existing threats. Russia is a multinational country that includes dozens of nationalities that have their own statehood and even their own Security Councils involved in ensuring national security. One may get the impression that in the Russian Federation national security is understood as the security of only the Russian nation, but this is not so. The concept of "national security" reflects the state, the level of security of all peoples and nations that are part of Russia.
Ensuring economic security is a guarantee of the independence of the country, the conditions for stability and efficiency of society, and the achievement of success. Therefore, ensuring economic security is one of the most important national priorities.
Russian Prime Minister Putin Vladimir Vladimirovich said that Russia has two possible development paths - either Russia will be a strong state, or this state will disappear from the atlas of the world, at least in the form in which it exists today. Many foreigners need Russia as a raw materials appendage to their economy, living off the sale of their resources. This is a disastrous path for Russia. In order to survive, the state needs to build its economic policy taking into account the requirements of the technogenic development of the world community in the 21st century, it is necessary to find our growth points in the form of new technologies, in which we must not catch up, but outstrip foreign competitors. The concept of the country's economic security includes not only maintaining the socio-political and military stability of the state at a sufficient level, but, above all, the development of the economy with its inclusion in the globalization processes taking place today in the world community.
Frivolity and attempts to minimize the threatening dangers are unacceptable here. The role of science in developing the concept of economic security is very important and responsible. It is fundamentally important to uncover the essence of the problem, identify real threats, and offer reliable and effective methods to counter them.
The relevance of the research topic is determined by the need to strengthen the positions of the Russian economy in the modern world, especially during the economic crisis, as well as to pursue a more active economic policy.
This paper discusses some issues of the country's economic security, as well as the directions of development of the Russian economy in order to reflect threats to the economic security of Russia.
The purpose of this course work is to study the concept, structure, legal framework and strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation.
The objectives of this study are: consideration of theoretical provisions relating to economic security, analysis of the current state of Russia's economic security, identification of the main directions for increasing the economic security of Russia.
It can be said without exaggeration that the development of problems of ensuring guaranteed internal and external security of the country, all its aspects, and especially economic security, is a priority task for specialists in the field of state and municipal administration.
Chapter 1. Economic policy of the state and economic security
1.1. The concept, essence and criteria of the country's economic security.
In the 1970s, the term "economic security" first appeared. It quickly became widespread in the developed capitalist countries. It was then, defending a realistic assessment of the current international situation, that representatives, primarily of the countries of Western Europe, advocated the use of economic methods to ensure national security.
The most intensive research in the field of economic security of the Russian Federation began with the creation of the Interdepartmental Commission of the Security Council on Economic Security, although numerous studies of Russian economists, sociologists, political scientists and researchers in a number of related disciplines have been devoted to the problems associated with this concept.
The Interdepartmental Commission of the Security Council on Economic Security was formed in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation "On Security", "Regulations on the Security Council", approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of June 3, 1992, No. 547 "On the Formation of the Security Council of the Russian Federation" and Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of October 20, 1993 No. 1686, "On improving the activities of interdepartmental commissions of the Security Council of the Russian Federation." In essence, the listed documents introduced the concept of economic security. The concept of economic security in the most general sense means the ability and readiness of the economy to provide decent living conditions and personal development, socio-economic and military-political stability of society and the state, the ability to withstand the influence of internal and external threats. Economic security is the material basis of both national security as a whole and practically all of its components (food, energy, scientific and technical, environmental, informational, etc.).
The events of October 10-11, 1994, connected with the sharp depreciation of the ruble (Black Tuesday), heightened the interest of both the scientific community and the general population in economic security. In April 1995, by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation, the Interdepartmental Commission of the Security Council on Economic Security was formed, as a result of which the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (basic provisions) was developed, approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated April 29, 1996 No. 608.
The purpose of the State Strategy is to ensure such development of the economy, which would create acceptable conditions for life and personal development, socio-economic and military-political stability of society and maintaining the integrity of the state, successfully countering the influence of internal and external threats. Without ensuring economic security, it is impossible to solve any of the tasks facing the country, both domestically and internationally.
The implementation of the State Strategy should create the necessary conditions for achieving the overall goals of national security. In particular, ensure:
Protection of the civil rights of the population, improving the quality of their lives, guaranteeing peace in the country and tranquility in society;
Effective solution of internal and external political, economic and social tasks, based on national interests;
Active influence on the processes in the world affecting the national interests of Russia.
Economic security is organically included in the system of state security, as its basis, along with its components such as ensuring the country's reliable defense capability, maintaining social peace in society, and protecting against environmental disasters. Here everything is interconnected, and one direction complements the other: there can be no military security in a weak and inefficient economy, just as there can be neither military security nor an effective economy in a society torn apart by social conflicts. But, considering certain aspects of security, one cannot bypass their economic aspects.
At present, economic security is traditionally regarded as the most important qualitative characteristic of the economic system, which determines its ability to maintain normal living conditions for the population, sustainable provision of resources for the development of the national economy, as well as the consistent implementation of national-state interests.
Economic security is understood as such a state of the economy and government institutions, which ensures the guaranteed protection of national interests, the socially oriented development of the country as a whole, and sufficient defense potential.
Ensuring economic security is a guarantee of the country's independence, a condition for the stability and effective functioning of society, and the achievement of success. This is explained by the fact that the economy is one of the vital aspects of the activity of society, the state and the individual, and, therefore, the concept of national security will be an empty word without assessing the viability of the economy, its strength against possible external and internal threats. Therefore, ensuring economic security is one of the most important national priorities.
Economic security itself has a complex internal structure, in which the most important elements can be distinguished:
Economic independence is not absolute because the international division of labor makes national economies interdependent on each other. Under these conditions, economic independence means the ability to control national resources, achieve a level of production, efficiency and product quality that ensures its competitiveness and allows it to participate on an equal footing in world trade, cooperation ties and the exchange of scientific and technological achievements. This concept has a complex structure and means, firstly, the ability of the economy to maintain the sovereignty of the country and the geopolitical position in the world, to adapt to new conditions of development; secondly, a systematic assessment of the state of the economy from the standpoint of protecting the national interests of the country; thirdly, the readiness of government institutions to counteract the threats and challenges of post-industrial development by increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of management, as well as creating economic and legal conditions that exclude criminalization.
The stability and sustainability of the national economy, which implies the protection of property in all its forms, the creation of reliable conditions and guarantees for entrepreneurial activity, the containment of factors that can destabilize the situation (the fight against criminal structures in the economy, the prevention of serious gaps in the distribution of income that threaten to cause social upheavals, etc.) d.).
The ability for self-development and progress, which is especially important in today's dynamically developing world. Creation of a favorable climate for investments and innovations, constant modernization of production, raising the professional, educational and general cultural level of workers become necessary and mandatory conditions for the stability and self-preservation of the national economy. Development should go in the following directions:
The ability of the economy to function in the mode of expanded reproduction, that is, to ensure GDP growth in the next decade (within at least 7-8 percent per year);
Increasing the competitiveness of the economy not only in the extractive industries, but primarily in the manufacturing industries and increasing (by 5-6 times) the share of innovatively active enterprises;
Improving the well-being of the population, which means a steady increase in their real incomes, wages, a faster increase in pensions and benefits;
Reducing by 3-4 times the layer of poor people and the formation of the middle class of citizens with an appropriate level of effective demand;
The reliability of the banking system and the ability of the consolidated budget to finance the social obligations of the state, maintain business activity and high market conditions, and prevent surges in the change in the ruble exchange rate; sufficiency of the money supply and credit resources to ensure high long-term GDP growth rates;
Increase in the structure of foreign trade turnover of the share of exports of products of manufacturing industries;
Maintaining the level of imports, especially food, at a safe level (approximately 25 percent of retail food turnover);
Independence of Russia in strategically important areas of scientific and technological progress, especially in the field of defense industries, space technology, nuclear industry, mechanical engineering;
Prevention of excessive differences in the levels of development and well-being of the population of the regions.
Thus, economic security is a set of conditions and factors that ensure the independence of the national economy, its stability and sustainability, the ability to constantly update and improve itself.
For a better understanding of the essence of economic security, it is important to understand its relationship with the concepts of “development” and “sustainability”. Development is one of the components of economic security. After all, if the economy does not develop, then the possibilities of its survival, as well as its resistance and adaptability to internal and external threats, are sharply reduced. Stability and security are the most important characteristics of the economy as a single system. They should not be opposed, each of them in its own way characterizes the state of the economy. The stability of the economy characterizes the strength and reliability of its elements, vertical, horizontal and other links within the system, the ability to withstand internal and external "loads". Security is the state of an object in the system of its connections in terms of the ability to survive in the face of internal and external threats, as well as the action of unpredictable and difficult to predict factors.
The more stable the economic system, the more viable the economy, and hence the assessment of its security will be quite high. Violation of proportions and connections between different components of the system leads to destabilization and is a signal of the transition of the economy from a safe state to a dangerous one.
The essence of economic security is realized in a system of criteria and indicators. The criterion of economic security is an assessment of the state of the economy in terms of the most important processes that reflect the essence of economic security. Safety criteria include assessments of:
Resource potential and opportunities for its development;
The level of efficiency in the use of resources, capital and labor and its compliance with the level in the most developed and advanced countries, as well as the level at which external and internal threats are minimized;
Competitiveness of the economy;
Integrity of the territory and economic space;
Sovereignty, independence and ability to resist external threats,
Social stability and conditions for the prevention and resolution of social conflicts.
The system of indicators-indicators, which received a quantitative expression, allows you to signal in advance about the imminent danger and take measures to prevent it.
For economic security, it is not the indicators themselves that matter, but their threshold values. Threshold values are limiting values, non-compliance with the values of which prevents the normal course of development of various elements of reproduction, leads to the formation of negative, destructive trends in the field of economic security.
It is important to emphasize that the highest degree of security is achieved on the condition that the entire set of indicators is within the acceptable limits of their threshold values, and the threshold values of one indicator are achieved without detriment to others. Therefore, we can conclude that beyond the threshold values, the national economy loses its ability to dynamic self-development, competitiveness in external and internal markets, becomes an object of expansion of foreign and transnational monopolies, is corroded by ulcers of corruption, crime, suffers from internal and external robbery of national wealth.
Among the indicators of economic security are:
Indicators of economic growth (dynamics and structure of national production and income, indicators of volumes and rates of industrial production, sectoral structure of the economy and dynamics of individual sectors, capital investments, etc.);
Indicators characterizing the natural resource, production, scientific and technical potential of the country;
Indicators characterizing the dynamism and adaptability of the economic mechanism, as well as its dependence on external factors (inflation rate, consolidated budget deficit, the effect of external economic factors, the stability of the national currency, internal and external debt);
Quality of life indicators (GDP per capita, level of income differentiation, provision of the main groups of the population with material goods and services, working capacity of the population, the state of the environment, etc.).
Threshold levels of safety reduction can be characterized by a system of indicators of general economic and socio-economic significance, reflecting, in particular:
The maximum permissible level of decline in economic activity, production volumes, investment and financing, beyond which it is impossible to independently develop the country on a technically modern, competitive basis, preserve the democratic foundations of the social system, maintain defense, scientific and technical, innovative, investment and educational and qualification potential ;
The maximum permissible decrease in the level and quality of life of the bulk of the population, beyond which there is a danger of uncontrolled social, labor, interethnic and other conflicts; there is a threat of loss of the most productive part of the national "human capital" and the nation as an organic part of a civilized community;
The maximum permissible level of cost reduction for the maintenance and reproduction of natural and ecological potential, beyond which there is a danger of irreversible destruction of elements of the natural environment, loss of vital resource sources of economic growth, as well as significant areas of residence, production and recreation, causing irreparable damage to the health of the current and future generations, etc.
Summarizing the above, we can say that economic security is the ability of the economy to ensure the effective satisfaction of social needs at the national and international levels. In other words, economic security is a combination of internal and external conditions that favor the effective dynamic growth of the national economy, its ability to meet the needs of society, the state, the individual, to ensure competitiveness in external and internal markets, guaranteeing against various kinds of threats and losses.
Two conclusions can be drawn from this:
First. The economic security of the country must be ensured, first of all, by the efficiency of the economy itself, that is, along with the protective measures taken by the state, it must protect itself on the basis of high labor productivity, product quality, etc.
Second. Ensuring the country's economic security is not the prerogative of any one state department or service. It must be supported by the entire system of state bodies, by all links and structures of the economy.
1.2. Normative-legal basis of the economic security of the country.
The legislative branch of state power, through laws, forms the legal foundations of economic security, outlines the range of state values and interests under state protection, establishes a system of state bodies specializing in ensuring economic security, determines their competence, provides for the possibility, grounds and types of legal liability for misconduct individuals and legal entities recognized as subjects of law. The main activities of the chambers of the Federal Assembly in the field of ensuring economic security are carried out on an ongoing basis through the structure of committees of the Federation Council and the State Duma in cooperation with the relevant departments of the apparatus of the Federal Assembly (information and analytical department of the Federation Council and the analytical center of the State Duma).
An important role in ensuring economic security was played by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 “On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation”
In March 1994, i.e. more than three years after the start of the "reform" of the economy, the government adopted a decree on the development of the "Basic Provisions of the State Strategy in the Field of Ensuring the Economic Security of the Russian Federation." The document was prepared and its draft in January 1995 was considered and approved by the Security Council. However, it took almost 1.5 years for it to become a document, since it was only in April 1996 that the President signed Decree No. 608 "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)". The most important element of Russia's state security is economic security. In accordance with the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)", the economic security of Russia is the state of protection of the economic interests of the individual, society and the state from internal and external threats, based on independence , efficiency and competitiveness of the country's economy.
The objects of economic security of the Russian Federation, in accordance with the Decree, are the individual, society, the state and the main elements of the economic system, including the system of institutional relations.
Without ensuring economic security, it is impossible to solve the tasks facing the state, both at the national and international levels.
Thus, the state strategy of economic security, being an integral part of the national security of Russia, pursues the goal of ensuring the protection of the population by improving the level and quality of life, effectively solving internal economic and social problems, as well as influencing world processes, taking into account national state interests.
The current situation in the Russian economy requires the definition of an economic security strategy. However, all ongoing economic measures are mostly impulsive, fragmented.
Despite the complexity of the transition period, Russia has a huge potential to ensure its economic security not only within the country, but also abroad. The foreign economic orientation of the state strategy lies in the effective realization of the advantages of the international division of labor, in the participation of the country in its equal integration into world economic relations, in the elimination of its dependence on foreign countries in matters of economic and technical cooperation.
The objects of economic security, in addition to the individual and the state, are the main elements of the economic system and economic activity.
The state economic security strategy includes:
1) characterization of external and internal threats to the economic security of Russia as a set of conditions and factors that create a danger to the vital economic interests of the individual, society and the state; identification and monitoring of factors that undermine the stability of the socio-economic system of the state, in the short and medium term (3-5 years) perspective;
2) determination of criteria and parameters that characterize national interests in the field of economy and meet the requirements of Russia's economic security;
3) the formation of economic policy, institutional reforms and the necessary mechanisms to eliminate or mitigate the impact of factors that undermine the stability of the national economy.
The implementation of the economic state strategy should be carried out through a system of specific measures implemented on the basis of qualitative indicators and quantitative indicators - macroeconomic, demographic, foreign economic, economic, technological, etc.
Thus, only in May 1997 was the concept of national security adopted, which was supposed to combine the forces and means of the Russian special services and law enforcement agencies - primarily the Department of Economic Security of the FSB (though formed only in 1998), as well as the relevant units of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, GRU, the Federal Tax Police Service and the State Customs Committee.
On January 10, 2000, the second version of the Russian National Security Concept was adopted. This document defines the fundamental initial provisions for the national security of the country, which should become the basis for the formation of the domestic and foreign policy of the state. It analyzes Russia's place in the world community, defines its national interests, processes and phenomena that threaten them.
The protection of the country's national interests in the economic sphere plays a paramount role in ensuring Russia's national security. Ultimately, the provision of all elements of national security: defense, environmental, informational, foreign policy, and others depends on the country's economic capabilities. At the same time, the development of a program of priority and long-term measures to ensure the economic security of Russia and practical steps in this direction should be based on a clear understanding of modern threats.
In accordance with the concept of national security: “in the sphere of the economy, threats are complex in nature and are caused, first of all, by a significant reduction in the gross domestic product, a decrease in investment, innovation activity and scientific and technical potential, the stagnation of the agricultural sector, an imbalance in the banking system, the growth of external and internal state debt, a trend towards the predominance of fuel and raw materials and energy components in export deliveries, and food and consumer goods, including basic necessities, in import deliveries. The state of the domestic economy, the imperfection of the system of organization of state power and civil society, the socio-political polarization of Russian society and the criminalization of public relations, the growth of organized crime and the increase in the scale of terrorism, the aggravation of interethnic and complication of international relations create a wide range of internal and external threats to the national security of the country. The weakening of the scientific, technical and technological potential of the country, the reduction of research in strategically important areas of scientific and technological development, the outflow of specialists and intellectual property abroad threaten Russia with the loss of leading positions in the world, the degradation of high-tech industries, increased external technological dependence and undermining the defense capability of Russia.
Negative processes in the economy underlie the separatist aspirations of a number of constituent entities of the Russian Federation. This leads to increased political instability, weakening the single economic space of Russia and its most important components - production, technology and transport links, financial, banking, credit and tax systems.
Economic disintegration, social differentiation of society, devaluation of spiritual values contribute to increased tension in relations between the regions and the center, posing a threat to the federal structure and the socio-economic structure of the Russian Federation.
The greatest efficiency in the implementation of the legislative powers of the Federal Assembly can be achieved through interaction with the information and analytical divisions of the Federation Council and the State Duma, committees of the Federal Assembly, the Presidential Administration, the Security Council apparatus, and the Government apparatus. However, coordination between these bodies on economic security issues is currently not effective enough. Various bodies participate in ensuring national security independently of each other without coordinating plans and results of work. This dispersion damages the quality of work and reduces the level of public administration. Obviously, the functional and organizational issues of ensuring national and economic security need further improvement.
Chapter 2. Prospects for the Russian economy.
Among the main directions of economic policy, it is advisable to single out the following areas, which are relevant today both for countries with developed market economies and for Russia:
opportunistic policy;
economic growth policy;
structural policy;
Regional policy;
employment policy;
Anti-inflation policy;
Investment policy;
Social politics.
All these directions intersect, and sometimes contradict each other. The government, depending on the situation, chooses priorities.
Particular attention of the Government of the Russian Federation in the medium term is paid to the implementation of priority national projects in the field of healthcare, education, housing for the population, as well as the development of the agro-industrial complex.
In addition, the Government of the Russian Federation intends to develop measures aimed at increasing the effectiveness of programs in the field of social policy and improving the mechanisms for providing social assistance. In this regard, it is necessary to ensure the coordination of the activities of all authorities providing social assistance in the implementation of relevant programs, to promote the increase of regional and interregional labor mobility.
It is planned to continue the implementation of the administrative reform and civil service reform, which are aimed at ensuring publicity and regulation of the activities of state authorities and further reducing their redundant functions.
To ensure the innovative direction of economic growth, it is necessary to increase the role of scientific research and development, the transformation of scientific potential into one of the main resources for sustainable economic growth by creating an innovation system, forming markets for innovative capital and information and consulting services in the innovation sphere, improving the regulatory legal framework for protecting the rights to intellectual property, staffing innovation economy. It is necessary to create favorable conditions for the introduction of advanced technologies into production, including the integrated and balanced development of innovation infrastructure.
In order to develop the Russian regions, it is necessary to move from the inefficient alignment of the economic development of the regions to the creation of conditions that stimulate the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities to mobilize the available resources for economic growth. This should be achieved by improving the efficiency of public administration, the formation and development of production clusters, and the improvement of interbudgetary relations aimed at stimulating reforms in the regions.
To solve problems related to the elimination of infrastructural and technological constraints, it is necessary to develop transport infrastructure as a condition for sustainable economic development, contributing to the growth of trade, information transfer volumes, production capacities, and changes in the structure of the economy. This task can be successfully solved only with the active participation of business.
The development of competition and the reduction of the non-market sector will be ensured by creating and improving market institutions, developing small businesses, and ensuring equal and fair competition. With a general improvement in the business climate and the creation of economic incentives for intersectoral capital flows, conditions will be created to increase the attractiveness of the processing industries and the service sector.
On April 19, 2007, the Russian Government approved the socio-economic development forecast for 2008. and for the period up to 2010. The Ministry of Economic Development and Trade (MEDT) presented an updated scenario for the country's development in the medium term, which focuses on economic diversification, strong investment and consumer demand, faster development of the manufacturing industry and the growth of non-commodity exports. The domestic economy will reduce dependence on oil prices, officials promise. They do not foresee domestic macroeconomic risks and believe that the indicators of economic development have reached indicators of stability.
According to economists, the presented forecast looks optimistic, and there are some prerequisites for this. Last year, successful in many respects of the country's economic well-being, and the first quarter of 2007. demonstrated the acceleration of the economy. The fact that the Russian economy will move away from growth based on oil and gas exports and will be based on the manufacturing industry and technology can only be welcomed, experts say.
In the forecast of the socio-economic development of the country for 2008-2010. the following parameters are set. Inflation forecast for 2007 is 7-8%, in 2008. - 6-7%, for 2009 - 5.5-6.5%, for 2010 - 5-6%. The forecast for GDP is: for 2007. - 6.5%, for 2008 - 6.1%, for 2009 - 6%, for 2010 - 6.2%. At the same time, the head of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade German Gref believes that Russia may reach higher GDP growth rates than those included in the three-year forecast. This can happen if the investment activity of enterprises is higher and the price of oil exceeds official expectations.
Industrial production growth forecast for 2007 is 5.2%, for 2008. - 5.1%, for 2009 - 4.8%, for 2010 - 5.2%. The growth of investments in fixed capital, according to the forecast of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade of the Russian Federation, will be: in 2007. - 12.8%, in 2008 - 11.9%, in 2009 - 10.5% and in 2010. - 11.4%.
In addition, the officials focused on indicators related to the social sphere. Real disposable income of Russians in 2007 will grow by 9.8% in 2008. - by 9.1%, in 2009. - by 8% in 2010. - by 7.5%. At the same time, real wages, according to the forecast, in 2007 will increase by 12.8% in 2008. - by 10.8% in 2009. - by 8.8% and in 2010. – by 8.2%. Unemployment is expected to decrease from 7.3% in 2006 to to 6.8% in 2010 At the same time, the number of registered unemployed should grow, which indicates structural changes in this area.
The turnover of retail trade will grow in 2007. by 11.6% in 2008 - by 10.5%, in 2009. - by 9.1%, in 2010. - by 8.4%. The positive trade balance of the Russian Federation in the medium term will gradually decrease. Thus, according to the forecast of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade, in 2007 it will amount to 100.8 billion dollars, in 2008. - 67.6 billion dollars, in 2009. - 34.7 billion dollars, and in 2010. already $3.2 billion
Economists note that by raising the forecast for economic growth, officials are betting on strong domestic investment and consumer demand. According to their estimates, the expected growth rates of the economy as a whole look very plausible: the economy still has a huge reserve for growth associated with the possibility of increasing its efficiency (reducing energy intensity, increasing labor productivity, etc.) and 6% per year seems to be a normal growth rate for her.
High consumer demand will be able to provide growth in the processing sectors of the industry. The clearly marked arrival of foreign manufacturers, localizing certain industries, not only contributes to the forecasted growth, but may also have an additional positive impact on the economy. There are no obvious domestic or external threats to growth, with the exception of a collapse in world commodity prices, but this threat is becoming less significant every year due to the same diversification of the economy. At the same time, there are several points in the forecast that raise questions: the prospects for the oil and oil refining sector look underestimated, and the prospects for non-commodity exports look overestimated. Many analysts are also positive about the socio-economic development forecast prepared by the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade. And they suggest that against the background of a possible shortage of labor, one of the priorities for the government should be migration policy. High growth rates of wages and pensions will lead to a further increase in the disposable income of the population, in connection with which the increase in consumption will continue to be one of the key factors for the growth of the Russian economy.
However, without ensuring economic security, it is impossible to solve the tasks facing the state, both at the national and international levels.
2.2. The current state of Russia's economic security
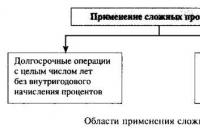
The structure of economic security problems is shown in Scheme 1.
Scheme 1. The structure of economic security problems.
Let's return to the State Strategy for Economic Security. This document defines the criteria and parameters of economic security to be monitored.
Criteria of economic security, defined as factors that determine the emergence of threats to economic security, are formulated as follows:
1. The ability of the country's economy to sustainable growth.
2. Dependence of the country's economy on imports of the most important types of food and products, the production of which can be organized in the country.
3. Levels of external and internal debt.
4. Reproduction of strategic resources.
5. Levels of poverty and unemployment.
6. Stability of the financial system.
7. Rationalization of the structure of foreign trade.
8. Accessibility for the population of education, culture, medical and social services, passenger transport, mass communications, as well as housing and utilities.
9. Maintaining the scientific potential of the country.
10. Relations with the CIS member states.
Each of these factors has an established set of indicators that can be found on the website of the State Committee of the Russian Federation on Statistics.
An analysis of the economic security categories of developed countries and Russia shows that the Russian Federation faces a number of threats that are not typical for developed countries. These threats include the need to integrate into the already established system of international institutions; difficulties in identifying the position of the system associated with the crisis of the bodies responsible for collecting statistical information, and as a result, the impossibility of making optimal management decisions; on the territory of a number of constituent entities of the Russian Federation there are legal acts that are contrary to federal legislation; Russia has vast unguarded borders. At the same time, the Russian Federation, as a country developing in a global economy, is faced with the entire traditional complex of threats inherent in the era of globalization.
The strategic national interests of Russia in the economic sphere are multifaceted, but, summing up, they can be represented in three most important areas: long-term sustainable economic growth outpacing the average world, European and Asian GDP growth rates, increasing the competitiveness of the country's economy and its citizens, conquering new niches in commodity and financial markets; the growth of well-being, the quality of life of Russians and the recognition of their role in the global cultural space.

More specifically, the implementation of Russia's national interests in the economic sphere can be expressed as follows: the ability of the economy to function in the mode of expanded reproduction, that is, to ensure GDP growth of at least 7-8 percent per year in the next decade; increasing the competitiveness of the economy not only in the extractive industries, but primarily in the manufacturing industries and increasing the share of innovatively active enterprises by 5-6 times; improving the well-being of the population, which means a steady growth of its real incomes, wages, a faster increase in pensions and benefits; reduction by 3-4 times of the layer of poor people and the formation of the middle class of citizens with an appropriate level of effective demand; the reliability of the banking system and the ability of the consolidated budget to finance the state's social obligations, maintain business activity and high market conditions, and prevent fluctuations in the change in the ruble exchange rate; sufficiency of the money supply and credit resources to ensure high long-term GDP growth rates; increase in the structure of foreign trade turnover of the share of exports of products of manufacturing industries; maintaining the level of imports, especially food, at a safe level (about 25 percent of retail food turnover); Russia's independence in strategically important areas of scientific and technological progress, especially in the field of defense industries, space technology, nuclear industry, mechanical engineering; maintaining a single economic space and preventing excessive differences in the levels of development and well-being of the population of the regions.
The practical experience of different countries, including ours, shows that threats to national security may not manifest themselves in an open and acute form for a long time, but this does not mean that nothing threatens us or that any crisis can be easily overcome. In order to timely prevent threats to Russia's national interests in the economic sphere, it is advisable to constantly monitor indicators of economic security. 19 such indicators have been identified, reflecting the most important areas in the real and financial sectors of the economy, in the social sphere (see Table 1). It is these indicators that are used as threshold values for economic security. They characterize the limiting values, ignoring which hinders the normal course of development of the economy and the social sphere and leads to the formation of destructive trends in the field of production and the standard of living of the population.
Thresholds should acquire the status of quantitative parameters approved or approved at the state level, compliance with which should become an indispensable element of government forecasts and development programs, as well as budgeting. Unfortunately, this did not happen, and there are still no approved quantitative parameters of threshold values.
Table 1 shows that the threshold values of the indicators quite accurately signal the state of Russia's economic security. The situation cannot be characterized as unambiguous, with an assessment of “good” or “bad”. Some of the indicators in 2005 were below the threshold values. This is the inflation rate, budget deficit, public debt. The volume of gold and foreign exchange reserves many times exceeds the limits of the threshold value.
If the level of monetization corresponded to the limit value of the indicator, we can make an unambiguous conclusion about the improvement of the financial situation. However, it is two times lower, which indicates the underdevelopment of the banking sector, the distrust of investors in banks, the insufficient inclination of the population to organized forms of savings, and the weak development of non-cash payments. The economic and political risks in investing are still very high.
The increase in financial and banking reserves occurs due to the infringement of financial opportunities for the development of the real sector of the economy, innovation and social spheres. All indicators signal the unfavorable situation of these sectors of the economy. The share of food supplied by imports in total food resources is much (15 percentage points) above the threshold value, which makes the economy vulnerable to unfavorable developments in the foreign exchange market. Total GDP is well below the threshold. Consequently, in order to achieve the goal of doubling GDP by 2012, it is necessary to significantly accelerate the rate of economic growth.
Unfortunately, the health of the Russian population is much worse than in industrialized countries. In general, according to the integral indicator of health, Russians are in 68th place in the world. The average working capacity of a Russian worker, measured by the number of years of work, loss of working time due to illness and accidents, activity at work, is half that of a US worker.
A significant personal characteristic of human resources is morality. This quality was pointed out by Aristotle in his work "Nicomachean Ethics". During the years of reforms, such negative traits of morality among workers as lack of initiative, aggressiveness, conflict, cynical attitude towards society, the state and the individual, bribery, racketeering, and corruption have developed. Also, its technical and production component is of great importance for ensuring the economic security of the state. It is understood as the ability of the country's industry in the event of a disruption in foreign economic relations or internal socio-economic shocks to promptly compensate for their negative consequences, sustainably carry out expanded reproduction, and satisfy public (including defense) needs. It is closely connected with both material and social factors of production. As a result of significant imports of machinery and equipment to Russia, an increasingly tangible dependence on Western supplies began to take shape. It is especially high in metalworking, metallurgical and chemical equipment. In the event of an aggravation of the economic situation or the unleashing of direct military confrontation, such dependence can lead to significant economic difficulties. That is why it is so necessary to produce high-quality and sufficient quantities of machine-technical products at home. At the same time, an analysis of the data of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation shows that high-tech industries - the production of machine tools, forging and pressing machines, radio-electronic equipment, computers, modern means of communication - is slightly more than 5% of the 1991 level. The share of mechanical engineering in the total volume of industrial output has decreased three times.
The industry of Russia is currently focused mainly on the production of an intermediate product - fuel and raw materials. Industries producing end-use products account for only about two-fifths of industrial production. The fixed assets of industrial enterprises in the real sector of the economy are worn out by more than half, and in the fuel and energy complex, the depreciation is already reaching almost 80%.
The technological component of economic security implies such a state of the country's scientific and technical potential, which guarantees, in the shortest possible time, the independent development of the latest technological solutions that provide a breakthrough in the leading sectors of civil and defense production. Increasing Russia's self-sufficiency in key technologies, building up technological potential based on the latest scientific and technological achievements will undoubtedly strengthen the country's economic security. The mass use of promising technologies will contribute to an accelerated transition of the economy to an intensive development model, a significant change in the export-import structure of the Russian economy, and the elimination of its economic dependence on foreign countries.
In the third millennium, the advanced countries of the world - the USA, the countries of Europe and Japan - are on the verge of a new stage of scientific and technological progress, the introduction of the latest technologies of the 21st century in all spheres of life.
The leading direction in the scientific and technical sphere is the humanization of technical progress, the strengthening of the life-supporting branch of scientific and technical progress, the shift of priorities towards biology, biochemistry, biophysics, medical sciences, information services, i.e. in the direction of those areas of science and technology that improve the quality of life of people.
The second important direction of scientific and technical progress is the reduction of energy intensity and metal consumption of social production. The developed countries have made significant progress along this path, gradually moving to a type of economic growth in which the satisfaction of the production and personal needs of people can be carried out with a smaller specific volume of resources involved in production. The implementation of this direction will contribute to the sustainable development of individual countries and the global economy.
Industrially developed countries pay exclusive attention to the development of information technologies. The development of information networks and satellite communications makes it easy to overcome national borders and makes the life of society more and more global. The development of a complex of the latest information technologies - the Internet - is compared with the invention and spread of printing.
For our country, the challenge of globalization means the need to gradually move away from energy and raw material exports to a more balanced participation by integrating domestic scientific and technological potential into the world economy, exporting science-intensive products and services, and joining strategic alliances.
An important element of the economic security system is the food component, which implies the ability of the agricultural sector of the economy to provide the country's population with food, and industry - with the necessary agricultural raw materials.
Today, the danger of losing the country's food independence is becoming very real. The archaism of agriculture and the food complex of Russia as a whole has sharply aggravated as a result of the chosen version of the agrarian reform. The haste in the destruction of existing structures and economic ties, the aggravation of price disproportions between industry and agriculture, the almost complete opening of the domestic market for food imports - all this undermines the basis for the country's self-sufficiency in food. The marketability of agriculture has declined markedly. The monopoly of agricultural machinery manufacturers, the swelling of intermediary structures, ill-conceived tax and credit policies make agricultural production inefficient. The share of imported food is 30%. According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Food, the share of imports for meat and meat products is 34%, milk and dairy products - 18%, sugar (including raw sugar) - 73%, vegetable oil - 42%, fish and fish products - 50%. In large cities, especially in Moscow and St. Petersburg, the share of many types of imported goods reaches 80%7. These and other data show that the critical food threshold has been significantly exceeded. This can lead to price dictatorship, as well as to the destruction of domestic production, the capture of the Russian domestic market.
The current unfavorable conditions create a real threat of loss of the country's food independence, which can become a fait accompli if the executive authorities and business entities do not take effective measures to overcome it.
The energy component plays an important role in the system of economic security, which involves ensuring the stability of energy supplies for the needs of the national economy and the defense complex. The Russian economy is becoming increasingly fuel and raw materials. At the same time, the energy component can become a constraint on economic growth. The increase in production will cause an increase in domestic fuel consumption. Meanwhile, the fuel industry is currently not ready to significantly increase the volume of its products. Almost all large and medium oil fields are involved in exploitation, they are mostly in the late stage of development. The increase in explored reserves for almost all types of fuel resources did not compensate for production over a long period. For example, in the last 20 years, Gazprom has not invested in the development of large fields, since it was forced to act as a national creditor for the entire Russian economy. The former head of Gazprom, Rem Vyakhirev, recently cited the facts of the terrible financial condition of Gazprom - he is owed $7.5 billion, and his own debt is $4.5 billion, so there is no money to invest in gas production.
We need a clear and transparent structural policy in the fuel and energy complex, which would determine the priorities in the industry, ensuring the economic independence of the country.
The deep energy crisis that hit Primorye last winter convinced us of the need to reform the energy system of the Russian Federation. The energy system of the country, which was formed during the period of the planned-administrative economy, in the conditions of the formation of market, competitive relations in all spheres of society, needs significant modernization and reconstruction. Moreover, this must be done very deliberately, taking into account the accumulated domestic and foreign experience in the interests of the entire national economy.
The information component of economic security implies such a procedure for the mutual exchange of economic, social, scientific, technical and military information within the national economic complex and foreign partners, which will guarantee the proper secrecy of doing business in the interests of the state, society and economic entity.
The information function of the economic security system consists in obtaining by the system as a whole and its elements the information necessary for the implementation of a coordinated and purposeful activity to achieve the set goals.
The requirements for the implementation of this function will be determined by the necessity and sufficiency of the information provided to the consumer in accordance with his requests and needs.
Information danger occurs when the magnitude and probability of possible information damage is greater than the threshold value requiring measures to prevent it, to protect the security object.
The concept of information security is opposite to the concept of information danger and means protection from significant information damage.
In recent years, the importance of ensuring information security in all spheres of public life, including economic ones, has increased. This is due to a number of reasons: the rapid development of the capabilities of information technology and technology, the intensification of economic confrontation between states, transnational corporations and firms, the increasing impact on the public consciousness of various groups of the population, the interests and needs of customers and suppliers.
Informatization of the financial and economic sphere has both a positive and a negative impact on its development. The following facts testify to the negative impact on the economic consciousness and actions of Russian citizens: hundreds of fraudulent financial pyramids, promoted by various television channels, allowed fraudsters to rob millions of gullible Russian citizens, and unscrupulous advertising contributed to the sale of low-quality goods worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
According to experts, the computer is becoming the most active tool of economic struggle and crime. After all, money now is official information about the possession of a certain object of value, fixed on paper or magnetic, electronic media. In Western countries and some regions of Russia, credit cards have become widespread, replacing paper money. Forgery of credit cards, theft of money with the help of computers have taken on the character of a real disaster in the USA, Italy, and some other countries.
Industrial espionage (and counter-espionage) is also developing rapidly. In the US, the losses of private firms due to the theft of trade secrets are estimated at tens of billions of dollars a year. According to experts, hundreds of billions of dollars worth of valuable information about inventions, discoveries, "know-how" has been exported from Russia during the years of reforms.
An analysis of the main elements that make up the economic security of the Russian Federation shows that its threshold values in many cases exceeded the minimum allowable standards. Threats and dangers have gripped the leading sectors of the economy, touched upon the fundamental foundations for ensuring the life of a person and the state. All is not yet lost. But it is necessary to quickly develop an effective strategy for ensuring Russia's economic security.

Many threshold parameters of economic security were developed on the basis of domestic statistics and were agreed in 2000 with the relevant ministries and departments. They take into account the relevant parameters of the EU countries and can be used to assess the international global security of Russia. For a more detailed assessment of this, it is proposed to use a system of indicators that characterize Russia's place in the world economy: in territorial space, in population, in reserves and extraction of minerals, in forest resources, in financial and banking assets, in exports and imports, in global GDP. and GDP per capita. These indicators, in comparison with the United States, the Eurozone, Japan and the global economy as a whole, are presented in Table 2. It is enough to look at the table to understand that they indicate deep disproportions between indicators characterizing, on the one hand, territorial space, natural resource potential and its use, and on the other - the financial potential, GDP, international trade (export-import), the level and quality of life. Our natural resource potential is many times greater than the financial potential, GDP, exports and GDP per capita. Many disproportions did not develop overnight; in the last 15 years they have worsened, especially in terms of social indicators.
The threshold values of the levels of economic security of the Russian Federation given (in Table 1) in relation to the beginning of the 21st century, unfortunately, have not changed much today. If we evaluate the level of public debt, the weakening of scientific and technical potential, the destruction of the industrial foundations of the national economy, regional economic disintegration, a sharp differentiation in income and an increase in unemployment, the occurrence of emergencies, the outflow of financial resources abroad, then according to these indicators, the economic security of the Russian Federation continues to decline.
Based on the results of 2008, we have to state that Russia failed to "wait out the storm in a safe harbor." The crisis has fully affected all spheres of our economy, serious problems have arisen in the real sector, and in the financial and social spheres. By the beginning of 2009, the Russian economy entered an industrial recession, accompanied by a depreciation of the ruble, rising unemployment and suspension of investment programs. The national financial system turned out to be unprepared for the global shock of 2007-2008, and Russia followed the path of more developed countries - through the financial crisis to industrial decline. The domestic economy is apparently experiencing its first full-fledged market crisis, aggravated by the weakness of the financial system, which easily "imported" the shock from abroad.
Since the end of 2008, the Russian economy has been moving into a qualitatively different mode of functioning. The key parameters of this period will be associated with relatively low oil prices (“loss of rent”), falling industrial output and rising unemployment. Although the impetus for the start of the current processes was the events in the world financial markets and the recession in developed countries, the degree of this influence was associated with internal causes and the structure of the economy, meaning the strong dependence of the primary industries on exports, an undeveloped private financial system, and unresolved problems in economic policy. .
World GDP is projected to fall in 2009 by almost half a percentage point, the decline in GDP in the US could reach 2.6-2.7 percent, in Japan - up to 5-5.8. The EU economy may shrink by 2.1-2.5 percent. Practically in all countries the incomes of the population will decrease significantly. Positive growth rates will continue in India and China, but even there they will fall by almost half compared to previous years. In Russia, GDP could also fall by more than 2%.
The impact of the global economic crisis on Russia has its own characteristics associated with the accumulated deformations of the economic structure, the underdevelopment of a number of market institutions, including the financial system.
The main problem of the Russian economy is still a very high dependence on the export of natural resources. In recent years, the state has done a lot in terms of developing the processing industry, services, transport, but oil and gas exports, exports of other raw materials and metals still play a key role in the economy. As a result of the crisis, not only prices, but also demand fell for almost all Russian raw material exports.
The second problem is the lack of competitiveness of non-resource sectors of the economy. When problems began in the commodity sectors, there were no industries that could "support" the economy. Moreover, problems from primary industries began to spread to related ones.
The result is a significant drop in industrial production, an increase in the number of unemployed, a decrease in wages and a number of other negative consequences. This is especially noticeable in those cities and regions in which there are large raw materials enterprises, and which, in the conditions of constant growth in prices for raw materials, were very well off.
The third problem is the underdevelopment of the financial sector and banks. Many Russian enterprises, especially rapidly developing in recent years, entering foreign markets, could not count on financing from within the country. Credits of the Russian banking system were more expensive, credit terms were shorter. Companies were forced to borrow abroad. During the crisis, foreign capital markets became inaccessible to enterprises.
In recent years, the national economy has developed largely due to external sources - high prices for raw materials, "cheap" loans from foreign banks, now Russia needs to find internal sources of growth to overcome the crisis and ensure long-term sustainable development.
In October-December 2008, when the global economic crisis began to have a serious impact on the Russian economy, the Government began implementing anti-crisis measures. The anti-crisis measures of the first stage made it possible to prevent the growth of the crisis, its transition into forms that threaten the economic security of Russia. Ensuring economic security, of course, implies not only the classification of interests, threats, criteria and thresholds, but also mechanisms for protecting the national interests of the country in the field of economy.
In 2009 and in subsequent years, the Government of the Russian Federation intends to significantly intensify the use of all available tools of economic and social policy in order to prevent irreversible destructive processes in the economy that undermine the country's long-term development prospects, while also ensuring the solution of strategic tasks.
To overcome the economic crisis on the part of the state, the responsibilities of the federal executive authorities and authorities of the subjects of the Federation to ensure the economic security of Russia must be clearly defined, which must be carried out at all stages of the economic activity of the state: when determining the concept and main directions of economic policy, transforming the financial and banking system of the country, analysis of the course and forecast of socio-economic development, development and approval of the state budget, adoption of the most important regulations and government decisions on economic issues, in the preparation and examination of laws.
It is necessary to move from developing a national security concept to a long-term national security strategy. As a separate document, it is expedient to prepare and approve a long-term economic security strategy, given that the corresponding concept, adopted in 1996, no longer reflects modern realities. These documents should form the basis of a long-term strategy for the socio-economic development of Russia until 2025, as well as the corresponding programs of the constituent entities of the Federation.
It is not possible to do without the creation of a special body responsible for the development and implementation of long-term strategies. For all subjects there are a number of common security problems, this is, first of all, the development of infrastructure in the energy sector, transport system, information, communications, financial and banking system. There are many disproportions in these segments of the economy that threaten Russia's long-term sustainable development. Solving these problems requires coordination, cooperation and cooperation.
2.3. Globalization as a Threat to Economic Security
In a narrow sense, globalization is the process of an avalanche-like formation of a single global financial and information space based on new, mainly new computer technologies. In a broader sense, this term refers to the process of formation and development of transnational monopolies that have an overwhelming impact on the independent development of countries outside the G 7. Ensuring the economic security of the Russian Federation and its priorities is the cornerstone of Russia's integration into the world economy. Only with a clear development and strict adherence to an economic security strategy can Russia take its rightful place in the system of the global economic space.
For Russia, as a federal multinational state with a large territory and difficult socio-economic and climatic conditions, the problem of economic security is largely regional in nature and specific.
The state of the Russian economy is characterized by the continued danger of its regionalization. This is manifested in the rupture of traditional economic ties, the crisis of the federal transport and energy infrastructures, the crisis of mutual settlements, which paralyzes interregional economic ties.
As a result, the economic systems of remote Russian regions are attracted to regional foreign centers of economic influence (Kaliningrad region - to Germany and Poland; Primorye and Sakhalin - to Japan; Transbaikalia, Eastern Siberia - to China). In the future, a situation is possible when the degree of integration of these regions into the economic systems of foreign countries will exceed their integration ties with the Russian economy.
In connection with the course of disintegration processes in the economies of the former Soviet republics, attempts by foreign political forces to subordinate the economies of these republics to their own political, economic and military interests (Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova, Ukraine) are noticeable. These actions cause direct damage to the interests of the Russian Federation.
Repulsing the aggression of international terrorists and our own separatists in the North Caucasus is associated with large financial and material costs. The actions of the separatists affect not only the military, but also the economic security of the state.
Along with the above-mentioned features of ensuring economic security, attention should also be paid to the information and technical component of the globalization process. There is a gradual process of establishing information control of the leading Western countries over other states, all spheres of their activity. He received the name "indirect wars" or "indirect impact."
Obtaining a variety of information, its generalization and analysis make it possible to predict the development of the situation in the country, as well as to develop specific measures of external political and economic impact on a particular state.
In addition, the use of modern electronic information systems that provide individual access to each person participating in the economic process can, through daily impact, change the consciousness and ideas of entire social groups. There is a real possibility of programming people's behavior through the formation of a false idea of the state of affairs, mental pressure, changes in value orientations.
The introduction of modern electronic information systems makes it possible to establish control over the financial and economic activities of every citizen, enterprise and organization.
The use of global information networks creates the necessary conditions for the implementation of a whole range of measures of covert impact on the economy, while providing significant difficulties in identifying the source of the threat and the moment of the start of aggressive actions.
On the other hand, the use of electronic automation tools in the daily practice of financial structures that allow remote operations has made it possible to carry out such actions in order to carry out various kinds of theft. The spread of automated information networks in our country will cause an intensive increase in crime in this area, which, if not properly countered, will be capable of causing significant economic damage.
The negative trends accompanying the development of informatization are largely restrained by a certain lag in equipping domestic enterprises and organizations with electronic computers and modern means of communication. Therefore, against the backdrop of the growing globalization process, there is a certain reserve of time for solving the above problems in the Russian economy. In conclusion, here is a quote from the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation:
The Russian Federation intends to resolutely and firmly ensure its national security. The created legal democratic institutions, the established structure of the state authorities of the Russian Federation, the broad participation of political parties and public associations in the implementation of the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation are the key to the dynamic development of Russia in the 21st century.
2.4. The main directions of increasing the economic security of the country
Main tasks and measures in the field of ensuring national security
1. In the National Security Concept of the Russian Federation, approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of December 17, 1997 N 1300 (as amended by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of January 10, 2000 N 24), section IV Ensuring the national security of the Russian Federation defines the following main tasks :
2. Timely forecasting and identification of external and internal threats to the national security of the Russian Federation.
3. Implementation of operational and long-term measures to prevent threats.
4. Ensuring the sovereignty and territorial integrity of the Russian Federation, the security of its border area.
5. The rise of the country's economy, the implementation of an independent socially oriented economic course.
6. Overcoming the scientific, technical and technological dependence of the Russian Federation on external sources.
7. Ensuring on the territory of the Russian Federation the personal security of a person and a citizen, his constitutional rights and freedoms.
8. Improving the system of state power of the Russian Federation, federal relations, local self-government and the legislation of the Russian Federation, the formation of harmonious interethnic relations, strengthening order and maintaining the socio-political stability of society.
9. Ensuring strict observance of the legislation of the Russian Federation by all citizens, officials, state bodies, political parties, public and religious organizations.
10. Ensuring equal and mutually beneficial cooperation, primarily with the leading countries of the world.
11. Raising and maintaining the military potential of the state at a sufficiently high level.
12. Strengthening the non-proliferation regime for weapons of mass destruction and their means of delivery.
13. Taking effective measures to identify, prevent and suppress intelligence and subversive activities of foreign states directed against the Russian Federation.
The main tasks and measures in the internal economic activity of the state.
1. Legal support for reforms and the creation of an effective mechanism for monitoring compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
2.Strengthening state regulation in the economy.
3. Taking the necessary measures to overcome the consequences of the economic crisis, the preservation and development of scientific, technical, technological and industrial potential.
4. Transition to economic growth while reducing the likelihood of man-made disasters.
5. Increasing the competitiveness of domestic industrial products, improving the well-being of the people.
6. Elimination of deformations in the structure of the economy with the provision of advanced growth in the production of science-intensive products.
7.Support for industries that form the basis of expanded reproduction, with the provision of employment.
8.Strengthening the state. support of investment and innovation activity.
9. Strengthening the banking system.
10. Providing enterprises with access to long-term loans, creating real targeted programs for industrial restructuring.
11.Advanced development of competitive industries, expansion of the market of high technologies. To this end, measures should be taken to stimulate the transfer of new military technologies to civilian production, a mechanism should be introduced to identify and develop progressive technologies, the development of which will ensure the competitiveness of Russian enterprises in the world market.
12. Concentration of financial and material resources in the priority areas of science and technology.
The main measures to achieve the goals set are formulated as follows.
1. The most important measure is to support leading scientific schools, accelerate the formation of a scientific and technical reserve and a national technological base,
2. Attracting private capital, including through the creation of funds and the use of grants, the implementation of development programs for territories with high scientific and technical potential,
3. Creation and support of the state infrastructure that ensures the commercialization of research and development with simultaneous protection of intellectual property at home and abroad,
4. Development of a public network of scientific and technical information.
5. Maintenance of life and economic development of the crisis areas of the North.
Even a brief analysis of modern threats allows us to conclude that there is a need for a radical change in approaches to ensuring the country's economic security. The growth of these threats is largely due to miscalculations in the choice of strategy and tactics of Russian reforms. I believe that all economic transformations should proceed from such a concept in order to prevent Russia from losing its national and economic independence.
In the course of reforms, any transformations in society and the economy, during the economic crisis, the economy is especially vulnerable to threats to economic security. As world experience shows, during such periods, the instability of the economy increases, and its normal functioning is disrupted. We also had this problem. To resolve it, the following measures are proposed:
· The state should take control of the development of the economy, because the United States, while preaching liberalization in other countries at home, is pursuing a very tough policy on import tariffs, protecting its own market, and supporting agricultural producers. And it was the state that, with its state order and a number of other measures, pulled the US economy out of the depression of the 1930s and is trying to do the same at the moment.
· Under no circumstances should we join the WTO now, stronger foreign competitors will simply crush Russian producers. Another reform of customs tariffs is needed, with the aim of protecting domestic producers, and not opening the market for foreign companies to enter.
· An important task is to restore ties with the Warsaw Pact countries and the CIS countries, it is necessary to return sales markets for the Russian economy, it is desirable to create trade unions such as NAFTA.
· Strict measures are needed to prevent the illegal export of capital abroad.
· The stock market, in its current form, is highly dependent on the speculative game of non-residents. This is a kind of casino. It is necessary to make the Russian market more competitive, its architecture less distorted, to finally introduce tax incentives for investment in securities and start creating a "financial platform" Russia "". Emphasis should be placed on the development of the corporate bond market with a long maturity.
· A downturn in the world economy is expected in the near future, so it is necessary to develop the domestic Russian market and increase the solvency of the population.
· Property management should be improved, both in the private and public sectors. Do not privatize profitable state-owned enterprises for a penny, as is happening now. And fire those managers who advise it.
· It is necessary to conduct a full investigation into the privatization of the largest Russian enterprises in order to nationalize the enterprises privatized with major violations and inefficiently managed by the real owners, and for efficient enterprises with a transparent financial structure, to resolve all small violations of the law and close cases. Thus, the owners will be firmly convinced that this is their property and the state will no longer make claims for old offenses.
· Reduce the current bias of the national economy in favor of the export-oriented sector of the economy by placing large-scale state orders in the military-industrial complex, nuclear, machine-building, aviation and aerospace, chemical and pharmaceutical, electronic industries, and a number of other areas that ensure the creation of goods with high added value. It is necessary to ensure maximum transparency of the entire investment process, for constant monitoring and control.
· Create tax incentives for enterprises cooperating in their activities with enterprises from other regions. Moreover, doing this is smarter than the created benefit for small businesses in the form of the abolition of VAT for enterprises with a quarterly turnover of less than one million rubles. After that, other enterprises simply refused to work with beneficiaries, due to the non-reimbursement of VAT by the state.
· Reconsider the restructuring plan for RAO UES, which in its present form only leads to a multiple increase in electricity prices, a break in the common energy space and the removal of the most economically profitable power plants into the ownership of management and large foreign energy companies.
· By all means to increase the well-being of the population, through an increase in wages for state employees, recognition by the state of debt to citizens and enterprises, amnesty for the debts of the latter.
· Building a state policy in the field of interaction with national TNCs, by acquiring a blocking stake in them for the provision by the state of equipment, land plots and certain infrastructure.
Conclusion
The main component of economic security is the economic development of the state. World experience shows that GDP growth and low inflation are by no means always a characteristic of improving the welfare of the population and increasing the competitiveness of the national economy.
In the course of this course work, the directions of the economic policy of the state and the strategy of the economic policy of Russia were studied. The state economic policy sets as its main goal to observe the interests of the state, society as a whole, socially unprotected segments of the population, while not forgetting the rights and freedom of the individual. The state ensures that, in conditions of economic freedom, public interests are not infringed upon by the aspirations and interests of individual regions, social groups, industries, monopolies, entrepreneurs, and individuals. State regulation is also aimed at protecting the interests of future generations, protecting the environment, preventing its pollution, and the death of nature.
The paper also attempts to describe some of the most serious problems of the country's economic security. To solve the latter, the Russian government needs to create a concept of national security and national development, an integral part of which should be economic security and economic development.
It is not possible to do without the creation of a special body responsible for the development and implementation of long-term strategies. For all subjects there are a number of common security problems. This is, first of all, the development of infrastructure in the energy sector, transport system, information, communications, financial and banking system. There are many disproportions in these segments of the economy that threaten Russia's long-term sustainable development. Solving these problems requires coordination, cooperation and cooperation. When choosing an economic development path, one should not blindly follow the lead of representatives of a potential adversary - TNCs, the IMF, the EBRD, economists of various levels like Andrei Illarionov.
It's time to become effective owners of your country, your people. There is no more time for throwing, today or never.
List of used literature
1. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 On the state strategy of economic security of the Russian Federation (Basic provisions) // Reference legal system "ConsultantPlus";
2. Bogomolov V.A. Economic security: Textbook for universities / V.A. Bogomolov - M.: Unity, 2006. - 303 p.;
3. Glazyev S. The basis for ensuring the economic security of the country / S. Glazyev // Russian Economic Journal. 1998. - No. 8.- S. 27-29;
4. Govorova N. Economic policy: strategy and tactics / N. Govorova // Problems of theory and practice of management. 2006. - No. 4. - S. 25-37;
5. Dmitriadi G.M. Security of Russia and its economic policy [Text] / G.M. Dmitriadi - M.: Lenand, 2005. - 218 p.;
6. Ershov M. The most important mechanisms of economic policy / M. Ershov // World economy and international relations. - 2004. - No. 6. - S. 3-12;
7. Illarionov A.I. Criteria of economic security / A.I. Illarionov // Questions of Economics. 2004. - No. 10. - S. 34-37;
8. Kudrin A.L. Economic policy and the federal budget of 2006 / A.L. Kudrin // Finance. - 2006. - No. 2. - S. 3-8;
9. Plisetsky D. Economic security: monetary and financial aspects / D. Plisetsky // World economy and international relations. 2004. - No. 5. - S. 28-32;
10. Senchagov V.K. Economic security of Russia: General course: Textbook [Text] / ed. VK. Senchagova - M.: Delo, 2005. - 896 p.;
11. V. Senchagov, On the essence and foundations of Russia's economic security strategy. "Economic Issues" No. 1, 1995 www.russia-today.ru/2007/no_06/06_reflections.htm;
12. The Government of the Russian Federation approved the plan for the development of the economy until 2010 [electronic resource] / Access mode // www.top.rbc.ru/economics/19/04/2007/98624.shtml.
13. Materials of the State Committee of the Russian Federation on Statistics
14. Materials of the Center for Macroeconomic Analysis and Forecasting, INP RAS
15. http://russia-today.ru/2007/no_06/06_reflections.htm - V. Senchagov How to ensure the economic security of Russia / V. Senchagov // Russian Federation today. 2007. - No. 6.
L. Abalkin, Economic security of Russia: threats and their reflection. "Economic Issues" No. 12, 1994
V. Senchagov, On the essence and foundations of Russia's economic security strategy. "Economic Issues" No. 1, 1995
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)" // RG. 1996. May 14; SZ RF. 1996. April 29. No. 18. Art. 2117.
Economic threats are understood as a set of conditions that infringe on the economic interests of society, disrupting the reproductive process
The concept of national security of the Russian Federation. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 24, 10.01.2000
“Russia – Asia-Pacific. The problem of currency regulation and economic security”, ed. Rudko-Selivanova V.V., Vladivostok "Dalnauka", 1998
- ECONOMY
- ECONOMIC SECURITY
- NATIONAL SECURITY
- EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL THREATS
The need for security is the main, fundamental need, both of the life of an individual, and of the state and society. In the conditions of the formation of a market economy, the sphere of safe existence has narrowed so much that the constant and massive dissatisfaction of this need has a negative impact on the development of the functioning of citizens, families, organizations, the state and society as a whole, aggravating the crisis state of all spheres of its life.
- The leaders of cryptocurrencies in 2018, their impact on the financial market and the real sector of the economy
- Bank deposit insurance and its role in improving the efficiency of a commercial bank
- Factors directly affecting the professional judgment of an accountant
The first mention of security was made in the 28th chapter of the book of Ezekiel of the Old Testament of the Bible. Translated from the Greek, the term "security" means "to control the situation." In a broad scientific sense, security is understood as the protection of natural-physiological, socio-economic, ideal-spiritual and situational needs for resources, technologies, information and moral ideals necessary for the life and development of the population. Economic security occupies a special place among the various types of security. This is due to the fact that all types of security one way or another cannot be sufficiently implemented without economic support.
The urgency of the problem of economic security became real in the era of the formation of capitalist relations and national states in the 17th - 18th centuries. It was then that in the countries of European civilization the idea was formed and developed that the state has as its main goal the general welfare and security.
Economic security is the basis of the country's national security.
The term "national security" first appeared in the United States. The American approach is based on understanding national security through national resilience - a state that provides sufficient economic and military power to withstand the dangers and threats to its existence, emanating both from other countries and from within one's own country.
National economic security- this is the protection of the country's economy from internal and external adverse factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the economy, undermine the achieved standard of living of the population.
In Russia, the development of an economic security strategy began with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 311-r dated March 9, 1994, according to which the Ministry of Economy of Russia, with the participation of federal executive authorities and together with the interdepartmental commission of the Security Council on economic security, was instructed to develop the "Basic provisions of the strategy in the field of ensuring economic security of the Russian Federation".
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation "On the State Strategy for the Economic Security of the Russian Federation (Basic Provisions)" was signed on April 29, 1996.
In this Decree, economic security was defined as the ability and readiness of the economy to provide decent living conditions, the military-political stability of society and the integrity of the state, to resist the influence of internal and external negative factors and to be the material basis of national security.
Guarantees of economic security are a necessary condition for ensuring the stable development of the national economy.
Threats to economic security- such phenomena and processes that negatively affect the economic condition of the country, limit the economic interests of the individual, society, state, create a danger to national values and the national way of life.
Threats to economic security are divided into internal and external.
Internal Threats - this is the inability to self-preservation and self-development, the weakness of the innovative principle in development, the inefficiency of the system of state regulation of the economy, the inability to find a reasonable balance of interests in overcoming contradictions and social conflicts in order to find the most painless ways for the development of society.
External threats- this is a change in the conjuncture of world prices and foreign trade, sharp fluctuations in the exchange rate of the ruble, an excess of capital outflow over its inflow (foreign investment); excessive import dependence, overload of exports with commodities.
The most dangerous threats to the economic security of the Russian Federation that have been in effect over the past 10 years:
- Loss of production potential due to high depreciation of fixed assets. The wear and tear of machinery and equipment, although it decreased after the financial crisis of 1998, is at a critical level, amounting to more than 60%.
- External debt, the danger of an aggravation of the financial crisis. The total amount of external debt, according to the balance of payments, in 2003 amounted to 182.4 billion dollars. At the moment, the federal budget is in surplus and there is no external debt.
- Unstable investment activity. In 2000, for the first time, there was a significant increase in investments - 17.4%. However, in 2001 the rates dropped sharply to 10%, in 2002 to 2.6%, and in 2003 they rose again to 12.5%.
- Low competitiveness of products. The share of imports in the resources of retail trade decreased from 48-52% in 1994-1998. up to 35% by the beginning of 2000. However, later the effect of import substitution was exhausted. Domestic products again ceased to be competitive. In 2001, the share of imports in the resources of retail trade again amounted to 41%, in 2002 - 4 3 , in 2003 - 44%.
- The high level of poverty of the population and the low quality of life of most of the Russian people. The proportion of the population with incomes below the subsistence level decreased significantly in 2003 compared to 2000 (36%), but still amounts to more than 20% and is more than 2 times higher than the threshold value. The ratio of the incomes of the 10% of the most wealthy to the incomes of the 10% of the least wealthy strata of the population has remained at the level of 14 in recent years.
- Capital flight. According to expert estimates, unlicensed export of capital in 1992-2000. amounted to over $200 billion.
The constituent structural elements of the economic security of the state are: human resources, technical and production, technological, food, energy, management and information elements.
Undoubtedly, the main element that ensures the economic security of any country is human resources not only in quantitative but also in qualitative terms. Unfortunately, the health of the Russian population is much worse than in industrialized countries.
Of great importance for ensuring the economic security of the state is its technical and production component. As a result of a significant increase in imports of machinery and equipment to Russia, an increasingly tangible dependence on Western supplies began to take shape.
Technological component economic security implies such a state of the scientific and technical potential of the country, which guarantees in the shortest possible time the independent development of the latest technological solutions that provide a breakthrough in the leading sectors of civil and defense production
Developed countries have made significant progress towards reducing the energy and metal intensity of social production, gradually moving to a type of economic growth in which the production and personal needs of people can be met with smaller specific volumes of resources involved in production.
Industrialized countries pay exclusive attention to the development information technologies. The development of information networks and satellite communications makes it easy to overcome national borders and makes the life of society more and more global.
An important element of the economic security system is food component, assuming the ability of the agricultural sector of the economy to provide the population of the country with food, and industry - with the necessary agricultural raw materials. Today, the danger of losing the country's food independence is becoming very real. The monopoly of agricultural machinery manufacturers, the swelling of intermediary structures, ill-conceived tax and credit policies make agricultural production inefficient.
The role of economic security in the system energy component, which involves ensuring the stability of energy supplies for the needs of the national economy and the defense complex. Let us emphasize once again that the Russian economy is increasingly acquiring a fuel and raw material orientation, which is a negative trend. At the same time, the energy component can become a constraint on economic growth.
In order to create a national structure of its economy that is adequate to market requirements, Russia must go through the painful path of determining its priorities in all areas and at all levels of society and economy. After all, it should not just join the modern world economy, but predict its role and place in the global division of labor.
It is to be hoped that the problems of economic security will take their rightful place in Russia's national security system, and that the reformist policy will be guided by the Concept of National Economic Security, which will probably be developed soon. I hope that its implementation will be carried out quickly, competently and will not entail any negative consequences, and Russia will again take its place among the developed countries.
Bibliography
- STATE STRATEGY OF THE ECONOMIC SECURITY OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION (Basic Provisions) approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of April 29, 1996 No. 608 [Electronic resource] - access mode: http://www.scrf.gov.ru/documents/23.html
- Poverty Assessment Report of June 28, 2004: Department for Combating Poverty and Economic Management Region of Europe and Central Asia [Electronic resource] - access mode: http://www.credit-union.ru/files/materials/17/PAR_062304_Rus. pdf
- DOCTRINE OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF RUSSIAN SCIENCE (APPROVED BY THE DECREE OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION OF JUNE 13, 1996 N 884): [Electronic resource] - access mode: http://infopravo.by.ru/fed1996/ch04/akt17487.shtm
- Science Indicators: 2009; Statistical collection. - M.: SU-HSE, 2009 - 352s.
- The concept of long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the period up to 2020 (Approved by the Government of the Russian Federation on November 17, 2008 No. 1662-r): [Electronic resource] - access mode: http://www.ifap.ru/ofdocs/rus /eng006.pdf
- Korzhov G.V. "Economic Security of Russia: Foreign Relations". Moscow: Informdinamo, 1996; page 9.
- Lisichkin V.A. Russia under the rule of a plutocracy / Lisichkin V.A., Shelepin L.A. - Algorithm, 2003 - 290s.
- National innovation system and state innovation policy of the Russian Federation. Background report to the OECD review of the national innovation system of the Russian Federation. - M., 2009-210s.