The act of conservation of the construction object sample. Accounting for the conservation of fixed assets. When carrying out conservation measures, special attention should be paid to
Conservation is a set of measures designed to ensure the safety and serviceability of a fixed asset during its downtime. At the same time, the organization can, but is not obliged to transfer the idle operating system to conservation.
Decor. The decision on conservation is made by order of the head of the organization. In this order, it is necessary to indicate the conservation period and list the activities that need to be carried out to transfer the OS to conservation p. 63 of the Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets. After these activities are carried out, an act should be drawn up on the transfer of the OS to conservation. The act must indicate:
- OS transferred to conservation;
- date of transfer of fixed assets for conservation;
- activities that were carried out to transfer the fixed assets to conservation;
- the cost of these activities.
This act, approved by the head of the organization, will be the primary document in order to:
- take into account the cost of conservation in the costs;
- to suspend depreciation for fixed assets transferred to conservation for more than three months.
The reopening of the fixed assets is also formalized by an act approved by the head of the organization.
VAT. If fixed assets are used in activities subject to VAT:
- input VAT on goods (works, services) purchased for fixed assets conservation is deductible paragraph 1 of Art. 172 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the input VAT previously accepted for deduction on fixed assets transferred to conservation is not restored Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 06/20/2006 N ShT-6-03 / [email protected] .
Property tax. During the conservation period, the cost of fixed assets is not excluded from the base for paragraph 1 of Art. 374, pp. 1, 2 tbsp. 375 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There is only one exception: if the law of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation provides for tax exemption for mothballed fixed assets and the organization complies with the conditions for granting this benefit.
income tax. Non-operating expenses include costs Letter of the Ministry of Finance of September 15, 2010 N 03-03-06 / 1/590:
- for conservation - on the date of approval by the head of the organization of the act of conservation;
- for the maintenance of mothballed fixed assets (including protection) - on the last day of the month in which these costs were incurred;
- for re-preservation - on the date of approval by the head of the organization of the act on re-preservation of the fixed assets.
Property tax calculated from the value of mothballed fixed assets is taken into account in other expenses Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 22.08.2012 N ED-4-3 / [email protected] .
If the operating system for which it was applied is preserved, then it is not necessary to restore it when transferring to conservation.
paragraph 2 of Art. 322 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
USN. Expenses for mothballing, re-mothballing, as well as for the maintenance of mothballed fixed assets are not included in tax expenses.
If fixed assets are transferred for conservation for a period of more than three months, the cost of which has not yet been fully taken into account in the costs, then the inclusion in the costs of the costs of acquiring this fixed asset is suspended for the period of conservation Letters of the Federal Tax Service of December 14, 2006 N 02-6-10 / [email protected], Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated 18.01.2007 N 18-03/3/ [email protected] .
In accounting the object transferred to conservation continues to be listed as part of the fixed assets.
For fixed assets mothballed for three months or less, depreciation during the mothballing period is charged at.
For fixed assets mothballed for a period of more than three months clause 23 PBU 6/01:
- from the first day of the month following the month of transfer to conservation, depreciation is terminated;
- from the first day of the month following the month in which the fixed asset was reactivated, depreciation is resumed in the same amount as before conservation.
OS conservation postings
Sample order for the transfer of fixed assets for conservation
Sample act on conservation of fixed assets
Proper documentation of conservation is a prerequisite for recognizing the costs of its implementation when calculating corporate income tax. Such a decision is made by order of the head of the company. The document must indicate the conservation period, list the activities that need to be carried out (clause 63 of the Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets). After all these operations have been carried out, an appropriate act should be drawn up. Its unified form does not exist, so the document is drawn up in an arbitrary form. The act is signed by the members of the commission and approved by the head. Do not forget to indicate in the document the economic feasibility of conservation. In addition, the act must indicate: the name of the OS itself, transferred to conservation; the date of the transfer, the activities that were carried out to “freeze” the funds, and the amount of costs incurred.
The finished primary document will be the basis for taking into account the costs
for conservation in expenses, as well as to suspend depreciation on fixed assets.
Separate sub-account
After the manager signs the order and approves the act, you can transfer fixed assets to conservation mode. At the same time, the object continues to be listed in accounting
as part of fixed assets, it remains on account 01 on a separately created sub-account "Fixed assets for mothballing".
Depreciation
Let me remind you that depreciation refers to expenses for ordinary activities, regardless of the results of the organization's work and is reflected in the accounting of the reporting period in which it is accrued (clause 5, paragraph 5, clause 8, clause 16 PBU 10/99). For a fixed asset mothballed for three months or less, depreciation during the downtime is charged
in the usual way. If the OS is “frozen” for a period of more than three months (clause 23 PBU 6/01, clause 63 of the Methodological Instructions dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n), then from the first day of the month following
after the month of transfer to conservation, depreciation is terminated.
Maintenance costs
Keep in mind: the cost of maintaining a fixed asset during the period of suspension of its operation does not increase the initial cost of fixed assets, this follows from paragraph 14 of PBU 6/01. These expenses refer to the period when the object is not involved in production activities. Consequently, they are not taken into account when forming the cost of production. In addition, these expenses are recognized as other expenses and are reflected in the accounting in the month of their implementation on the debit of account 91, subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses”. Postings for the conservation of fixed assets will be as follows:
Debit 01 sub-account "Fixed assets for conservation"
Credit 01 sub-account "Fixed assets in operation"
- OS "frozen";
Debit 91/2 Credit 10 (60, 70, 69)
- reflected the cost of conservation;
Debit 01 sub-account "Fixed assets in operation"
Credit 01 sub-account "Fixed assets for conservation"
- OS is reopened.
Input VAT
Now let's look at taxation. If fixed assets are used in activities subject to VAT, then the “input” tax on goods (works, services) purchased for conservation is deductible (clause 1, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, VAT previously accepted for deduction on funds transferred for conservation is not restored. The Federal Tax Service of Russia adheres to this position in a letter dated June 20, 2006 No. ШТ-6-03 / [email protected]
Benefit on property
During the conservation period, the value of fixed assets is not excluded from the property tax base, regardless of how the tax is calculated - based on the cadastral or book value (clause 1 of article 374, clauses 1, 2 of article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is only one exception: if the law of the subject of the Russian Federation provides for tax exemption for mothballed fixed assets.
income tax
According to subparagraph 9 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code, to calculate income tax
the following expenses are taken into account in non-operating expenses: for conservation (as of the date of approval by the head of the organization of the act on “freezing” fixed assets), for the maintenance of mothballed fixed assets (including repair and protection - on the last day of the month in which
these costs are incurred). for re-preservation (as of the date of approval by the head of the organization of the act on re-preservation of the fixed assets).
The above rules were announced by the Ministry of Finance in a letter dated September 15, 2010
No. 03-03-06/1/590. Property tax calculated from the value of mothballed fixed assets is taken into account in other expenses (clause 1 clause 1 article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Federal Tax Service announced this in a letter dated August 22, 2012 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected]
With USN
The costs of mothballing, re-mothballing, as well as the maintenance of fixed assets in the tax expenses of "simplifiers" are not taken into account. If fixed assets are transferred for a “freeze” for a period of more than three months, the cost of which has not yet been fully taken into account in expenses, then the inclusion in expenses of the costs of acquiring this fixed asset is suspended for the period of conservation (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 14, 2006 No. 02-6-10 / [email protected], Federal Tax Service for Moscow dated January 18, 2007 No. 18-03 / 3 / [email protected]).
EXAMPLE
The organization acquired under a sale and purchase agreement and put into operation in May 2016 production equipment. Its contractual value is 944,000 rubles. (including VAT 144,000 rubles). The equipment belongs to the third depreciation group. The useful life is 38 months (based on the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 1, 2002 No. 1).
Due to a temporary decrease in orders at the end of May 2016, the OS object was transferred
by decision of the head for conservation for more than three months from June 1 to September 30, 2016.
Depreciation is charged on a straight-line basis. Income and expenses are determined on an accrual basis. Then, based on the established useful life (38 months), the monthly depreciation amount will be 21,052.63 rubles. (800,000 rubles / 38 months). Accrual starts on the first day of the month following the month in which the object was accepted for accounting, in this case, from June. At the same time, the accrual of depreciation deductions when transferring an asset to fixed assets by decision of the head for conservation for a period of more than three months is suspended. In this case, the object was mothballed by decision from June 1 to September 30, 2016. Therefore, depreciation for the period June-September 2016 is not charged. And starting from October, depreciation on the OS object is accrued in the generally established manner. In accounting, the accountant should make the following entries:
In May 2016:
Debit 08 Credit 60
- 800,000 rubles, expenses for the purchase of equipment are reflected;
Debit 19 Credit 60
- 144,000 rudders, VAT shown by the equipment supplier is reflected;
Debit 68-VAT Credit 19
- 144,000 rubles, accepted for deduction of VAT presented by the equipment supplier;
Debit 01 "OS in operation" Credit 08
- 800,000 rubles, the purchased equipment is reflected in the fixed assets;
Debit 60 Credit 51
- 944,000 rubles, payment for equipment was transferred to the supplier.
In June 2016:
Debit 01 “OS on conservation” Credit 01 “OS in operation”
- 800,000 rubles, reflects the initial cost of equipment transferred to conservation.
After conservation:
Debit “OS in operation” Credit 01 “OS on conservation”
- 800,000 rubles, the initial cost of the equipment is reflected in the composition of the fixed asset in operation.
Starting October 2016 for 38 months:
Debit 20 (26.44) Credit 02
- 21,052.63 rubles, depreciation on equipment has been charged.
Selling an object
Since the object transferred for conservation for a period of more than three months is excluded from the depreciable property, it refers to other property. Therefore, the income from its sale can be reduced by the price of its acquisition and other costs associated with the purchase. However, the Federal Tax Service in a letter dated January 12, 2016 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] pointed out the fallacy of this approach. Officials explained that in this case, the cost of purchasing fixed assets will be counted as expenses twice: through the depreciation mechanism and when selling the fixed assets. And this is unacceptable
by virtue of the interpretation of paragraph 5 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let me remind you: the announced norm stipulates that the amounts reflected in the company's expenses are not subject to re-inclusion in the expenses. Accordingly, according to the Federal Tax Service, the provisions of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code do not apply when selling a “frozen” fixed asset.
In the letter, the Service cites examples from judicial practice in support of its position.
So, in the decision of the 11th Arbitration Court of Appeal dated December 9, 2009 in case No. A55-9340 / 2009 and the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated June 25, 2007 in the case
No. A56-51992/2005, the judges point out the unlawfulness of the application by merchants of the provisions of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation when selling fixed assets that are on conservation. In other words, in such situations, the income from the sale of a “frozen” object is reduced by its residual value, which is defined as the difference between the original valuable fixed assets and the amount accrued for the period of operation.
If the property is sold at a loss, then the resulting minus is included in the company's other expenses in equal shares over a period determined as the difference between the useful life of the property and the actual period of its operation before the sale.
READER QUESTIONDue to the seasonal nature of the work and the peculiarities of the technological cycle, our company temporarily does not use depreciable fixed assets.
Where should the costs of maintaining mothballed fixed assets be attributed? Is it possible and necessary to charge depreciation, property tax and transport tax in such situations?
Our expertise
Yu.B. Melnikova,
Leading Tax Consultant
and tax disputes of the department of legal
consulting CJSC ACG “RBS”
According to sub. “a” p. 4 PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”, approved. By order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 01 No. 26n, an asset accepted for accounting as a fixed asset (hereinafter referred to as fixed assets) must be used in the production of products, when performing work or providing services, or for the management needs of the organization.
If an object is registered, but is temporarily not used in production, it can be mothballed. Since the current legislation does not establish the procedure for the conservation of fixed assets, this procedure can be carried out in accordance with the registration procedure developed within the organization (as a rule, on the basis of an order or order of the head).
CONSERVATION OF THE OBJECT
Usually, a special commission is first created, the composition of which is approved by the head of the enterprise and includes representatives of the administration, accounting, engineering workers, etc. It is this commission that decides on the need to conserve certain OS objects.
Registration of conservation of the OS object
The order (instruction) of the head must contain:
the reason for the conservation of the OS;
date of transfer to conservation;
conservation period;
residual value of the property.
Confirmation of the transfer of the OS object for conservation is the act of conservation drawn up after the inventory of the conserved OS.
THE DOCUMENTS
An approximate procedure for conducting an inventory of mothballed objects is reflected in the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations, approved. Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
There is no unified form of the act on the conservation of OS objects. The organization itself must develop its form and approve it in the accounting policy. This document must be signed:
the head of the enterprise;
members of the commission;
heads of subdivisions for which the conservation objects of property are listed.
Reflection of conservation in accounting
If the head of the organization has decided to mothball the equipment, the fixed asset transferred for mothballing continues to be accounted for in accounting on account 01 “Fixed assets”. The transfer of an object to another quality is shown only in analytical accounting. Thus, fixed assets that are on conservation must be accounted for separately, therefore, a separate sub-account “Fixed assets on conservation” should be opened for account 01 “Fixed assets”. In case of transfer of fixed assets for conservation for a period of more than 3 months, depreciation is not charged for them in accounting (paragraph 23 of PBU 6/01). If the conservation period is shorter, depreciation is charged in accordance with the generally established procedure.
As in accounting, for the purposes of tax accounting, fixed assets transferred for conservation for more than 3 months are excluded from the composition of depreciable property (clause 3 of article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Usually, OS objects that are located in a certain technological complex or have a completed cycle of the technological process are transferred for conservation.
It should also be noted that for the purposes of taxation of profits, the period during which an object of fixed assets is mothballed increases its useful life (clause 3, article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). After the reactivation of such property, depreciation on it is charged in the same manner as before the transfer to conservation.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciation on an asset is terminated from the 1st day of the month following the month in which the cost of such an asset was fully written off, or when this asset was removed from the depreciable property for any reason. In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such a basis is the transfer of fixed assets for conservation for a period of more than 3 months.
In PBU 6/01 there is no direct indication of the date of termination of depreciation for fixed assets transferred to conservation, therefore it is most reasonable to follow the general rule fixed in clause 22 of PBU 6/01. Thus, as in tax accounting, the date of termination of depreciation should be considered the 1st day of the month following the month in which the asset was transferred to mothballing. This condition can be fixed in the accounting policy for accounting purposes.
EXPENSES DURING THE TRANSFER OF OBJECTS FOR CONSERVATION
THE DOCUMENTS
If in accounting and tax accounting the same conditions are established for accounting for mothballed fixed assets, accountants will be able to avoid the occurrence of temporary differences according to PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax settlements”.
When transferring fixed assets for conservation, an organization may incur certain costs, for example:
transportation of mothballed objects to the place of their temporary storage;
associated with bringing mothballed objects to a state in which they can be stored;
for security, etc.
In accordance with PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”, approved. By order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 6, 1999 No. 33n, the costs associated with the maintenance of mothballed fixed assets should be included in non-operating expenses, since these fixed assets do not participate in production activities. Such expenses cannot be attributed to expenses for ordinary activities.
In tax accounting, the costs associated with the mothballing and reactivation of production facilities and facilities, including the costs of maintaining mothballed production facilities and facilities, are also included in non-operating expenses. This is stated in sub. 9 p. 1 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
EXAMPLE
Stroypodryad OJSC is engaged in construction and has a tractor on its balance sheet, the initial cost of which is 300,000 rubles.
The amount of accrued depreciation amounted to 150,000 rubles. The amount of monthly depreciation deductions is 3000 rubles.
In March 2005, due to the lack of orders, the head of the organization issued an order on the conservation of this OS object for the period from April to July 2005 (4 months). The cost of maintaining the mothballed facility amounted to 10,000 rubles.
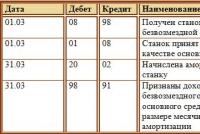
On the basis of the act of conservation in the accounting department of OAO Stroypodryad in April 2005, the following entry must be made:
D 01 sub-account “Fixed assets in conservation” - K 01 sub-account “Fixed assets in operation” - 300,000 rubles. – the tractor was transferred to conservation.
The tractor was put into conservation from April 2005, so depreciation was no longer charged from May 2005. In April 2005, the accountant made a posting:
D 20 - K 02 - 3000 rubles. - depreciation charged.
The period during which the tractor is mothballed increases its useful life.
For the costs of maintaining the mothballed fixed assets object, the accountant made the following entry:
D 91 subaccount “Other expenses” - K 20 (10, 70, 69) - 10,000 rubles. - reflects the costs of maintaining a mothballed tractor.
In August 2005, the tractor was taken out of conservation.
D 01 sub-account “Fixed assets in operation” - K 01 sub-account “Fixed assets in conservation” - 300,000 rubles. – the tractor is decommissioned.
In the same month, in the tax accounting, the tractor was included in the depreciable property. It should be noted that the depreciation posting after the withdrawal of the object from mothballing in August 2005 must be made only in September 2005.
Conservation property tax
There is an opinion among accountants that property tax is not paid from fixed assets transferred to conservation. However, equipment transferred for conservation is subject to property tax in accordance with the generally established procedure. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, movable and immovable property, which is recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets, is recognized as an object of taxation, and mothballed fixed assets, as already mentioned, continue, albeit separately, to be listed as part of the fixed assets, therefore, they are taxed. There are no exceptions to this rule.
Transport tax
Is it necessary to pay transport tax if the organization has a mothballed car that is not involved in traffic and does not have license plates on the balance sheet?
According to the author, in this situation, transport tax will not have to be paid on the grounds given in Art. 357 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, indicating that vehicles registered in the prescribed manner are recognized as the object of taxation.
Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation of January 27, 2003 No. 59 “On the procedure for registering vehicles”, as amended. On 26.03.05, the Rules for the registration of motor vehicles and trailers for them in the traffic police of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia were approved. According to clause 38 of these Rules, the following documents are issued for registered vehicles in the manner prescribed by the regulatory legal acts of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia:
vehicle registration certificate according to the established model;
vehicle passport;
registration plates corresponding to state standards of the Russian Federation.
A vehicle from which license plates have been removed and handed over to the traffic police is not considered registered in the prescribed manner and, accordingly, is not allowed for operation. Such a vehicle is not subject to transport tax.
Hello! In this article we will talk about the conservation of fixed assets.
Today you will learn:
- Under what conditions and for what purpose is conservation of OS carried out;
- What are the stages of its implementation;
- What happens to taxes and depreciation during fixed assets conservation.
What is OS Conservation
Conservation is a set of measures to temporarily stop the use of one or more fixed assets of the organization. Conservation involves the resumption of operation of the OS after a documented period.
The word itself comes from the Latin conservatio - "preservation", which indicates the ultimate goal of the whole event - to save both the object itself and part of the funds on the company's settlement accounts, thanks to a reduction in costs.
The conservation of an object can be compared to the anabiosis of a crocodile, when, under unfavorable conditions, this animal burrows into the sand and all its vital functions slow down. So the object slows down its life inside the enterprise and - the main characteristic - temporarily does not bring economic benefits to its owners. By law, this “hibernation” cannot exceed three years. But practice shows that the period of conservation of fixed assets can be extended.
Reasons for OS conservation
This event is used, for example, in such cases:
- Completion of seasonal work when objects cannot be used at other times (snow removal equipment, harvesting machines);
- Temporary downtime in production (looms with short supply of threads);
- Reducing production due to economic realities (non-use of one of the workshops);
- Breakdown of the object and its transfer for repair, including in the absence of the necessary parts (repair of the tractor due to malfunctions).
What does conservation really mean?
To do this, you must provide a plan of action in two directions:
- actual preservation;
- Reflection in the documentation and in the accounting program.
The first item includes all actions related directly to your main tool. While the property is idle, you need to keep it safe and in good condition.
For example, in agriculture, a special technique is used to treat fields with herbicide. This equipment is needed only in spring and summer, in cold weather it needs to be allocated a place in a closed hangar, periodically start the engine, and protect the hangar from thieves.
On the other hand, conservation must be recorded in documents - it is not enough just to actually stop using the property and put it under lock and key.
Consequences of conservation
Conservation is a voluntary procedure. Even if you do not use your building, equipment or car for the needs of the organization, and they are covered with dust, the tax authorities cannot oblige you to carry out this procedure.
This begs the question - if the law does not oblige you to re-register the status of an unused asset, why do you need extra trouble? Let it stand until needed again. Only the benefits that will significantly outweigh the inconvenience and cost of it can persuade you in favor of documentary preservation.
However, there are some common points:
|
Paragraph |
If conservation |
If you do without conservation |
|
Maintenance of the main asset |
Pay less income tax. Maintenance costs, security salaries, depreciation of the warehouse, heating, lighting can be attributed to non-operating expenses, since the fixed assets no longer serve to make a profit. Therefore, the taxable base can be reduced by the amount of these expenses when calculating income tax |
Pay the same income tax, as in the current operation of the OS. Without official conservation, all expenses on this OS will be recognized as expenses for the implementation of the company's core activities. Therefore, you will not be able to reduce the tax base when calculating profits by the amount of these expenses. |
|
Depreciation |
Not charged. In case of conservation for a period of three or more months, depreciation charges are terminated. Depreciation is resumed when the fixed assets are reactivated and is brought to an end until all fixed assets are depreciated. The basis for calculating property tax is not reduced, since the residual value of fixed assets is not reduced due to depreciation |
Charged every month based on useful life. Thus, the base for calculating property tax decreases every month - that is, you pay less and less for a particular fixed asset. And at the same time, you have to reckon with sometimes significant monthly expenses in connection with depreciation |
|
Useful life |
Extended over the depreciation period. If, after reactivation, it turns out that the FTI has expired, then depreciation on the object will still be charged, and the FTI will actually be extended for this period. The inconvenience is that, despite the absence of physical wear and tear, there is still moral wear and tear, and such a “freeze” will make the OS even older and sometimes unusable due to moral obsolescence |
Goes its own way until it ends. SPI for a specific OS is approved by the organization itself, but within the time fork for each depreciation group prescribed by law in the Classification |
|
Reflection in 1C |
Sub-account and ticks on depreciation. For convenience, it is customary to add sub-account 01.1 OS for conservation to the synthetic, that is, the general account 01 Fixed assets. 1C allows you to disable depreciation by fixed assets by checking the box "Affects depreciation" in the "Conservation" section in the event directory |
Accounting is carried out without separation of OS. In 1C, by default, depreciation is charged on the OS |
What property can be conserved
If the property belongs to fixed assets - that is, it is reflected in the accounting on account 01 - conservation can be carried out.
Recall that not any property of the company can be attributed to the fixed assets.
For this, four conditions must be met:
|
condition number |
essence |
Examples. Yes - the condition is met (applies to the OS), no - not met, does not apply to the OS |
| The object is used in production, rented out, needed for work or services, and is also involved in management |
Yes: company car. Needed in management - carries the head on official needs Not: a marble monument on the territory of the enterprise, left over from the previous owners |
|
| The object has been used for more than one year |
Yes: the building where the company is located Not: product packaging |
|
| 3. | The company is not going to resell the object |
Yes: computers for office workers Not: batch of computers purchased by the company for sale |
| The object can bring economic benefits in the future |
Yes: perennial fruit trees (for selling fruits) Not: annual plantings to decorate the territory |
OS examples: houses, structures, transport, tools, office equipment, household inventory, land, water, subsoil.
Not related to OS: finished products, materials and goods in stock. Materials or objects in transit or in the assembly.
No one is conserving natural resources (land, water, subsoil), which is easily explained: according to the law of the Russian Federation, depreciation is not charged on these objects. Since often fixed assets are conserved in order to suspend depreciation deductions, this reason does not work in this situation.
Why are natural resources not depreciated? It is believed that they can be used indefinitely and they will not "wear out", although in fact they can be depleted with active use.
The procedure for registration of conservation
The conservation procedure is strictly regulated for budgetary and state institutions. With regard to commercial enterprises, practice shows that the tax authorities are more loyal to the registration of conservation.
In order for conservation to be considered legal and you, with a clear conscience, could stop accruing depreciation on the OS, you need to take several steps:
- The management of the company calculates whether it is advisable to carry out conservation. The decision is made at general meetings.
- When a decision is made, an order is issued.
- OS is being inventoried.
- An act is drawn up on the transfer of fixed assets for conservation.
- Information is reflected in the 1C program.
|
Characteristic |
Order on the transfer to conservation of fixed assets |
Act of conservation of fixed assets |
|
Purpose |
reflects intent |
Confirms a fait accompli |
|
obligatory |
Is a required document |
Is a desirable document |
|
Who signs |
Initiated and signed by the head of the company |
All members of the commission appointed in the order + head |
|
What information does |
— Reasons for the transfer to conservation; - On what period; - Responsible for the event; — Responsible for proper storage of unused OS |
— List of facilities for decommissioning; — Date of commencement of conservation; - What activities will be carried out during OS downtime; - Conservation costs. |
| Unified view |
Arbitrary View |
Learn more about fixed asset depreciation: an overview
Depreciation - this is a gradual decrease in the cost of fixed assets due to its wear and tear through the monthly inclusion of a share of its cost in.
How are these write-off shares calculated? Their value is directly related to the concept of the useful life of fixed assets (SPI). The value of the term is partially chosen by the organization, but only within the specified limits. These frameworks are prescribed in an official document - OS classifications.
In this classification, all possible fixed assets are divided into ten groups. The first group lists those OS, whose STI is from one to two years. In the last, tenth group - OS with a service life of more than thirty years.
Example. Hunting and sporting weapons belong to the fifth depreciation group with DTI from seven to ten years. An organization may establish a PTI for its TOS for seven, eight, nine, or ten years, at its discretion.
After choosing a SPI with a linear depreciation system (in many ways the most convenient), it is calculated how much will have to be depreciated per month. For example, if a hunting weapon cost 70,000 rubles with a STI of 7 years, you will need to write off:
- 70,000/7 = 10,000 rubles per year.
- 10,000/12 = 833.3 rubles per month.
What happens to depreciation during the conservation of fixed assets
If the conservation does not exceed three months, depreciation is accrued according to fixed assets in the usual way. With a longer period, as we have already considered, depreciation is suspended.
Depreciation ceases to accrue from the first day of the month following the month in which the conservation order was issued. For example, if the conservation is approved on August 15, from September 1, it is no longer accrued.
Temporarily not charging depreciation is often one of the main goals of conservation and a legal way to avoid doing so. On the one hand, this is not very profitable in the long run. After all, fully depreciated property is listed on the balance sheet with zero value, therefore, it does not need to pay property tax, while the “frozen” asset will hang on the balance sheet with the same value, and not with the residual value.
On the other hand, if the owner has a whole fleet of equipment with a huge cost and, as a result, with a huge depreciation due to a decline in production, he will not be able to include this depreciation in the cost of finished products - otherwise it will skyrocket.
On the procedure for paying taxes in case of conservation of fixed assets
The conservation of fixed assets does not exempt the enterprise from paying transport tax (if the fixed assets relate to vehicles), as for it, it is also still payable.
All these cases are regulated by law, but conservation does not appear among them. Therefore, when conserving fixed assets, it is not necessary to look for primary documents with the specified VAT when purchasing fixed assets and transfer it to the budget.
Sale of objects for conservation
The sale of objects under mothballing has features typical of the sale of depreciable property, despite the fact that depreciation is suspended during long-term mothballing.
The similarity lies in the fact that with such a sale, the seller has the right to reduce the declared profit by the residual value of fixed assets - the value that remained after the accrued depreciation before conservation.
Example. The company bought the device in the amount of 120,000 rubles. According to the classification, it will be used for five years (60 months). Monthly depreciation amounted to 2000 rubles. Three years have passed, for which the accrued depreciation has reduced the cost of the device by 72,000 rubles. The current residual value was 48,000 rubles (120,000 - 72,000).
The whole fourth year the device was mothballed. After that, the device was sold for 82,600 rubles, including VAT of 12,600 rubles.
For tax purposes, sales income amounted to 70,000 (82600 - 12600).
The company declares a profit of 22,000 rubles (the amount of 70,000, reduced by the residual value of the device - 48,000 rubles).
If the residual value exceeds the proceeds from the sale, the difference between these figures will be recognized as a loss.
In this case, you need to establish the actual life of the facility - that is, take months of downtime. And it is from this figure that the period for writing off the loss is calculated. The loss is distributed in equal shares by months of the found period as part of other expenses.
OS depreservation procedure
After some time, management may come to the conclusion that the company again needs to actively use the mothballed OS objects.
For this purpose, an appropriate order for reactivation is issued.
Reactivation - a set of measures to resume the operation of the OS.
At the same time, depreciation is charged again - from the first day of the month after the month in which the order for reactivation was issued.
Conservation of an object under construction is necessary in cases where the construction of the object cannot be completed within the planned period. The reason may be the lack of money to complete the project in full, adverse weather conditions, and so on. Conservation is a process that involves the resumption of construction work in the future. That is why contract contracts are not broken, but suspended for a certain period.
Many people confuse the concept of conservation and stopping construction work. In the latter case, activities can be resumed, but the replacement of the investor is a prerequisite. During conservation, the person who financed the project remains unchanged. In addition, the stoppage of construction allows the construction to be realized or liquidated in the future.
To understand the topic, we will consider the features of the conservation of an object, the procedure for performing such work, the necessary documents, the subtleties of drawing up an act of expenses (estimates) and other nuances.
The term "conservation" in relation to an unfinished object implies a temporary cessation of construction activities on the territory of the object with mandatory paperwork and the implementation of a set of measures to save the already built part of the structure. Such actions have to be resorted to by the technical customer (developer) in cases where there are no funds to perform the work, weather conditions have worsened, or other force majeure circumstances have arisen.
The conservation process is documented, in the form of an order or instruction, where the following information is indicated:
- The period of development of a package of papers that are used during conservation.
- Inventory activities.
- Subjects and companies that are responsible for the preservation of the object.
- The amount of money that is required to complete the tasks.
Conservation order
The conservation procedure, as well as the work related to this process, is carried out by the developer and the contractor. This category also includes other entities, namely investors, subcontractors, and so on.
 If the customer has decided that it is necessary to suspend the construction of the structure, he notifies the contractor, as well as the local authorities that issued the permit for the construction of the facility. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 752) states that the customer who initiates the conservation process is obliged to pay the contractor:
If the customer has decided that it is necessary to suspend the construction of the structure, he notifies the contractor, as well as the local authorities that issued the permit for the construction of the facility. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 752) states that the customer who initiates the conservation process is obliged to pay the contractor:
- For completed work.
- For reimbursement of costs associated with the conservation of the process of erecting a structure.
As noted earlier, the suspension of construction work is not a reason for the suspension of contractual relations. As soon as the organizational measures are completed, the developer begins to carry out work on the conservation of the unfinished object in order to preserve the existing elements and continue construction in the future.
Contractor
Practice shows that the implementation of conservation measures is entrusted to the contractor, which acts for the customer's money. This type of activity is not considered in the contract and is not displayed in the estimate, so the necessary calculations are performed separately. As a rule, the work is performed by a construction company, after which the estimate is agreed with the customer.
The documentation contains the following information:
- The cost of doing the work.
- Calculations of measures for the installation, repair or restoration of structures.
- Building security.
The construction contract agreement specifies the activities that must be completed first, as well as the actions of the participants in case of suspension of construction and installation in order to avoid disputes in the future.
Inventory
One of the main activities in the performance of work on the conservation of an unfinished object is an inventory. This process is organized taking into account the requirements of guidelines agreed and approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (Order No. 49). For work, an inventory commission is appointed, which includes participants in the construction process and agreements between the parties.
The commission performs an inspection and, at the end of the work, makes an inventory of the mothballed structure. It indicates the name of the building, the amount of installation and construction work already completed, the costs of implementing measures, as well as the reasons for the "freeze" of construction.
Papers are drawn up taking into account the current work schemes and materials, namely, acts of acceptance and delivery of work, drawings (design, workers), available estimates, as well as log books of work done. A summary of the measures taken is carried out taking into account the papers that were drawn up and filled in during the construction work.
The task of the inventory process is to fix the real state of the building, taking into account all the nuances. The ongoing work is also useful in that with its help it is possible to determine the current inconsistencies with led accounting. Prepared and certified papers are sent to the customer for the purpose of storing and ensuring the preservation of the unfinished building, the construction of which is planned to be resumed in the future.
Required documents
 Inventory is only the first stage of registration of conservation procedures. After that, an act is drawn up on the "freezing" of construction work, drawn up in the form of KS-17 (approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation). The following information is reflected in the finished document:
Inventory is only the first stage of registration of conservation procedures. After that, an act is drawn up on the "freezing" of construction work, drawn up in the form of KS-17 (approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation). The following information is reflected in the finished document:
- The name and purpose of the object, the construction of which is "frozen".
- The day construction began.
- Estimated price of works under the agreement.
- The actual cost of the activities performed.
- Customer costs.
- Expenses that the contractor has to endure during the conservation of the structure, as well as its protection.
On the basis of the act, another document is drawn up - an estimate of future work. After completing the required calculations, the developer's accounting department pays the funds to the contractor. At the same time, specialists work with the accounts of firms, submit reports to supervisory authorities.
Why is it necessary to conserve a house?
Conservation of a structure is a set of measures that are aimed at preventing damage, future destruction or deterioration in the parameters of communications, equipment and the building itself. In addition, with the help of conservation, it is possible to ensure the safety of people and the environment. This means that the construction site and the unfinished building must be in a state in which their stability, strength characteristics and safety (for materials, structures, equipment) are guaranteed. This requirement is spelled out in the Rules, which are approved by a decree of the Russian government (approved by order No. 802).
Conservation is a necessary measure that is implemented in the absence of funds to continue work, as well as during periods of rainy or winter seasons, when materials deteriorate due to low temperatures and other negative factors.
List of works
Conservation measures include a set of measures in relation to various elements of an already finished structure.
Foundation
If the foundation of the building is made with pillars or piles, there is no need to protect it. Such elements are in the ground, and their safety is ensured by the available materials. The strip foundation deserves special attention. In relation to it, the following works are performed:
- Structural elements that are above the ground are covered with inexpensive roofing material.
- To maintain the integrity of the waterproofing, it is required to be covered with a special insulation that is not exposed to moisture.
- To prevent the material from flying off, it is pressed with heavy objects, such as bricks.
In order to avoid problems in the process of further construction, before the "freezing" of construction work, it is important to let the concrete gain brand strength. For this, measures must be taken after 28 days from the date of pouring.
Basement
 If the contractor managed to complete the work on the production of the basement, but did not close it, you will have to make a boardwalk with subsequent coating with film material. Such foresight allows you to protect the basement from snow and the subsequent formation of water.
If the contractor managed to complete the work on the production of the basement, but did not close it, you will have to make a boardwalk with subsequent coating with film material. Such foresight allows you to protect the basement from snow and the subsequent formation of water.
It is recommended to cover the floor with gravel or perform a cement-sand screed. These measures allow avoiding the rise of groundwater during the thaw period. If there is an unfilled pit along the perimeter of the walls, it should be filled before the cold weather in order to exclude the accumulation of water and its pressure on the basement walls during the solidification process. If the design provides for openings for communications, it is recommended to close them with plywood or metal, followed by pressing.
In the case when the ceiling is mounted, it should be isolated with a film or roofing material. The pressing of the material is carried out with the help of boards around the entire perimeter.
house with walls
Special attention deserves the conservation of an individual residential building, in which walls have been erected. If the building is built of stone or brick, it will better endure conservation in the presence of door and window blocks, as well as roofing. If the roof is not finished, ceilings are placed above the wall material. This is done to protect the gaps between concrete and bricks from moisture.
If the building is made of wood, there is no need to install doors and windows - it is enough to close the openings with plywood or boards. In this case, the normal circulation of air masses is ensured. As a result, a log or timber hibernates without problems.
In general, the conservation process involves the following work:
- Creation of structures that will take on the design loads.
- Installation of equipment that secures unstable elements of the building.
- Release of pipelines and tanks, welding of large openings and hatches
- Bringing the equipment to a safe state.
- Disconnection of communications (except those used for the safety of the building).
- Protection of the object from access by unauthorized persons.
Budgeting
To estimate the scope of work and potential costs for the implementation of the activity, an estimate is drawn up. A design company is involved in its development. The prepared estimate is used by the contractor when performing work under an additional agreement to the contract.
The costs of the contractor for the performance of conservation work are not indicated in the estimate. That is why, before the start of conservation measures, the parties must draw up an additional agreement and stipulate in it the issue of the cost of the work performed.
In conclusion, the customer and the contractor sign an estimate for the work, as well as an act of suspension of construction work, drawn up in the form of KS-17.